|
Radial Axle
A radial axle is an axle on a railway locomotive or carriage which has been designed to move laterally, along the arc of a circle, when entering a curve to reduce the flange and rail wear. William Bridges Adams was an early developer of radial axles. Radial axles were widely used on carriages in the late 19th century before the adoption of bogies. They were also used on the leading or trailing axles of locomotives, particularly tank locomotives. The idea was tried successfully by William Adams on the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) in 1882 with his 415 class. Radial axles were also used in locomotives designed by F.W. Webb of the London and North Western Railway, and by William Stroudley and R. J. Billinton of the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR (known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton)) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogie
A bogie ( ) (or truck in North American English) comprises two or more Wheelset (rail transport), wheelsets (two Railroad wheel, wheels on an axle), in a frame, attached under a vehicle by a pivot. Bogies take various forms in various modes of transport. A bogie may remain normally attached (as on many railroad cars and semi-trailers) or be quickly detachable (as for a dolly (trailer), dolly in a road train or in railway bogie exchange). It may include Suspension (vehicle), suspension components within it (as most rail and trucking bogies do), or be solid and in turn be suspended (as are most bogies of continuous track, tracked vehicles). It may be mounted on a swivel, as traditionally on a railway carriage or locomotive, additionally jointed and sprung (as in the landing gear of an airliner), or held in place by other means (centreless bogies). Although ''bogie'' is the preferred spelling and first-listed variant in various dictionaries, bogey and bogy are also used. Rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Wheel
The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located on a leading truck. Leading wheels are used to help the locomotive negotiate curves and to support the front portion of the boiler. Overview Many leading bogies do not have simple rotational motion about a vertical pivot. Bogies with a sliding motion controlled by springs was patented by William Adams in 1865. Other designs used swing links to take the weight of the bogie with a centering action. The first use of leading wheels is commonly attributed to John B. Jervis, who employed them in his 1832 design for a locomotive with four leading wheels and two driving wheels (a type that became known as the ''Jervis''). In the Whyte system of describing locomotive wheel arrangements, his locomotive would be classified as a 4-2-0, that is to say, it had four leading wheels, two dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
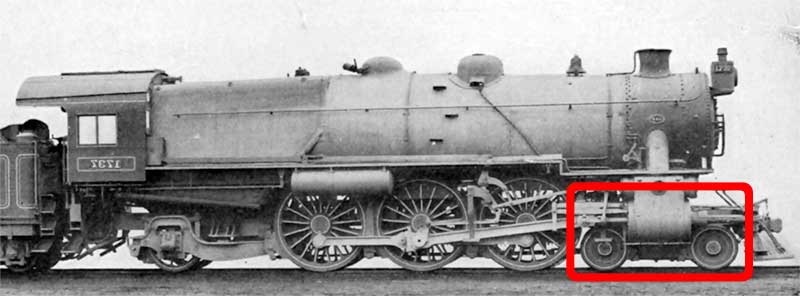
Trailing Wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, truck. On some large locomotives, a booster engine was mounted on the trailing truck to provide extra tractive effort when starting a heavy train and at low speeds on gradients. Trailing wheels were used in some early locomotives but fell out of favor for a time during the latter 19th century. As demand for more powerful locomotives increased, trailing wheels began to be used to support the crew cab and rear firebox area. Trailing wheels first appeared on American locomotives between 1890 and 1895, but their axle worked in rigid pedestals. It enabled boilers to be lowered, since the top of the main frames was dropped down behind the driving wheels and under the firebox. The firebox could also be longer and wider, increasing the heating su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Adams (locomotive Engineer)
William Adams (15 October 1823 – 7 August 1904) was an English railway engineer. He was the Locomotive Superintendent of the North London Railway from 1858 to 1873; the Great Eastern Railway from 1873 until 1878 and the London and South Western Railway from then until his retirement in 1895. He is best known for his steam locomotive, locomotives featuring the ''Adams bogie'', a device with lateral centring springs (initially made of rubber) to improve high-speed stability. He should not be mistaken for William Bridges Adams (1797–1872) a locomotive engineer who, confusingly, invented the ''Adams axle'' – a radial axle that William Adams incorporated in designs for the London and South Western Railway. History Adams was born on 15 October 1823 in Mill Place, Limehouse, London, where his father was resident engineer of the nearby East India Docks, East and West India Docks Company. After private schooling in Margate, Kent he was apprenticed to his father's works. The railw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exeter and Plymouth, and to Padstow, Ilfracombe and Bude. It developed a network of routes in Hampshire, Surrey and Berkshire, including Portsmouth and Reading. The LSWR became famous for its express passenger trains to Bournemouth and Weymouth, and to Devon and Cornwall. Nearer London it developed a dense suburban network and was pioneering in the introduction of a widespread suburban electrified passenger network. It was the prime mover of the development of Southampton Docks, which became an important ocean terminal as well as a harbour for cross channel services and for Isle of Wight ferries. Although the LSWR's area of influence was not the home of large-scale heavy industry, the transport of goods and mineral traffic was a major activity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
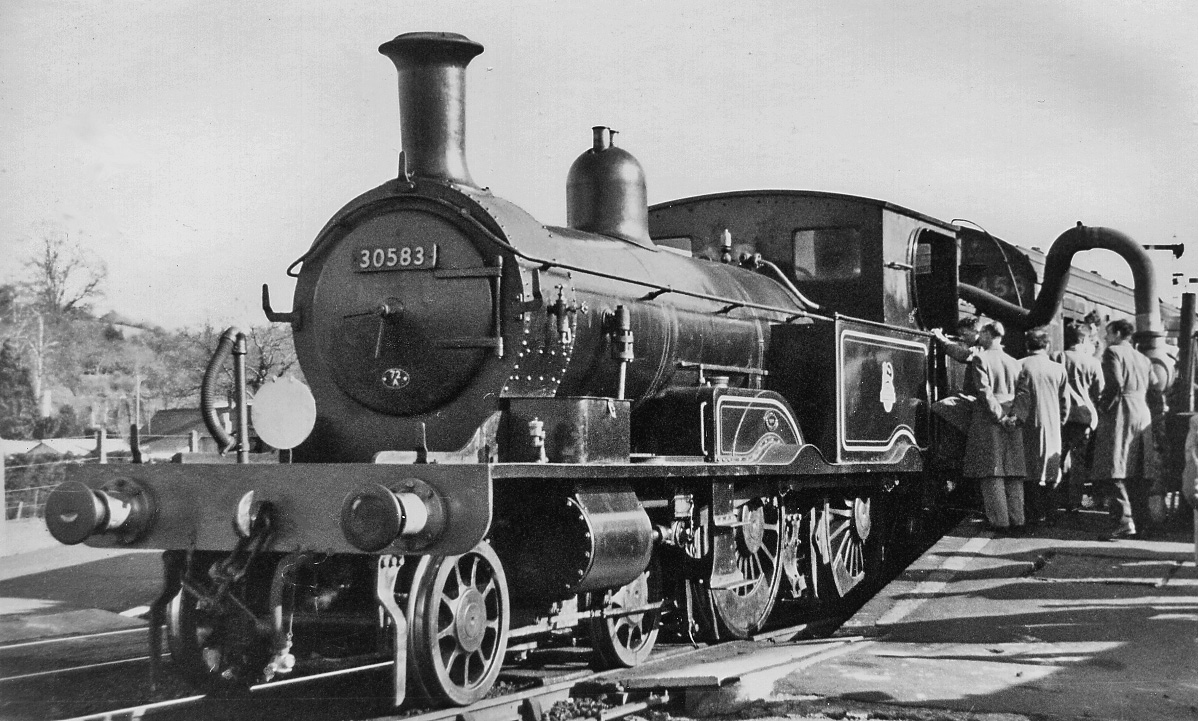
LSWR 415 Class
The LSWR 415 class is a 4-4-2T steam tank locomotive, with the trailing wheels forming the basis of its "Radial Tank" moniker. It was designed by William Adams and introduced in 1882 for service on the London and South Western Railway (LSWR). Originally rostered for suburban traffic, the class was soon displaced to the countryside by Dugald Drummond's M7 class. Most of the class was scrapped around the end of the First World War, and further decreases meant that all of them were due to be withdrawn by 1929. However, the class was noted for its long service on the Lyme Regis branch line, and three members of this long obsolete class were utilised on this duty until 1962, when suitable replacements became available. One has survived and can be found on the Bluebell Railway. Background This class, designed by William Adams, was the result of the work made to replace the stop-gap 46 Class on suburban services around London. In the event, they were also intended to supple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Webb (engineer)
Francis William Webb (21 May 1836 – 4 June 1906) was an English railway engineer, responsible for the design and manufacture of locomotives for the London and North Western Railway (LNWR). As the LNWR's chief mechanical engineer, he also exercised great influence in political and public life in the Cheshire town of Crewe, once being described as the 'King of Crewe'. Early life Webb was born in Tixall Rectory, near Stafford, the second son of William Webb, Rector of Tixall. Career Crewe Works Showing early interest in mechanical engineering, on 11 August 1851 at the age of fifteen he was articled as a pupil of Francis Trevithick at Crewe Works.Griffiths, p.51 Webb joined the drawing office in 1856, at the end of his training. He became Chief Draughtsman on 1 March 1859. On 1 September 1861 he was appointed Works Manager at Crewe and Chief Assistant to John Ramsbottom. Whilst Works Manager, Webb was responsible for the installation of Bessemer converters and the star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the LNWR was the largest joint stock company in the world. Dubbed the "Premier Line", the LNWR's main line connected four of the largest cities in England; London, Birmingham, Manchester and Liverpool, and, through cooperation with their Scottish partners, the Caledonian Railway also connected Scotland's largest cities of Glasgow and Edinburgh. Today this route is known as the West Coast Main Line. The LNWR's network also extended into Wales and Yorkshire. In 1923, it became a constituent of the London, Midland and Scottish (LMS) railway, and, in 1948, the London Midland Region of British Railways. History The company was formed on 16 July 1846 by the ( 9 & 10 Vict. c. cciv), which authorised the amalgamation of the Grand Junction Railway, London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway. This move was prompted, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Stroudley
William Stroudley (6 March 1833 – 20 December 1889) was an English railway engineer, and was one of the most famous steam locomotive engineers of the nineteenth century, working principally for the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR). He designed some of the most famous and longest-lived steam locomotives of his era, several of which have been preserved. Early career Born at Sandford-on-Thames, Oxfordshire, William Stroudley began work in 1847 at the local paper mill and in the same year he was apprenticed to John Inshaw's engineering firm in Birmingham. Over the next seven years he gained a variety of engineering experience on stationary engines and steam barges. From 1854 he trained as a locomotive engineer at Swindon Works under Daniel Gooch of the Great Western Railway, but soon moved to the Great Northern Railway under Charles Sacré at their Peterborough workshops, later becoming running foreman at the motive power depot there. In 1861 he was appointe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London, Brighton And South Coast Railway
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR (known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton)) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at its apex, practically the whole coastline of Sussex as its base, covering a large part of Surrey. It was bounded on its western side by the London and South Western Railway (L&SWR), which provided an alternative route to Portsmouth. On its eastern side the LB&SCR was bounded by the South Eastern Railway (England), South Eastern Railway (SER)—later one component of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR)—which provided an alternative route to Bexhill-on-Sea, Bexhill, St Leonards-on-Sea, and Hastings. The LB&SCR had the most direct routes from London to the south coast seaside resorts of Brighton, Eastbourne, Worthing, Littlehampton and Bognor Regis, and to the ports of Newhaven, East Sussex, Newhaven and Shoreham-by-Sea. It served ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannon Box Bearing
A cannon bearing or cannon box bearing is an arrangement of bearing (mechanical), bearings on a shaft (mechanical engineering), shaft, usually an axle, where two bearings are mounted in an enclosed tube. The function of the cannon box is to preserve the alignment of the two bearings, even if the overall tube is allowed to move. The two bearings will retain their same relative position. The bearing tube can be attached to the vehicle frame through either a pivot or springs. The name "cannon box" derives from the appearance of the hollow tube and from the John Wilkinson (industrialist)#Boring machine for steam engines, boring machines used to machine the accurately aligned bearing seats, the same machines developed for the boring (manufacturing), boring of cannon and for machining the cylinder (locomotive), cylinders of steam locomotives. Cannon box bearings are still found today, although much of the need for them was removed by the development of self-aligning ball bearings. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Joy (engineer)
250px, Joy Valve Gear Diagram Joy valve gear is a type of steam locomotive valve gear, designed by David Joy (3 March 1825 – 1903), Locomotive and Marine engineer, and patented (no. 929) on 8 March 1879. The British patent has not been found but the US patent (US252224 of 10 January 1882) has. Joy's gear is similar to Hackworth valve gear but has a compensating mechanism which corrects for "the slight inequality in the motion of the valve arising from the arc of the lever". The drawing (right) shows the Joy gear as applied to a London and North Western Railway locomotive. The US patent shows several modifications of the gear. In figure 6 of the patent, one of the levers has been replaced by a slide. On 10 January 1882, Mr. Joy received U.S. Patent No. 252,224 for the invention. Operation The movement is derived from a vertical link connected to the connecting rod. The vertical movement is translated into the horizontal movement required by the valve spindle by a die block m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |