|
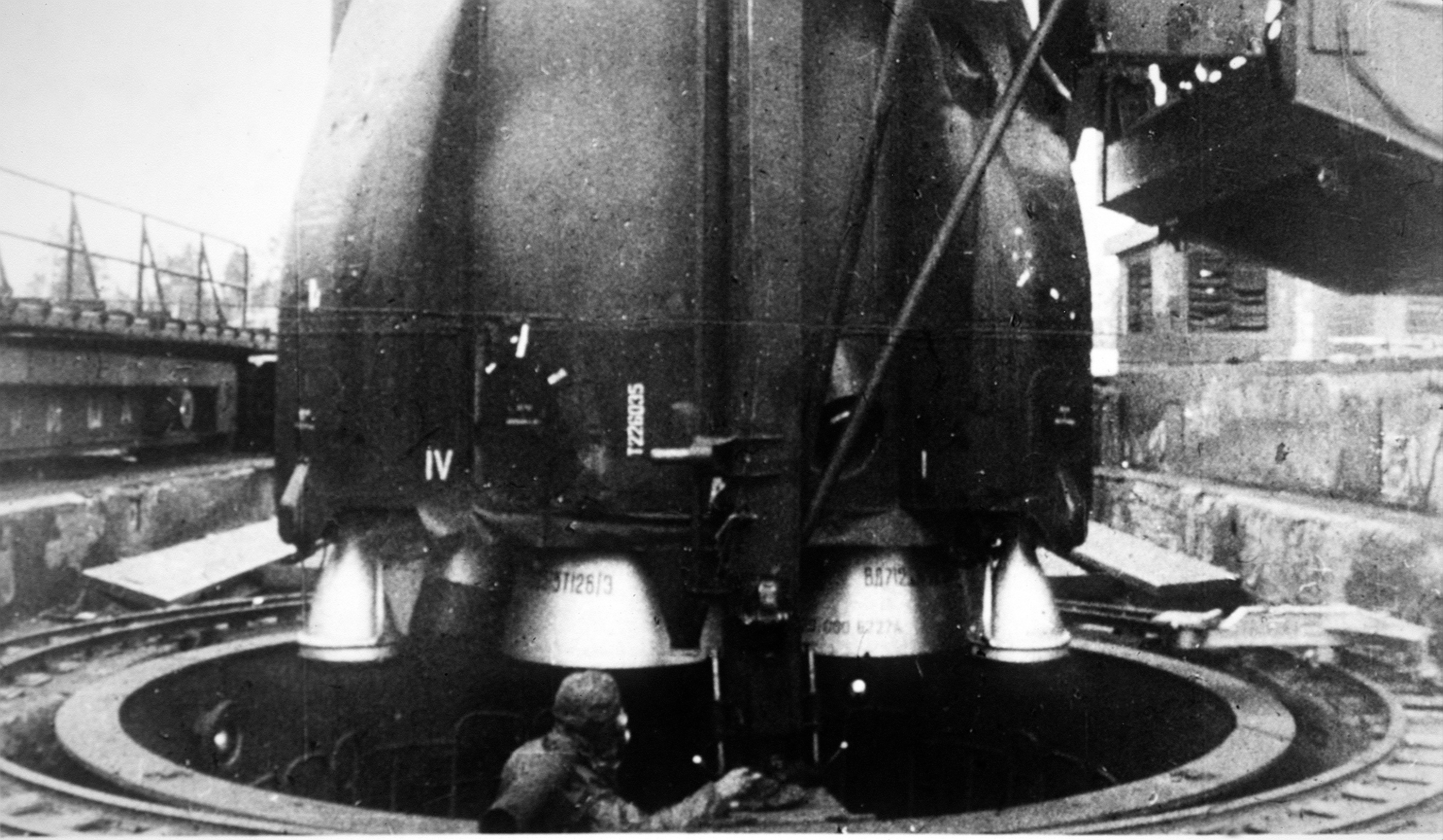
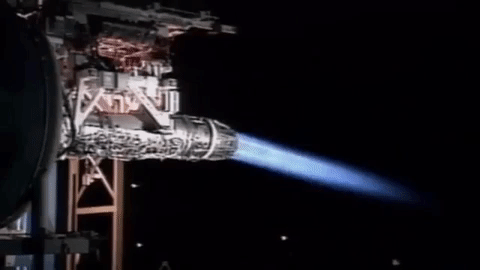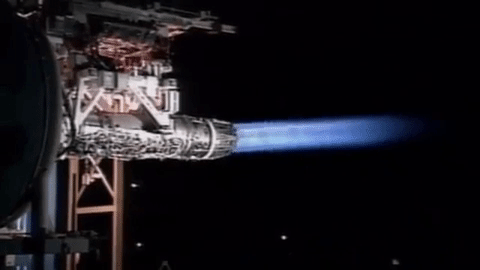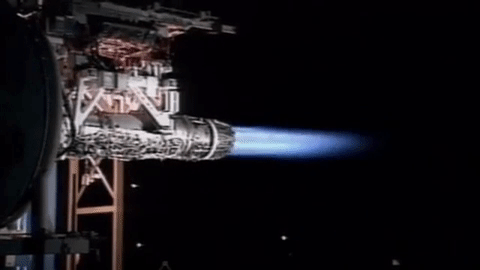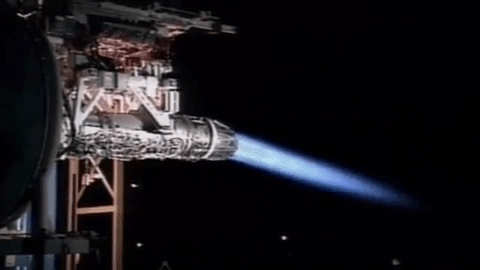
RD-0203
The RD-0210 (, GRAU index: 8D411K) is also known as the RD-465. It and its twin, the RD-0211, are rocket engines using unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) as fuel and dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) as oxidizer in an oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. They have a single nozzle, possess thrust vectoring and are the latest evolution in the RD-0203/4 lineage. They are the engines used on the Proton second stage. The RD-0213 is a fixed nozzle variation that is used on the RD-0212 module of the Proton third stage. Development When Chelomey's OKB-52 started their UR-200 ICBM project, they requested S. A. Kosberg's OKB-154 to develop the propulsion. They decided to use the same basic block for both the first and second stage. But to achieve the required performance, Kosberg had to develop a staged combustion engine, a then extremely aggressive feat. Only M. V. Melnikov of OKB-1 had designed a staged combustion engine before, the S1.5400, and it used a different propellant mix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voronezh Mechanical Plant
Voronezh Mechanical Plant (Russian: , ''ВМЗ'') is a Russian engine and heavy machinery manufacturing plant. It is located in the city of Voronezh, in the Voronezh Oblast. History Voronezh Mechanical Plant started as a diesel engine manufacturing plant, and has been the plant that serially manufactures the engines designed by Chemical Automatics Design Bureau (KBKhA). In later years, it has branched into producing oil and gas products like valves, manifolds and fittings. In January 2017, Roscosmos announced that firing tests revealed problems with the Voronezh-produced Proton rocket upper stage engines. According to the investigation, expensive alloys had been replaced by cheaper less heat-resistant alloys. Voronezh director-general Ivan Tikhonovich Koptev resigned. On November 1, 2019, enterprises ''ВМЗ'' and the Chemical Automatics Design Bureau were merged. Products Current engines Engines in production at the plant as of 2015: * RD-0110 - Upper stage engine of the So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernier Thruster
A vernier thruster is a rocket engine used on a spacecraft or launch vehicle for fine adjustments to the attitude or velocity. Depending on the design of a craft's maneuvering and stability systems, it may simply be a smaller thruster complementing the main propulsion system, or it may complement larger attitude control thrusters, or may be a part of the reaction control system. The name is derived from vernier calipers (named after Pierre Vernier) which have a primary scale for gross measurements, and a secondary scale for fine measurements. Vernier thrusters are used when a heavy spacecraft requires a wide range of different thrust levels for attitude or velocity control, as for maneuvering during docking with other spacecraft. On space vehicles with two sizes of attitude control thrusters, the main ACS (Attitude Control System) thrusters are used for larger movements, while the verniers are reserved for smaller adjustments. Due to their weight and the extra plumbing requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semyon Kosberg
Semyon Ariyevich Kosberg (''Семён А́риевич Ко́сберг'' in Russian) (October 1(14), 1903, Slutsk - January 3, 1965, Voronezh) was a Soviet engineer, expert in the field of aircraft and rocket engines, Doctor of Technical Sciences (1959), Hero of Socialist Labor (1961). In 1931, Semyon Kosberg graduated from the Moscow Aviation Institute. He then worked in some of the biggest planning organizations of the Soviet aircraft industry. In 1941, Kosberg was appointed chief designer of an aircraft design bureau, later known as OKB-154, which he ran until his death. He is known for his contributions to the creation of aircraft engines, mounted on the Lavochkin La-5, Lavochkin La-7, and other mass wartime aircraft. In 1946-1965, Kosberg supervised the development of a series of liquid fuel rocket engines, which would be mounted on the final stages of carrier rockets and put into orbit piloted spacecraft, satellites, and interplanetary automatic space stations. Semyon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Automatics Design Bureau
Chemical Automatics Design Bureau (CADB), also KB Khimavtomatika (, KBKhA), is a Russian OKB, design bureau founded by the NKAP (People's Commissariat of the Aircraft Industry) in 1941 and led by Semyon Kosberg until his death in 1965. Its origin dates back to a 1940 Moscow carburetor factory, evacuated to Berdsk in 1941, and then relocated to Voronezh city in 1945, where it now operates. Originally designated OKB-296 and tasked to develop fuel equipment for aviation engines, it was redesignated OKB-154 in 1946. In 1965 took over leadership. He was succeeded by in 1993, then by (RD-0124 Chief designer) in 2015. During this time the company designed a wide range of high technology products, including liquid propellant rocket engines, a nuclear reactor for space use, the first Soviet laser with an output of 1 MW and the USSR's only operational nuclear rocket engine. The company has designed more than 60 liquid propellant engines with some 30 having entered production. In Novem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Vasilyevich Melnikov
Michael is a common masculine given name derived from the Hebrew phrase ''mī kāʼēl'', 'Who slike-El', in Aramaic: ܡܝܟܐܝܠ (''Mīkhāʼēl'' ). The theophoric name is often read as a rhetorical question – "Who slike he Hebrew God El?", whose answer is "there is none like El", or "there is none as famous and powerful as God." This question is known in Latin as '' Quis ut Deus?'' Paradoxically, the name is also sometimes interpreted as, "One who is like God."Omnium Sanctorum Hiberniae"Michael - one who is like unto God"(This interpretation would be seen as heretical in some religions, but it is fairly common nonetheless.) An alternative spelling of the name is ''Micheal''. While ''Michael'' is most often a masculine name, it is also given to women, such as the actresses Michael Michele and Michael Learned, and Michael Steele, the former bassist for the Bangles. Patronymic surnames that come from Michael include '' Carmichael, DiMichele, MacMichael, McMichael, Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OKB-1
S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation "Energia" () is a Russian manufacturer of spacecraft and space station components. Its name is derived from the Russian word for energy and is also named for Sergei Korolev, Sergei Pavlovich Korolev, the first chief of its design bureau and the driving force behind early Soviet accomplishments in space exploration. Overview Energia is the largest company of the Russian space industry and one of its key players. It is responsible for all operations involving human spaceflight and is the lead developer of the Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz and Progress (spacecraft), Progress spacecraft, and the lead developer of the Russian end of the International Space Station (ISS). In the mid-2000s, the company employed 22,000–30,000 people. The enterprise has been awarded 4 Order of Lenin, Orders of Lenin, Order of the October Revolution and Russian Federation President's Message of Thanks. In addition, 14 cosmonauts employed by the company have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-36 (missile)
The R-36 () is a family of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and space launch vehicles (Tsyklon) designed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The original R-36 was deployed under the GRAU index 8K67 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-9 Scarp. It was able to carry three warheads and was the first Soviet MIRV (multiple re-entry vehicle, multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicle) missile. The later version, the R-36M, also known as RS20, was produced under the GRAU designations 15A14 and 15A18 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-18 Satan. This missile was viewed by certain United States analysts as giving the Soviet Union Pre-emptive nuclear strike, first strike advantage over the U.S., particularly because of its rapid silo-reload ability, very heavy throw weight and extremely large number of atmospheric re-entry, re-entry vehicles. Some versions of the R-36M were deployed with 10 warheads and up to 40 penetration aids and the missile's high thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Vectoring
Thrust vectoring, also known as thrust vector control (TVC), is the ability of an aircraft, rocket or other vehicle to manipulate the direction of the thrust from its engine(s) or motor(s) to Aircraft flight control system, control the Spacecraft attitude control, attitude or angular velocity of the vehicle. In rocketry and ballistic missiles that fly outside the atmosphere, aerodynamic Flight control surfaces, control surfaces are ineffective, so thrust vectoring is the primary means of Flight dynamics (fixed-wing aircraft), attitude control. Exhaust vanes and Gimbaled thrust, gimbaled engines were used in the 1930s by Robert H. Goddard, Robert Goddard. For aircraft, the method was originally envisaged to provide upward vertical thrust as a means to give aircraft vertical (VTOL) or short (STOL) takeoff and landing ability. Subsequently, it was realized that using vectored thrust in combat situations enabled aircraft to perform various maneuvers not available to conventional-en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OKB-52
NPO Mashinostroyeniya () is a rocket design bureau based in Reutov, Russia. During the Cold War it was responsible for several major weapons systems, including the UR-100N Intercontinental ballistic missile and the military Almaz space station program. India is Mashinostroyeniya's second largest customer after the Russian Federation for sale of P-70 Ametist, BrahMos, BrahMos-II and P-800 Oniks. History NPO Mashinostroyeniya was founded in 1944 to develop rockets for the Russian military. Under the leadership of cruise missile designer Vladimir Chelomey, the firm was lead developer of the Soviet Union's space satellites, cruise missiles, and intercontinental ballistic missiles. Originally part of the OKB-51 design bureau, it relocated to Reutov, and from 1955 to 1966 was designated OKB-52 (and also OKB-52 MAP). OKB-52 became later known as TsKBM. The OKB-52 was the main rival of OKB-1 (then the design bureau of Sergei Korolev, later renamed TsKBEM, today RSC Energia) during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |