|
Reichstag (North German Confederation)
The Reichstag () of the North German Confederation was the federal state's lower house of parliament. The popularly elected Reichstag was responsible for federal legislation together with the Bundesrat, the upper house whose members were appointed by the governments of the individual states to represent their interests. Executive power lay with the Bundesrat and the king of Prussia acting as ''Bundespräsidium'', or head of state. The Reichstag debated and approved or rejected taxes and expenditures and could propose laws in its own right. To become effective, all laws required the approval of both the Bundesrat and the Reichstag. Voting rights in Reichstag elections were advanced for the time, granting universal, equal, and secret suffrage to men above the age of 25. When the German Empire was established in 1871, the North German Reichstag formed the basis of the new Reichstag of the German Empire. Background The draft constitution Following Prussia's victory in the 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
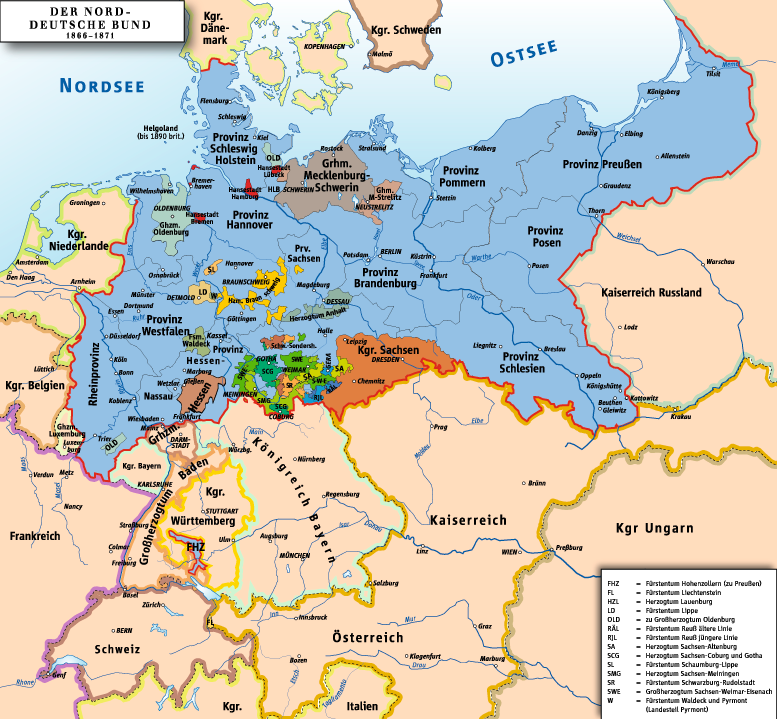
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation (german: Norddeutscher Bund) was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' federal state) that existed from July 1867 to December 1870. A milestone of the German Unification, it was the earliest continual legal predecessor of the modern German nation-state known today as the Federal Republic of Germany. The Confederation came into existence following the Prussian victory in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 over the lordship of two small Danish duchies (Schleswig-Holstein) resulting in the Peace of Prague, where Prussia pressured Austria and its allies into accepting the dissolution of the existing German Confederation (an association of German states under the leadership of the Austrian Empire), thus paving the way for the Lesser German version of German unification in the form of a fed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister President Of Prussia
The office of Minister-President (german: Ministerpräsident), or Prime Minister, of Prussia existed from 1848, when it was formed by King Frederick William IV during the 1848–49 Revolution, until the abolition of Prussia in 1947 by the Allied Control Council. History of the office Under the Kingdom of Prussia the Minister President functioned as the chief minister of the King, and presided over the Landtag (the Prussian legislature established in 1848). After the unification of Germany in 1871 and until the collapse in 1918, the office of the Prussian Minister President was usually held by the Chancellor of the German Empire, beginning with the tenure of Otto von Bismarck. Under the Free State of Prussia the Minister President was the head of the state government in a more traditional parliamentary role during the Weimar Republic. The office ceased to have any real meaning except as a kind of political patronage title after the takeover by the national government in 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
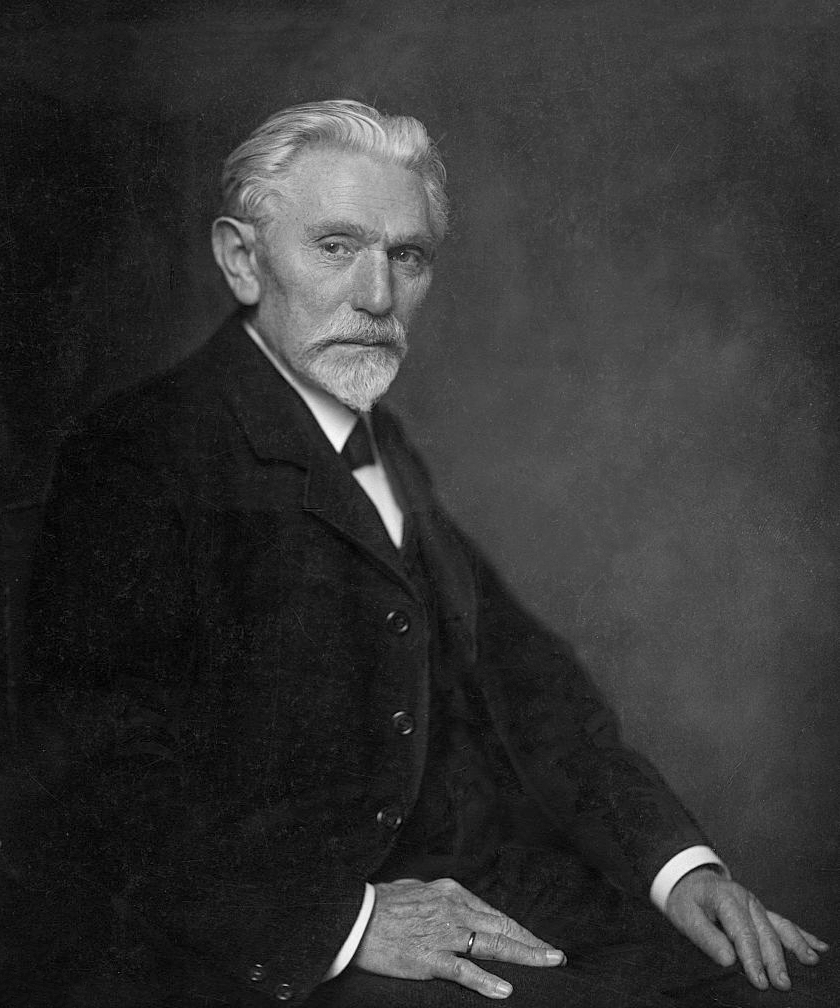
Eduard Von Simson
Martin Sigismund Eduard von Simson (10 November 1810 – 2 May 1899) was a German jurist and distinguished liberal politician of the Kingdom of Prussia and German Empire, who served as President of the Frankfurt Parliament as well as the first President of the German Parliament and of the Imperial Court. He was ennobled by Kaiser Frederick III in 1888. Education Eduard Simson was born in Königsberg, East Prussia, in a Jewish family. The family converted to Protestantism in 1823. After the usual course at the '' Gymnasium'' of his native town, he entered its university in 1826 as a student of jurisprudence, and specially of Roman law. He continued his studies at Berlin and Bonn, and, having graduated ''doctor juris'', attended lectures at the École de Droit in Paris. Returning to Königsberg in 1831 he established himself as a ''Privatdozent'' in Roman law, becoming two years later extraordinary, and in 1836 ordinary, professor in the faculty of the university. National Asse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Bebel
Ferdinand August Bebel (22 February 1840 – 13 August 1913) was a German socialist politician, writer, and orator. He is best remembered as one of the founders of the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Germany (SDAP) in 1869, which in 1875 merged with the General German Workers' Association into the Socialist Workers' Party of Germany (SAPD). During the repression under the terms of the Anti-Socialist Laws, Bebel became the leading figure of the social democratic movement in Germany and from 1892 until his death served as chairman of the Social Democratic Party of Germany. Biography Early years Ferdinand August Bebel, known as August, was born on 22 February 1840, in Deutz, Germany, now a part of Cologne. He was the son of a Prussian noncommissioned officer in the Prussian infantry, initially from Ostrowo in the Province of Posen, and was born in military barracks. The father died in 1844. As a young man, Bebel apprenticed as a carpenter and joiner in Leipzig."August ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democratic Workers' Party Of Germany
The Social Democratic Workers' Party of Germany (german: Sozialdemokratische Arbeiterpartei Deutschlands, SDAP) was a Marxist socialist political party in the North German Confederation during unification. Founded in Eisenach in 1869, the SDAP endured through the early years of the German Empire. Often termed the Eisenachers, the SDAP was one of the first political organizations established among the nascent German labor unions of the 19th century. It officially existed under the name SDAP for only six years (1869–1875). However, through name changes and political partnerships, its lineage can be traced to the present-day Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD). Origins VDAV and ADAV The SDAP was one of the earliest organizations to arise from German workers' unionizing activity, but it was not the first. At the group's founding in 1869, the fast-growing working class of the Industrial Revolution had already established several notable associations for workers' advocacy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxon People's Party
The Saxon People's Party (german: Sächsische Volkspartei) was a left-liberal and radical democratic party with socialist leanings in Germany, founded by Wilhelm Liebknecht and August Bebel on 19 August 1866 in Chemnitz, and integrated into the newly-founded Social Democratic Workers' Party (SDAP) on 8 August 1869. It was an alliance between liberal, anti-Prussian bourgeois and socialist workers' organizations in Saxony. It is considered one of the precursors to the Social Democratic Party of Germany. In the preamble to the Chemnitz program of the Saxon People's Party, they committed themselves to " ..fighting the enemies of German freedom and unity under all circumstances and in all areas ... It called for " ..the unrestricted right of self-determination of the German people .., the promotion of " ..general prosperity .. and " ..the liberation of work and the workers from any pressure and any bondage ..]". Founding Immediately after Prussia's victory against Austrian Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German-Hanoverian Party
The German-Hanoverian Party (german: Deutsch-Hannoversche Partei, DHP), also known as the Guelph Party (german: Welfenpartei), was a conservative, federalist political party in the German Empire and the Weimar Republic. History The party was founded in 1867 in protest of the annexation of the Kingdom of Hanover by the Kingdom of Prussia in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War.Vincent E McHale (1983) ''Political parties of Europe'', Greenwood Press, p420 They wanted the revival of the Kingdom of Hanover and the restoration of the sequestrated assets of the former ruling House of Welf. The party therefore was also called the ''Welfen'', and drew its strongest support from the rural areas around Hannover. In the Reichstag DHP deputies usually acted as allies of the anti-Prussian Centre Party parliamentary group under Ludwig Windthorst, who although a Catholic and leader of the Centre Party was a former Hanoverian Justice Minister who was loyal to the House of Welf. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservative Party (Prussia)
The Conservative Party was a party in Prussia founded in 1848 from the relatively loose cooperation of conservative associations, groups and members of parliament. The party split into the German Conservative Party The German Conservative Party (german: Deutschkonservative Partei, DkP) was a right-wing political party of the German Empire founded in 1876. It largely represented the wealthy landowning elite Prussian Junkers. The party was a response to Ger ... and the Free Conservative Party in 1876. Chairmen * Ernst Ludwig von Gerlach Electoral results German Reichstag/Bundestag References {{Party-stub Defunct political parties in Germany Political parties established in 1848 Politics of the German Empire 1876 disestablishments in Germany Political parties disestablished in 1876 Defunct conservative parties Politics of Prussia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Conservative Party
The Free Conservative Party (german: Freikonservative Partei, FKP) was a liberal-conservative political party in Prussia and the German Empire which emerged from the Prussian Conservative Party in the Prussian Landtag in 1866. In the federal elections to the Reichstag parliament from 1871, it ran as the German Reich Party (german: Deutsche Reichspartei, DRP). DRP was classified as centrist or centre-right by political standards at the time, and it also put forward the slogan " conservative progress". The Free Conservative Association achieved party status in 1867, comprising German nobles and East Elbian Junkers (land owners) like Duke Victor of Ratibor and Karl Rudolf Friedenthal, industrialists and government officials like Johann Viktor Bredt, Hermann von Hatzfeldt, Hermann von Dechend, Prince Karl Max von Lichnowsky or General Hans Hartwig von Beseler and scholars like Hans Delbrück and Otto Hoetzsch. It was distinguished from the German Conservative Party es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Progress Party
The German Progress Party (german: Deutsche Fortschrittspartei, DFP) was the first modern political party in Germany, founded by liberal members of the Prussian House of Representatives () in 1861 in opposition to Minister President Otto von Bismarck. History Upon the failed Revolutions of 1848, several deputies in the Landtag diet of Prussia maintained the idea of constitutionalism as it had been developed in the '' Vormärz'' era. In the 1850s, these Old Liberals gathered in a parliamentary group around Georg von Vincke, an originally conservative Prussian official and landowner (''Junker''). Vincke, former member of the Frankfurt Parliament, a polished orator and firebrand, had fallen out with Prime Minister Otto Theodor von Manteuffel over his reactionary policies and in 1852 even fought a duel with Bismarck after a heated verbal exchange in parliament (both men missed). When under the regency of William I of Prussia from 1858 the Prussian policies of the new era turned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Liberal Party (Germany)
The National Liberal Party (german: Nationalliberale Partei, NLP) was a liberal party of the North German Confederation and the German Empire which flourished between 1867 and 1918. During the Prussian-led unification of Germany, the National Liberals became the dominant party in the Reichstag parliament. While supporting the common ideals of liberalism and nationalism, the party contained two wings which reflected the conflicting claims of its Hegelian and idealistic heritage: one which emphasized the power of the state through the ''Nationalstaat'', and the other which emphasized the civil liberties of the ''Rechtsstaat''. Although this cleavage later proved fatal for its unity, the National Liberals managed to remain the pivotal party in the decades after unification by cooperating with both the Progressives and the Free Conservatives on various issues. Origins A first national liberal parliamentary group arose among right-wing deputies of the liberal German Progre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norddeutscher Bund
The North German Confederation (german: Norddeutscher Bund) was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' federal state) that existed from July 1867 to December 1870. A milestone of the German Unification, it was the earliest continual legal predecessor of the modern German nation-state known today as the Federal Republic of Germany. The Confederation came into existence following the Prussian victory in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 over the lordship of two small Danish duchies (Schleswig-Holstein) resulting in the Peace of Prague, where Prussia pressured Austria and its allies into accepting the dissolution of the existing German Confederation (an association of German states under the leadership of the Austrian Empire), thus paving the way for the Lesser German version of German unification in the form of a federal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1975%2C_MiNr_2050.jpg)

