|
Raja Todar Mal
Raja Todar Mal (1523-24 – 8 November 1589) was an Indian minister, economist, and military commander who served as the Finance Minister (Diwan-i-Ashraff) of the Mughal empire during the reign of Akbar I. He was also the Vakil-us-Sultanat (Counsellor of the Empire) and Joint Wazir. He was one of the premier nobles in the Mughal Empire and was a Mansabdar of 4000. He was one of the ''Navaratnas'' in Akbar's court. Under Todar Mal, there were 15 other Dewans nominated for 15 Subahs of Akbar. Life Todar Mal was born in the town of Laharpur in present-day Uttar Pradesh in a Hindu family, considered by historians as either Agrawal, Khatri or Kayastha. Todar Mal's father died when he was very young leaving no means of livelihood for him. Todar Mal started his career from the humble position of a writer but slowly moved up the ranks when Sher Shah Suri, the Sur emperor, assigned him to the charge of building a new fort of Rohtas in Punjab with the objective of preventing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance Minister
A ministry of finance is a ministry or other government agency in charge of government finance, fiscal policy, and financial regulation. It is headed by a finance minister, an executive or cabinet position . A ministry of finance's portfolio has a large variety of names around the world, such as "treasury", "finance", "financial affairs", "economy" or "economic affairs". The position of the finance minister might be named for this portfolio, but it may also have some other name, like "Treasurer" or, in the United Kingdom, "Chancellor of the Exchequer". The duties of a finance minister differ between countries. Typically, they encompass one or more of government finances, economic policy and/or financial regulation, but there are significant differences between countries: * in some countries the finance minister might also have oversight of monetary policy (while in other countries that is the responsibility of an independent central bank); * in some countries the finance m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vizier
A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister in the Near East. The Abbasids, Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a helper but afterwards became the representative and successor of the ''dapir'' (official scribe or secretary) of the Sasanian Empire, Sassanian kings. In modern usage, the term has been used for government Minister (government), ministers in much of the Middle East and beyond. Several alternative spellings are used in English, such as ''vizir'', ''wazir'', and ''vezir''. Etymology Vizier may be derived from the Arabic ''wazara'' (), from the Semitic root ''W-Z-R''. The word is mentioned in the Quran, where Aaron is described as the ''wazir'' (helper) of Moses, as well as the word ''wizr'' (burden) which is also derived from the same root. It was later adopted as a title, in the form of ''wazīr āl Muḥammad'' () by the proto-Shi'a leaders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sur Dynasty
The Sur Empire was an empire ruled by the Afghan (ethnonym), Afghan-origin Sur dynasty in North India, northern India for nearly 16 or 18 years, between 1538/1540 and 1556, with Sasaram (in modern-day Bihar) serving as its capital. It was founded by Sher Shah Suri. The Sur dynasty held control of nearly all the Mughal Empire territories along the Indo-Gangetic Plain, from Balochistan, Pakistan, eastern Balochistan in the west of Indus River to modern-day Rakhine State, Rakhine, Myanmar in the east. Even as Sher Shah Suri consolidated his power over North India, Eastern India was still considered to be the seat of Sur power in India. This is demonstrated by the fact that 8 of the 16 silver mint cities he established were in the region between Chunar and Padma Division, Fathabad. Reign of Sher Shah Suri War with the Bengal Sultanate and Mughal Empire (1537–1540) Sher Shah Suri's relentless campaigns on the Bengal Sultanate prompted its ruler to request aid from Humayun, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri (born Farid al-Din Khan; 1472 or 1486 – 22 May 1545), also known by his title Sultan Adil (), was the ruler of Bihar from 1530 to 1540, and Sultan of Hindustan from 1540 until his death in 1545. He defeated the Mughal Empire, founding the Sur Empire and establishing his rule in Delhi. The influence of his innovations and reforms extended far beyond his brief reign, being recognized as one of the greatest administrative rulers in India. During his time in power, he remained undefeated in battle and is renowned as one of the most skillful Afghan generals in history. By the end of his reign, his empire covered nearly all of Northern India. Born between 1472 and 1486 and given the name Farid Khan, his early childhood saw him flee from home due to internal family strife. He pursued an education in Jaunpur, where his rise to power began after his father offered him a managerial position over his jagirs. Sher Shah effectively governed these territories, gaining a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Museum Of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, colloquially referred to as the Met, is an Encyclopedic museum, encyclopedic art museum in New York City. By floor area, it is the List of largest museums, third-largest museum in the world and the List of largest art museums, largest art museum in the Americas. With 5.36 million visitors in 2023, it is the List of most-visited museums in the United States, most-visited museum in the United States and the List of most-visited art museums, fifth-most visited art museum in the world. In 2000, its permanent collection had over two million works; it currently lists a total of 1.5 million works. The collection is divided into 17 curatorial departments. The Met Fifth Avenue, The main building at 1000 Fifth Avenue, along the Museum Mile, New York, Museum Mile on the eastern edge of Central Park on Manhattan's Upper East Side, is by area one of the world's list of largest art museums, largest art museums. The first portion of the approximately building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kayastha
Kayastha (or Kayasth) denotes a cluster of disparate Indian communities broadly categorised by the regions of the Indian subcontinent in which they were traditionally locatedthe Chitraguptavanshi Kayasthas of North India, the Chandraseniya Kayastha Prabhus of Maharashtra, the Bengali Kayasthas of Bengal and Karan (caste), Karanas of Odisha. All of them were traditionally considered "writing castes", who had historically served the ruling powers as administrators, ministers and record-keepers. The earliest known reference to the term ''Kayastha'' dates back to the Kushan Empire, when it evolved into a common name for a writer or scribe. In the Sanskrit literature and Epigraphy, inscriptions, it was used to denote the holders of a particular category of offices in the government service. In this context, the term possibly derived from ('principal, capital, treasury') and - ('to stay') and perhaps originally stood for an officer of the royal treasury, or revenue department. Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khatri
Khatri () is a caste system in India, caste originating from the Malwa (Punjab), Malwa and Majha areas of Punjab region of South Asia that is predominantly found in India, but also in Pakistan and Afghanistan. The Khatris claim they are warriors who took to trade. In the Indian subcontinent, they were mostly engaged in mercantile professions such as banking and trade. They were the dominant commercial and financial administration class of late-medieval India. Some in Punjab often belonged to hereditary agriculturalist land-holding lineages, while others were engaged in artisanal occupations such as silk production and weaving. Khatris of Punjab, specifically, were scribes and traders during the medieval period, with the Gurmukhi, Gurumukhi script used in writing the Punjabi language, Punjabi language deriving from a standardised form of the Lahnda, Lāṇḍa script used by Khatri traders; the invention of the script is traditionally ascribed to Guru Angad. During the mediev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agrawal
Agrawal (Agarwal, Agerwal, Agrawala, Agarwala, Agarwalla, Aggarwal, Agarawal'', ''Agarawala'', or Aggrawal) is a Bania caste. The Banias of northern India are a cluster of several communities, of which the Agrawal Banias, Maheshwari Banias, Oswal Banias, Khatri Banias and Porwal Banias are a part. They are found throughout northern India, mainly in the states of Rajasthan, Haryana, Punjab, Jammu and Kashmir, Chandigarh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Delhi, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh. They are also found in the Pakistani provinces of Punjab and Sindh, though at the time of the partition of India, most of them migrated across the newly created border to independent India. Most Agrawals follow Vaishnava Hinduism or Jainism, while a minority adhere to Islam or Christianity. The Agrawal are the descendants of Maharaja Agrasen, a Kshatriya king of the Agroha Kingdom. He is one of the descendants of the Hindu deity Shri Ram. Their prime goddess was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. It is assumed that the term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Avestan scripture Vendidad which refers to land of seven rivers as Hapta Hendu which itself is a cognate to Sanskrit term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ''. (The term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ'' is mentioned in Rig Veda and refers to a North western Indian region of seven rivers and to India as a whole.) The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). Likewise the Hebrew cognate ''hōd-dū'' refers to India mentioned in Hebrew BibleEsther 1:1. The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Beveridge (1837–1929)
Henry Beveridge (9 February 1837 – 8 November 1929) was an Indian Civil Service officer and orientalist in India. Life and career Born in Inzievar, Fife, Scotland, Beveridge studied at the Royal Circus School, Fife, Edinburgh Academy and the University of Glasgow. In 1856 he entered Queen's College, Belfast, where his father had been appointed editor of The Banner of Ulster. In July 1857 he successfully passed the public examinations for the Indian Civil Service, joining the service in 1857. He left for India in 1857 and reached Calcutta in January 1858. After training he was posted to Mymensingh as Assistant Magistrate and Collector and was then transferred to Jhenaidah in 1861, to Jessore in January 1862, to Nadia in April 1862, to Midnapur in January 1863, and to Sylhet in February 1863. From November 1863 he was posted for one year to the Foreign Department, serving in Manipur on special duty, after which he was sent to Kuch Behar as Joint Magistrate and Deputy Colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Blochmann
Heinrich Blochmann, known as Henry Ferdinand Blochmann (8 January 1838 – 13 July 1878), was a German orientalist and scholar of Persian language and literature who spent most of his career in India, where he worked first as a professor, and eventually as the principal at Calcutta Madrasa, now Aliah University in present Kolkata. He is also remembered for one of the first major English translations of '' Ain-i-Akbari'', the 16th-century Persian language chronicle of Mughal emperor Akbar, published in 1873. Early life and background Born at Dresden on 8 January 1838, he was the son of Ernest Ehrenfried Blochmann, printer, and nephew of Karl Justus Blochmann. He was educated at the Kreuzschule and the University of Leipzig (1855), where he studied oriental languages under Heinrich Leberecht Fleischer, and then (1857) was in Paris. Career In 1858, Blochmann came to England, intent on visiting India, and enlisted in the British Indian Army in 1858 as a private soldier. Soon af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sohail Gate - Rohtas Fort By Hassan
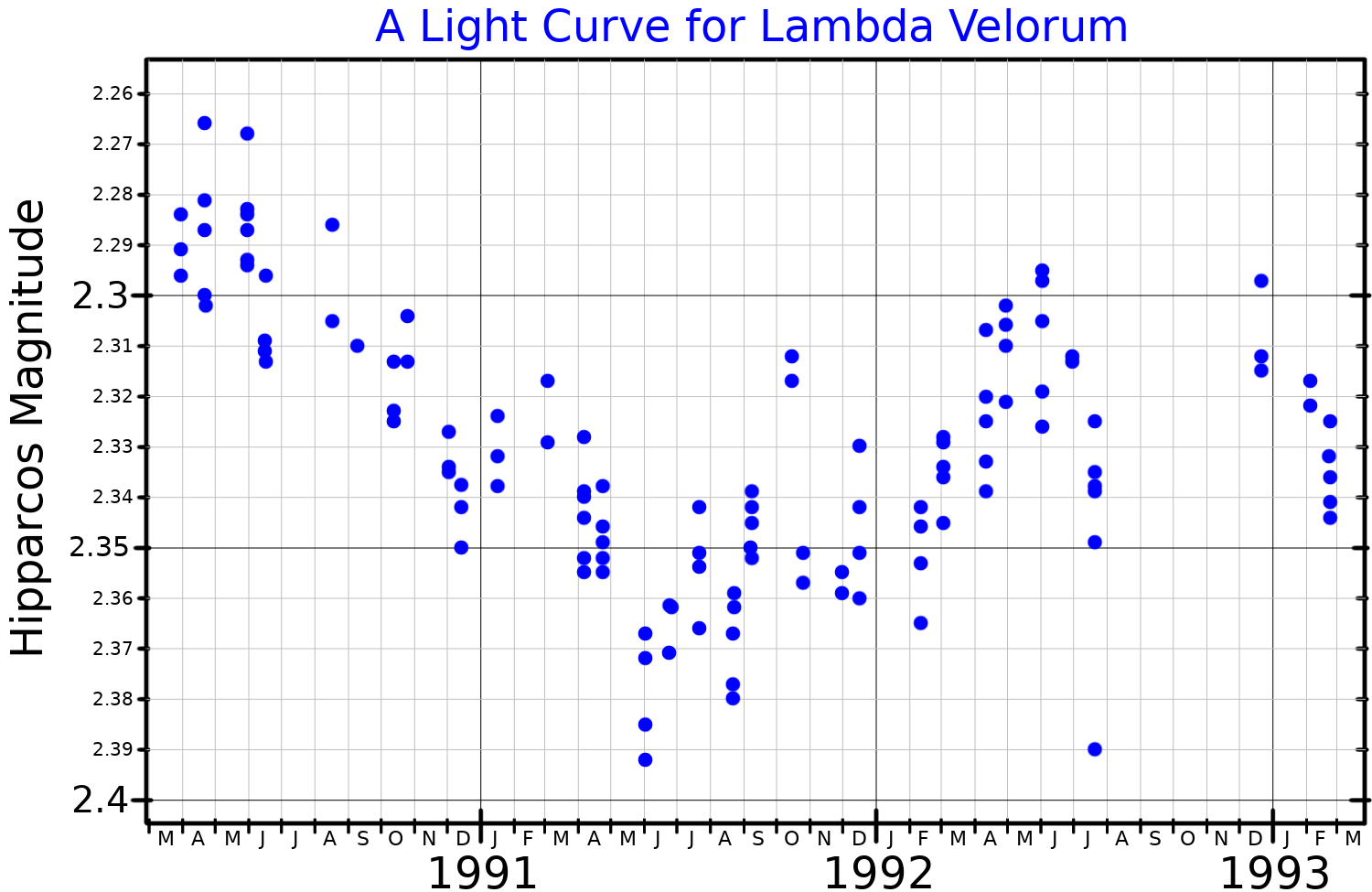
) Lambda Velorum (λ Velorum, abbreviated Lambda Vel, λ Vel), officially named Suhail , is a star in the southern constellation of Vela. With a mean apparent visual magnitude of 2.21, this is the third-brightest star in the constellation and one of the brighter stars in the sky. The distance to this star can be measured directly using the parallax technique, yielding an estimated from the Sun. Nomenclature ''λ Velorum'' ( Latinised to ''Lambda Velorum'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional Arabic name سهيل الوزن ''Suhail al Wazn'', but as a modern navigation star this was shortened to ''Suhail''. ' Suhail' (a common Arabic male first name) was traditionally used for at least three other stars: Canopus; Gamma Velorum (Suhail al Muhlif); and Zeta Puppis (Suhail Hadar). In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |