|
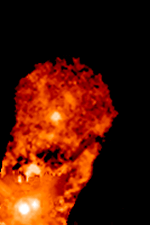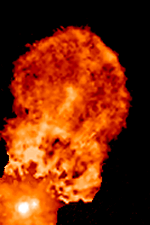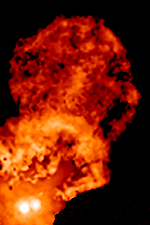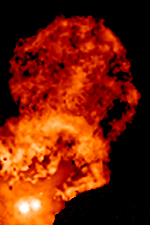
RW Aurigae
RW Aurigae is a young binary system in the constellation of Auriga about away, belonging to the Taurus-Auriga association of the Taurus Molecular Cloud. RW Aurigae B was discovered in 1944. System The two stars of the RW Aurigae system are separated by , equivalent to at the distance of RW Aurigae. The primary is a pre-main sequence star with a mass of , while the secondary has a mass of . These are loosely bound, and their orbital trajectory is nearly parabolic, with an orbital period of 1000−1500 years as evidenced by the structure of the ejected dust jets. The star system's orbit is retrograde compared to the rotation direction of the disk orbiting the primary star. RW Aurigae A is also suspected to be a close binary since 1999. Properties Both members of the binary are medium-mass objects still contracting towards the main sequence and accreting mass, RW Aurigae A at the rate of 0.1/Myr, and RW Aurigae B at the rate of 0.005/Myr. Their ages are equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Tauri Variable
T Tauri stars (TTS) are a class of variable stars that are less than about ten million years old. This class is named after the prototype, T Tauri, a young star in the Taurus star-forming region. They are found near molecular clouds and identified by their optical variability and strong chromospheric lines. T Tauri stars are pre-main-sequence stars in the process of contracting to the main sequence along the Hayashi track, a luminosity–temperature relationship obeyed by infant stars of less than 3 solar masses () in the pre-main-sequence phase of stellar evolution. It ends when a star of or larger develops a radiative zone, or when a smaller star commences nuclear fusion on the main sequence. History While T Tauri itself was discovered in 1852, the T Tauri class of stars were initially defined by Alfred Harrison Joy in 1945. Characteristics T Tauri stars comprise the youngest visible F, G, K and M spectral type stars (). Their surface temperatures are similar to those of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipparcos Objects
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the first high-precision measurements of the intrinsic brightnesses (compared to the less precise apparent brightness), proper motions, and parallaxes of stars, enabling better calculations of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial velocity measurements from spectroscopy, astrophysicists were able to finally measure all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting ''Hipparcos Catalogue'', a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision ''Tycho Catalogue'' of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. ''Hipp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durchmusterung Objects
In astronomy, Durchmusterung or Bonner Durchmusterung (BD) is an astrometric star catalogue of the whole sky, compiled by the Bonn Observatory in Germany from 1859 to 1903. The name comes from ('run-through examination'), a German word used for a systematic survey of objects or data. The term has sometimes been used for other astronomical surveys, including not only stars, but also the search for other celestial objects. Special tasks include celestial scanning in electromagnetic wavelengths shorter or longer than visible light waves. Original catalog The 44 years of work on the Bonner Durchmusterung (abbreviated BD), initiated by Friedrich Argelander and largely carried out by his assistants, resulted in a catalogue of the positions and apparent magnitudes of approximately 325,000 stars to apparent magnitude 9–10. The catalogue was accompanied by charts plotting the positions of the stars, and was the basis for the ''Astronomische Gesellschaft Katalog'' (AGK) and '' Smith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Draper Catalogue Objects
Henry may refer to: People *Henry (given name) *Henry (surname) * Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry Royalty * Portuguese royalty ** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal ** Henry, Count of Portugal, Henry of Burgundy, Count of Portugal (father of Portugal's first king) ** Prince Henry the Navigator, Infante of Portugal ** Infante Henrique, Duke of Coimbra (born 1949), the sixth in line to Portuguese throne * King of Germany **Henry the Fowler (876–936), first king of Germany * King of Scots (in name, at least) ** Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley (1545/6–1567), consort of Mary, queen of Scots ** Henry Benedict Stuart, the 'Cardinal Duke of York', brother of Bonnie Prince Charlie, who was hailed by Jacobites as Henry IX * Four kings of Castile: **Henry I of Castile **Henry II of Castile **Henry III of Castile **Henry IV of Castile * Five kings of France, spelt ''Henri'' in Modern French since the Renaissance to italianize the name and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumstellar Disks
A circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids, or collision fragments in orbit around a star. Around the youngest stars, they are the reservoirs of material out of which planets may form. Around mature stars, they indicate that planetesimal formation has taken place, and around white dwarfs, they indicate that planetary material survived the whole of stellar evolution. Such a disc can manifest itself in various ways. Young star According to the widely accepted model of star formation, sometimes referred to as the nebular hypothesis, a young star ( protostar) is formed by the gravitational collapse of a pocket of matter within a giant molecular cloud. The infalling material possesses some amount of angular momentum, which results in the formation of a gaseous protoplanetary disc around the young, rotating star. The former is a rotating circumstellar disc of dens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Tauri Stars
T Tauri stars (TTS) are a class of variable stars that are less than about ten million years old. This class is named after the prototype, T Tauri, a young star in the Taurus star-forming region. They are found near molecular clouds and identified by their optical variability and strong chromospheric lines. T Tauri stars are pre-main-sequence stars in the process of contracting to the main sequence along the Hayashi track, a luminosity–temperature relationship obeyed by infant stars of less than 3 solar masses () in the pre-main-sequence phase of stellar evolution. It ends when a star of or larger develops a radiative zone, or when a smaller star commences nuclear fusion on the main sequence. History While T Tauri itself was discovered in 1852, the T Tauri class of stars were initially defined by Alfred Harrison Joy in 1945. Characteristics T Tauri stars comprise the youngest visible F, G, K and M spectral type stars (). Their surface temperatures are similar to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Stars
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FU Tauri
FU Tauri is a brown dwarf binary system in the constellation of Taurus about away. The secondary is very close to the lower limit for brown dwarfs and several databases list it as a distant massive exoplanet. System The two stars of the FU Tauri system are separated by , equivalent to at the distance of FU Tauri. The primary is a brown dwarf with a mass of , while the secondary has a mass of . The secondary mass of is close to the dividing line between brown dwarfs and exoplanets, and it is often treated as an exoplanet. Properties Both members of the binary are low-mass objects still contracting towards the main sequence. Comparison with theoretical evolutionary tracks gives them ages of one Myr or less. However, the primary is more luminous than expected even for this age and it may be younger than the secondary. The primary has a temperature of , a radius of , and a bolometric luminosity of . The secondary has a temperature of and a bolometric luminosity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UX Orionis Variable
A Herbig Ae/Be star (HAeBe) is a pre-main-sequence star – a young () star of spectral types A or B. These stars are still embedded in gas-dust envelopes and are sometimes accompanied by circumstellar disks. Hydrogen and calcium emission lines are observed in their spectra. They are 2-8 Solar mass () objects, still existing in the star formation (gravitational contraction) stage and approaching the main sequence (i.e. they are not burning hydrogen in their center). Description In the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, Herbig Ae/Be stars are located to the right of the main sequence. They are named after the American astronomer George Herbig, who first distinguished them from other stars in 1960. The original Herbig criteria were: * Spectral type earlier than F0 (in order to exclude T Tauri stars), * Balmer emission lines in the stellar spectrum (in order to be similar to T Tauri stars), * Projected location within the boundaries of a dark interstellar cloud (in order to select re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RW Aurigae Variable
RW or rw may refer to: In arts and entertainment * ''The Real World'' (TV series), an American reality television show * ''Road Wild'', a World Championship Wrestling pay-per-view event * Robbie Williams, a British pop star * Robin Williams, an American actor * Roger Waters, British musician * Robot Wars (other) In mathematics, science and technology In computing * Read-write access to files or directories, in file system permissions * Read-write memory * Rewritable media * RenderWare, a 3-D rendering engine produced by Criterion Software Other uses in mathematics, science, and technology * Random walk, a mathematical process that can be used to explain phenomena in several disciplines * Reaction wheel, a type of flywheel used primarily by spacecraft for attitude control * Robertson–Walker metric, in cosmology * Robin Wight, botanist, noted as R.W. * RW is the designation for the 15th variable star named in a constellation: ** RW Andromedae, a Mira variable locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kessler Syndrome
The Kessler syndrome (also called the Kessler effect, collisional cascading, or ablation cascade), proposed by NASA scientist Donald J. Kessler in 1978, is a scenario in which the density of objects in low Earth orbit (LEO) due to space pollution is high enough that collisions between objects could cause a cascade in which each collision generates space debris that increases the likelihood of further collisions. In 2009 Kessler wrote that modeling results had concluded that the debris environment was already unstable, "such that any attempt to achieve a growth-free small debris environment by eliminating sources of past debris will likely fail because fragments from future collisions will be generated faster than atmospheric drag will remove them". One implication is that the distribution of debris in orbit could render space activities and the use of satellites in specific orbital ranges difficult for many generations. History NORAD, Gabbard and Kessler Willy Ley predict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |