|
Rangiriri
Rangiriri is a rural community in the Waikato District and Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It is located on the Waikato River near Lake Waikare in the Waikato District. State Highway 1 now bypasses Rangiriri. Rangiriri was the site of a major Māori defence structure during the time of the Invasion of the Waikato, the major campaign of the New Zealand Wars. The Battle of Rangiriri, which took place on 20–21 November 1863, cost both sides more than any other engagement of the land wars and also resulted in the capture of 183 Māori prisoners, which impacted on their subsequent ability to oppose the far bigger British force. Demographics Rangiriri settlement is in an SA1 statistical area which covers . The SA1 area is part of the larger Whangamarino statistical area. The SA1 area had a population of 90 in the 2023 New Zealand census, a decrease of 21 people (−18.9%) since the 2018 census, and a decrease of 9 people (−9.1%) since the 2013 census. There wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of The Waikato
The invasion of the Waikato became the largest and most important campaign of the 19th-century New Zealand Wars. Hostilities took place in the North Island of New Zealand between the military forces of the colonial government and a federation of Māori tribes known as the Kingitanga Movement. The Waikato is a territorial region with a northern boundary somewhat south of the present-day city of Auckland. The campaign lasted for nine months, from July 1863 to April 1864. The invasion was aimed at crushing Kingite power (which European settlers saw as a threat to colonial authority) and also at driving Waikato Māori from their territory in readiness for occupation and settlement by European colonists. The campaign was fought by a peak of about 14,000 Imperial and colonial troops and about 4,000 Māori warriors drawn from more than half the major North Island tribal groups. Plans for the invasion were drawn up at the close of the First Taranaki War in 1861 but the Colonial Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato River
The Waikato River is the longest river in New Zealand, running for through the North Island. It rises on the eastern slopes of Mount Ruapehu, joining the Tongariro River system and flowing through Lake Taupō, New Zealand's largest lake. It then drains Taupō at the lake's northeastern edge, creates the Huka Falls, and flows northwest through the Waikato Plains. It empties into the Tasman Sea south of Auckland, at Port Waikato. It gives its name to the Waikato region that surrounds the Waikato Plains. The present course of the river was largely formed about 17,000 years ago. Contributing factors were climate warming, forest being reestablished in the river headwaters and the deepening, rather than widening, of the existing river channel. The channel was gradually eroded as far up river as Piarere, leaving the old Hinuera channel through the Hinuera Gap high and dry. The remains of the old course are seen clearly at Hinuera, where the cliffs mark the ancient river edges. The Wai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Wars
The New Zealand Wars () took place from 1845 to 1872 between the Colony of New Zealand, New Zealand colonial government and allied Māori people, Māori on one side, and Māori and Māori-allied settlers on the other. Though the wars were initially localised conflicts triggered by tensions over disputed land purchases (by European settlers from Māori), they escalated dramatically from 1860 as the government became convinced it was facing united Māori resistance to further land sales and a refusal to acknowledge The Crown, Crown sovereignty. The colonial government summoned thousands of British troops to mount major campaigns to overpower the Māori King Movement, Kīngitanga (Māori King) movement and also conquest of farming and residential land for British settlers. Later campaigns were aimed at quashing the Pai Mārire religious and political movement, which was strongly opposed to the conquest of Māori land and eager to strengthen Māori identity. Religion of Māori people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato
The Waikato () is a region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipā District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, the northern King Country, much of the Taupō District, and parts of the Rotorua Lakes District. It is governed by the Waikato Regional Council. The Waikato stretches from Coromandel Peninsula in the north, to the north-eastern slopes of Mount Ruapehu in the south, and spans the North Island from the west coast, through the Waikato and Hauraki to Coromandel Peninsula on the east coast. Broadly, the extent of the region is the Waikato River catchment. Other major catchments are those of the Waihou, Piako, Awakino and Mōkau rivers. The region is bounded by Auckland on the north, Bay of Plenty on the east, Hawke's Bay on the south-east, and Manawatū-Whanganui and Taranaki on the south. Waikato Region is the fourth largest region in the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato Regional Council
The Waikato () is a Regions of New Zealand, region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipā District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton, New Zealand, Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki Plains, Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, the northern King Country, much of the Taupō District, and parts of the Rotorua Lakes District. It is governed by the Waikato Regional Council. The Waikato stretches from Coromandel Peninsula in the north, to the north-eastern slopes of Mount Ruapehu in the south, and spans the North Island from the west coast, through the Waikato and Hauraki to Coromandel Peninsula on the east coast. Broadly, the extent of the region is the Waikato River catchment. Other major catchments are those of the Waihou River, Waihou, Piako River, Piako, Awakino River (Waikato), Awakino and Mōkau River, Mōkau rivers. The region is bounded by Auckland Region, Auckland on the north, Bay of Plenty Region, Bay of Plen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Waikato (New Zealand Electorate)
Port Waikato is a New Zealand parliamentary electorate which existed for four parliamentary terms from 1996 to 2008, and was recreated by the 2019/20 electoral redistribution ahead of the 2020 election. It was held by Bill Birch for one term, and by Paul Hutchison for the following three terms. From 2020, it was held by Andrew Bayly. All of these were members of the National Party. During the campaign for the 2023 general election, the ACT Party candidate died. Only a poll for the party vote was held during this election; the electorate vote was determined in the 2023 Port Waikato by-election. Population centres The was notable for the significant change of electorate boundaries, based on the provisions of the Electoral Act 1993. Because of the introduction of the mixed-member proportional (MMP) electoral system, the number of electorates had to be reduced, leading to significant changes. More than half of the electorates contested in 1996 were newly constituted, and most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionary, missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people, with over half of Māori people, Māori regularly attending church services within the first 30 years. Christianity remains New Zealand's largest religious group, but no one denomination is dominant and there is no official state church. According to the 2018 New Zealand census, 2018 census 38.17% of the population identified as Christians, Christian. The largest Christian groups are Anglican Church in New Zealand, Anglican, Catholic Church in New Zealand, Catholic and Presbyterian Church in New Zealand, Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian church service, service conducted in New Zealand waters was probably to be carried out by F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pākehā
''Pākehā'' (or ''Pakeha''; ; ) is a Māori language, Māori-language word used in English, particularly in New Zealand. It generally means a non-Polynesians, Polynesian New Zealanders, New Zealander or more specifically a European New Zealanders, European New Zealander. It is not a legal term and has no definition under New Zealand law. ''Papa'a'' has a similar meaning in Cook Islands Māori. Etymology and history The etymology of is uncertain. The most likely sources are the Māori words or , which refer to an oral tale of a "mythical, human like being, with fair skin and hair who possessed canoes made of reeds which changed magically into sailing vessels". When Europeans first arrived they rowed to shore in longboats, facing backwards: In traditional Māori canoes or , paddlers face the direction of travel. This is supposed to have led to the belief by some, that the sailors were ''patupaiarehe'' (supernatural beings). There have been several dubious interpretati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
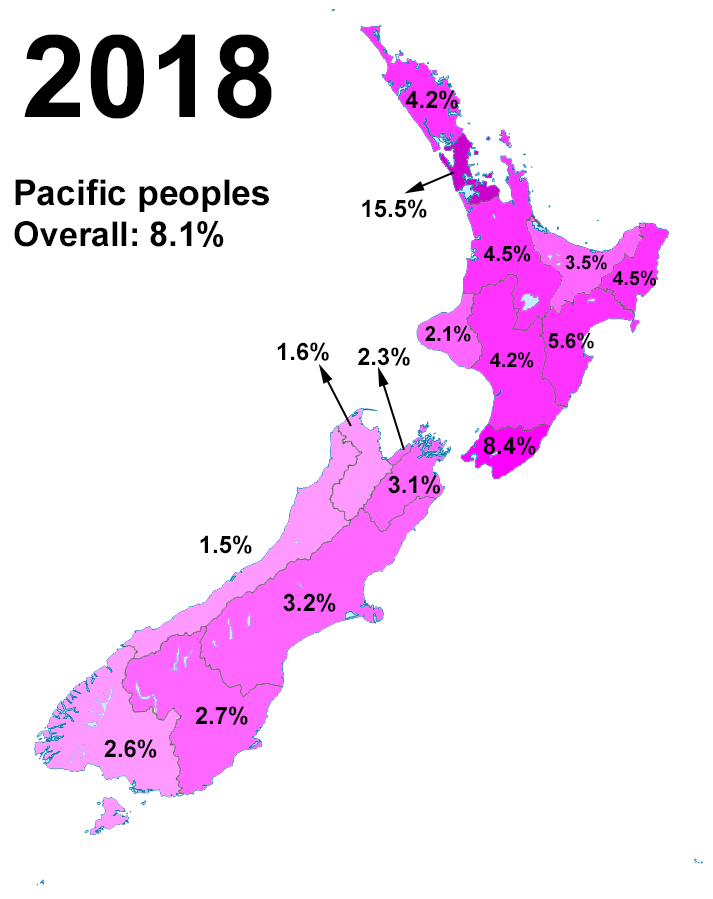
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders (also called Pacific Peoples) are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands (also known as Pacific Islander#New Zealand, Pacific Islanders) outside New Zealand itself. They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European New Zealanders, European descendants, indigenous Māori people, Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. Over 380,000 people identify as being of Pacific origin, representing 8% of the country's population, with the majority residing in Auckland. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both New Zealand Labour Party, Labour and New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian New Zealanders
Asian New Zealanders are New Zealanders of Asian ancestry (including naturalised New Zealanders who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). At the 2023 census, 861,573 New Zealanders identified as being of Asian ethnicity, making up 17.3% of New Zealand's population. The first Asians in New Zealand were Chinese workers who migrated to New Zealand to work in the gold mines in the 1860s. The modern period of Asian immigration began in the 1970s when New Zealand relaxed its restrictive policies to attract migrants from Asia. Terminology Under Statistics New Zealand classification, the term refers to a pan-ethnic group that includes diverse populations who have ancestral origins in East Asia (e.g. Chinese, Korean, Japanese), Southeast Asia (e.g. Filipino, Vietnamese, Malaysian), and South Asia (e.g. Nepalese, Indian (incl. Indo-Fijians), Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi, Pakistani). New Zealanders of West Asian and Central Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion In New Zealand
Irreligion in New Zealand refers to atheism, agnosticism, deism, religious scepticism and secular humanism in New Zealand society. Post-war New Zealand has become a highly secular country, meaning that religion does not play a major role in the lives of most people. Although New Zealand has no established religion, Christianity had been the most common religion since widespread European settlement in the 19th century. Demographics Statistics New Zealand gathers information on religious affiliation in the five-yearly census. Completing a census form is compulsory by law for every person in New Zealand on census night but respondents are able to object to answering the question of religious affiliation, and around 6% do object. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In New Zealand
Islam is the third-largest Religion in New Zealand, religion in New Zealand (1.5%) after Christianity in New Zealand, Christianity (32.3%) and Hinduism in New Zealand, Hinduism (2.9%). Small numbers of Muslim immigrants from South Asia and eastern Europe settled in New Zealand from the early 1900s until the 1960s. Large-scale Muslim immigration began in the 1970s with the arrival of Indo-Fijians, Indian Fijians, followed in the 1990s by refugees from various war-torn countries. According to the 2023 New Zealand census, there are 75,144 Muslim New Zealanders, representing 1.5% of the total population. The first Islamic centre in New Zealand opened in 1959 and there are now several mosques and two Islamic schools. The majority of Muslims in New Zealand are Sunni, with significant Shia and Ahmadiyya minorities. The Ahmadiyya Community has translated the Qur'an into the Māori language. History Early migration, 19th century The earliest Muslim presence in New Zealand dates bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |