|
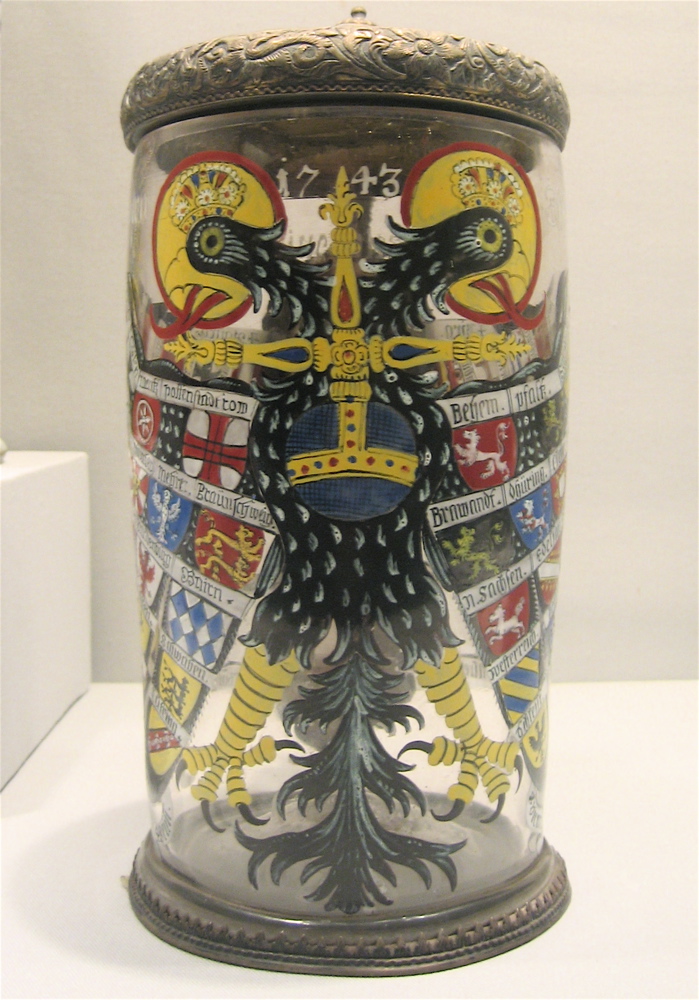
Reichsadlerhumpen
An Imperial Eagle beaker (german: Reichsadlerhumpen), or eagle glass, was a popular drinking vessel from the 16th until the late 18th century in the Holy Roman Empire. The enamelled glass was decorated with a double-headed eagle, usually in the shape of a Quaternion Eagle. The ''Reichsadler'' means "Imperial Eagle" or double-headed eagle which was the emblem of the empire, while " humpen" refers to a cylindrical drinking glass. These beakers became the essential medium to represent the most popular explanatory model for the emergence of the Empire: the quaternion theory as represented by Hans Burgkmair. The Imperial Eagle beakers showed the solidarity between the owner and the Empire and were very popular because of their decorativeness and luminous colors. But these drinking vessels were also valued for their generous size. Equally popular were the electors' beakers, which were decorated with illustrations of the emperor and electors as the most important representatives of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Works Of Art
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate-based glass that they are simply called by the name of the material. Despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enamelled Glass
Enamelled glass or painted glass is glass which has been decorated with vitreous enamel (powdered glass, usually mixed with a binder) and then fired to fuse the glasses. It can produce brilliant and long-lasting colours, and be translucent or opaque. Unlike most methods of decorating glass, it allows painting using several colours, and along with glass engraving, has historically been the main technique used to create the full range of image types on glass. All proper uses of the term "enamel" refer to glass made into some flexible form, put into place on an object in another material, and then melted by heat to fuse them with the object. It is called vitreous enamel or just "enamel" when used on metal surfaces, and "enamelled" overglaze decoration when on pottery, especially on porcelain. Here the supporting surface is glass. All three versions of the technique have been used to make brush-painted images, which on glass and pottery are the normal use of the technique. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
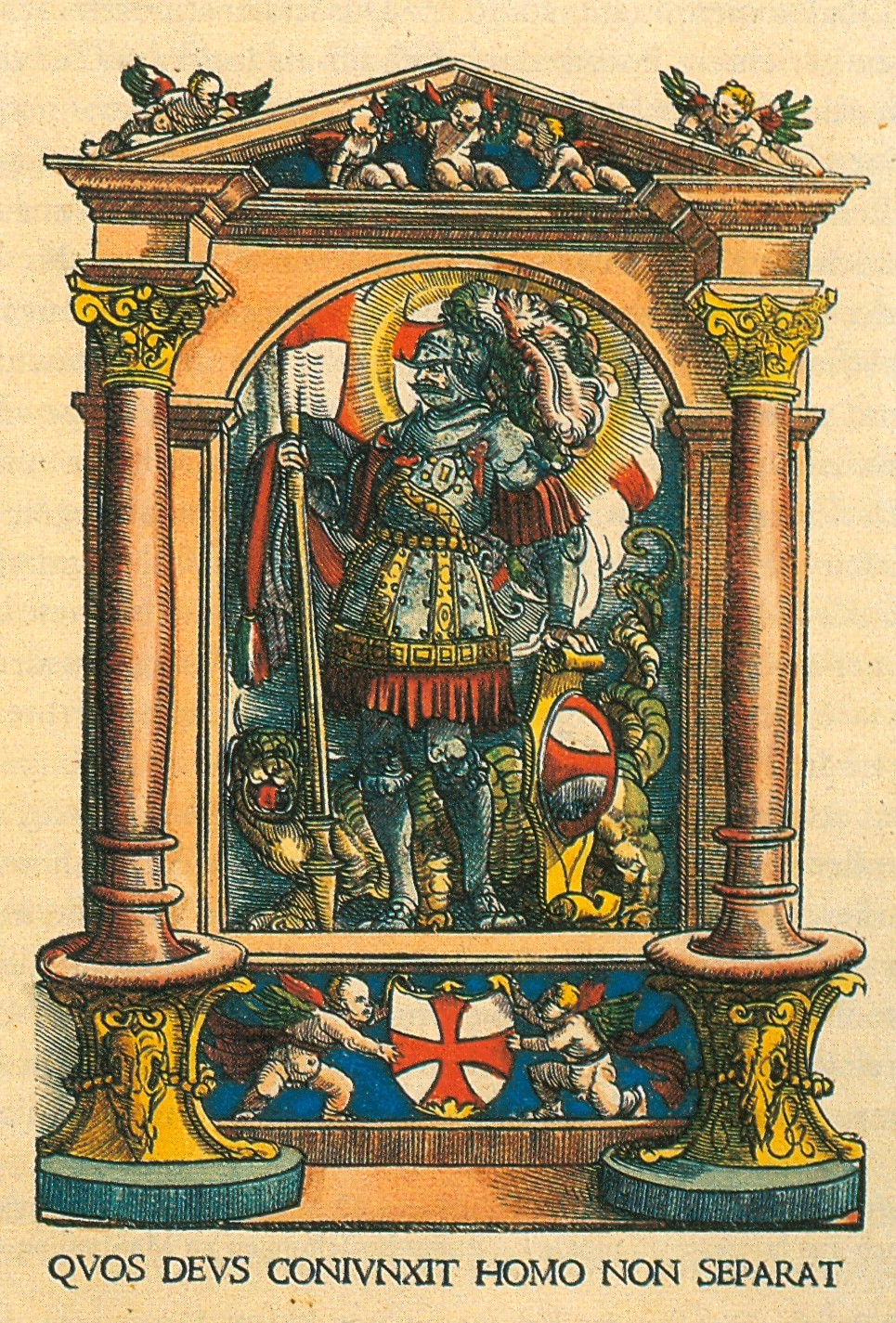
Quaternion Eagle
The Quaternion Eagle (german: Quaternionenadler; it, aquila quaternione), also known as the Imperial Quaternion Eagle (german: Quaternionen-Reichsadler) or simply Imperial Eagle (german: Reichsadler), was an informal coat of arms of the Holy Roman Empire. Introduced around 1510 by Hans Burgkmair, the Quaternion Eagle mixed two pre-existing concepts: the Imperial Quaternions and the Imperial Eagle (double-headed eagle). History Background The so-called imperial quaternions (german: Quaternionen der Reichsverfassung, , quaternions of the imperial constitution; from la, quaterniō, , group of four soldiers) were a conventional representation of the Imperial States of the Holy Roman Empire which first became current in the 15th century and was extremely popular during the 16th century. Apart from the highest tiers of the emperor, kings, prince-bishops and the prince electors, the estates are represented in groups of four. The number of quaternions was usually ten, in desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humpen
A beer stein ( ), or simply stein, is either a traditional beer mug made out of stoneware or specifically an ornamental beer mug sold as a souvenir or collectible. An 1894 article on beer mugs in the American ''Vogue'' magazine that describes various types of steins stated: "And it is to this .e. Germannation that we owe Wagner's music and the apotheosis of the beer mug." Such steins may be made out of stoneware, pewter, porcelain, or even silver, wood or crystal glass; they may have open tops or hinged pewter lids with a thumb-lever. Steins usually come in sizes of a half litre or a full litre (or comparable historic sizes). Like decorative tankards, they are often decorated in a nostalgic manner with allusions to Germany. Etymology The English word is attested from 1855. It is borrowed from German ', which has – aside from its prevailing meaning "stone" – elder regional meanings "beer mug" and "beer measure of 1 litre or 2 Schoppen". The word can be compared to Old Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Burgkmair
Hans Burgkmair the Elder (1473–1531) was a German painter and woodcut printmaker. Background Hans Burgkmair was born in Augsburg, the son of painter Thomas Burgkmair. His own son, Hans the Younger, later became a painter as well. From 1488, Burgkmair was a pupil of Martin Schongauer in Colmar. Schongauer died in 1491, before Burgkmair was able to complete the normal period of training. He may have visited Italy at this time, and certainly did so in 1507, which greatly influenced his style. From 1491, he worked in Augsburg, where he became a master and eventually opened his own workshop in 1498. Burgkmair was a Lutheran. Career German art historian Friedrich Wilhelm Hollstein ascribes 834 woodcuts to Burgkmair, the majority of which were intended for book illustrations. Slightly more than a hundred are “single-leaf” prints which were not intended for books. His work shows a talent for striking compositions which blend Italian Renaissance forms with the established German st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-headed Eagle
In heraldry and vexillology, the double-headed eagle (or double-eagle) is a charge associated with the concept of Empire. Most modern uses of the symbol are directly or indirectly associated with its use by the late Byzantine Empire, originally a dynastic emblem of the Palaiologoi. It was adopted during the Late Medieval to Early Modern period in the Holy Roman Empire on the one hand, and in Orthodox principalities (Serbia and Russia) on the other, representing an augmentation of the (single-headed) eagle or ''Aquila'' associated with the Roman Empire. In a few places, among them the Holy Roman Empire and Russia, the motif was further augmented to create the less prominent triple-headed eagle. The motif has predecessors in Bronze Age art, found in Illyria, Mycenaean Greece, and in the Ancient Near East, especially in Hittite iconography. It re-appeared during the High Middle Ages, from around the 10th or 11th centuries, and was notably used by the Eastern Roman Empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. Andrew Holt characterizes it as "perhaps the most powerful European state of the Middle Ages". The functioning of government depended on the harmonic cooperation (dubbed ''consensual rulership'' by Bernd Schneidmüller) between monarch and vassals but this harmony was disturbed during the Salian period. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne as emperor, reviving the title in Western Europe, more than three centuries after the fall of the earlier ancient West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armorial Of The Holy Roman Empire
Over its long history, the Holy Roman Empire used many different heraldic forms, representing its numerous internal divisions. Imperial coat of arms Coats of arms of Holy Roman Emperors The ''Reichsadler'' ("Imperial Eagle") was the heraldic eagle, derived from the Roman eagle standard, used by the Holy Roman Emperors and in modern coats of arms of Germany, including those of the Second German Empire (1871–1918), the Weimar Republic (1919–1933) and the "Third Reich" (Nazi Germany, 1933–1945). The same design has remained in use by the Federal Republic of Germany since 1945, but under a different name, now called ''Bundesadler'' ("Union Eagle" or "Federal Eagle", from German "Bund", genitive form "Bund''es''" meaning 'Union' or 'Federation', and "Adler" meaning 'Eagle'). Quaternion Eagle One rendition of the coat of the empire was the "Quaternion Eagle" (so named after the ''imperial quaternions'') printed by David de Negker of Augsburg, after a 1510 woodc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
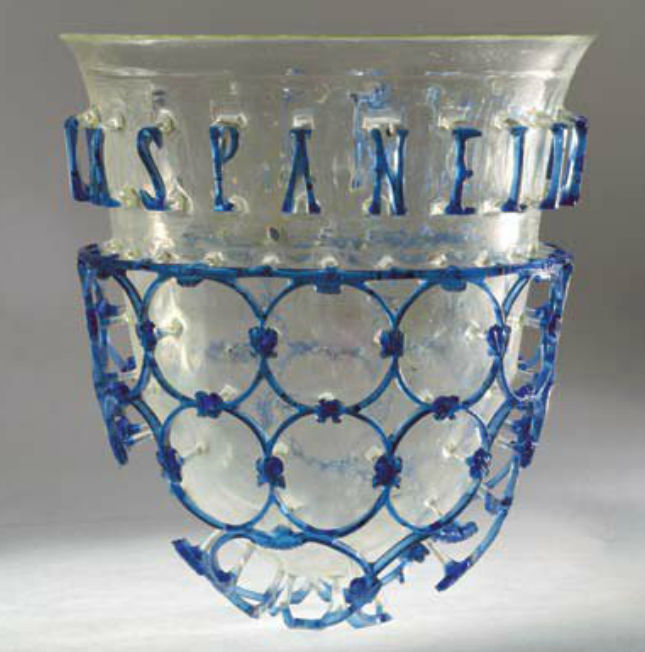
Cage Cup
A cage cup, also ''vas diatretum'', plural ''diatreta'', or "reticulated cup" is a type of luxury late Roman glass vessel, found from roughly the 4th century, and "the pinnacle of Roman achievements in glass-making". ''Diatreta'' consist of an inner beaker and an outer cage or shell of decoration that stands out from the body of the cup, to which it is attached by short stems or shanks. About fifty cups or, more often, fragments have survived, and there are only a few in near-complete condition. Most have a cage with circular geometrical patterns, often with an "inscription", or phrase in letters above the reticulated area as well. Some have a flange, or zone of projecting open-cut moulding, above the lower patterns and below the lettering (only illustrated here by the Cologne cup in the gallery). Even rarer are examples with scenes with figures, of which the Lycurgus Cup in the British Museum is the only complete example to survive, though there are other fragments. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |