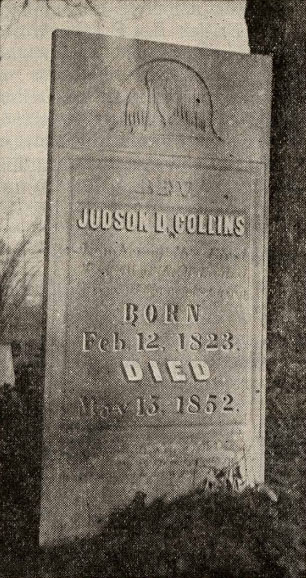|
R. S. Maclay
Robert Samuel Maclay, D.D. (; Pinyin: ''Mài Lìhé''; Foochow Romanized: ''Măh Lé-huò''; February 7, 1824 - August 18, 1907) was an American missionary who made pioneer contributions to the Methodist Episcopal missions in China, Japan and Korea. He served as the first president of Aoyama Gakuin University. Life Early life Robert Samuel Maclay was born on February 7, 1824 in Concord, Pennsylvania, one of nine children. His parents, Robert Maclay and Arabella Erwin Maclay, ran a tanning business in the local community. His father, a respected member of the Democratic Party, was raised up in the Presbyterian faith but became actively involved in the Methodist Episcopal Church, dedicating himself to spreading the Gospel, his mother an immigrant from the north of Ireland who shared her husband's religious devotion. Maclay entered Dickinson College in the fall of 1841 and was elected into the Belles Lettres Society. As a college student he was highly influenced by his prof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concord, Pennsylvania
Concord is an unincorporated community in Fannett Township, Franklin County, Pennsylvania, United States. The community is located on Pennsylvania Route 75, south-southwest of East Waterford. Concord has a post office, with ZIP code 17217. Concord was platted in 1797, and named after the Battle of Concord The Battles of Lexington and Concord were the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War. The battles were fought on April 19, 1775, in Middlesex County, Province of Massachusetts Bay, within the towns of Lexington, Concord, .... A post office called Concord has been in operation since 1811. References {{authority control Unincorporated communities in Franklin County, Pennsylvania Unincorporated communities in Pennsylvania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodist Episcopal Church
The Methodist Episcopal Church (MEC) was the oldest and largest Methodist denomination in the United States from its founding in 1784 until 1939. It was also the first religious denomination in the US to organize itself on a national basis. In 1939, the MEC reunited with two breakaway Methodist denominations (the Methodist Protestant Church and the Methodist Episcopal Church, South) to form the Methodist Church. In 1968, the Methodist Church merged with the Evangelical United Brethren Church to form the United Methodist Church. The MEC's origins lie in the First Great Awakening when Methodism emerged as an evangelical revival movement within the Church of England that stressed the necessity of being born again and the possibility of attaining Christian perfection. By the 1760s, Methodism had spread to the Thirteen Colonies, and Methodist societies were formed under the oversight of John Wesley. As in England, American Methodists remained affiliated with the Church of Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta in South China. With 7.5 million residents of various nationalities in a territory, Hong Kong is one of the most densely populated places in the world. Hong Kong is also a major global financial centre and one of the most developed cities in the world. Hong Kong was established as a colony of the British Empire after the Qing Empire ceded Hong Kong Island from Xin'an County at the end of the First Opium War in 1841 then again in 1842.. The colony expanded to the Kowloon Peninsula in 1860 after the Second Opium War and was further extended when Britain obtained a 99-year lease of the New Territories in 1898... British Hong Kong was occupied by Imperial Japan from 1941 to 1945 during World War II; British administration resumed after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henrietta Caroline Maclay
Henrietta may refer to: * Henrietta (given name), a feminine given name, derived from the male name Henry Places * Henrietta Island in the Arctic Ocean * Henrietta, Mauritius * Henrietta, Tasmania, a locality in Australia United States * Henrietta, Missouri * Henrietta, Johnson County, Missouri * Henrietta, New York * Henrietta, Ohio * Henrietta, Pennsylvania * Henrietta, Texas * Henrietta, West Virginia * Henrietta, Wisconsin, a county subdivision ** Henrietta (ghost town), Wisconsin, a ghost town * Henrietta Township: ** Henrietta Township, Michigan ** Henrietta Township, Hubbard County, Minnesota ** Henrietta Township, Lorain County, Ohio ** Henrietta Township, LaMoure County, North Dakota Fictional characters * Henrietta de Tristain a fictional character from the Japanese light novel/anime '' Zero no Tsukaima'' * Henrietta the coach, a fictional character of ''The Railway Series'' * Henrietta (Gunslinger), a fictional character from the Japanese manga/anime ''Gunslin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judson Dwight Collins
Rev. Judson Dwight Collins (; Pinyin: ''Kēlín''; Foochow Romanized: ''Kŏ̤-lìng''; February 12, 1823 - May 13, 1852) was the first Methodist missionary to China. Life On February 12, 1823, Judson Dwight Collins was born into a Methodist family in Rose, Wayne County, New York. His parents, Alpheus and Betsay Collins, were of English and German origin. After graduation from the first class of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor in 1845, Collins served as an instructor for two years at the Wesleyan Seminary at Albion College, teaching courses in Latin, Greek, chemistry, botany, and rhetoric. In 1847, Collins was called to New York, where he was ordained an elder and commissioned along with M. C. White and his wife to China. They sailed from Boston on April 15 and reached Foochow on September 6. To start an opening for the missionary work, Collins set up a school for boys in 1847 and another in 1848. He also worked with M. C. White on Bible translation and distribution o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moses Clark White
Moses Clark White (; Pinyin: ''Huáidé''; Foochow Romanized: ''Huài-dáik''; July 24, 1819 – October 24, 1900) was both an American Methodist pioneer missionary in China and a physician. Life Moses Clark White was born in Paris, Oneida County, New York on July 24, 1819. White matriculated at Wesleyan University in 1842 and graduated in 1845. After graduation from Wesleyan, he spent two years in Yale studying medicine and theology, and sometimes preached in the nearby town of Milford, Connecticut. On March 13, 1847, White married Jane Isabel Atwater of Homer, who came from Cortland County, New York and was then a teacher in the Sabbath School in Rochester, N.Y. In September 1847 Moses White and Jane, along with Judson Dwight Collins, arrived in Foochow, beginning their missionary work there. Jane, however, fell sick shortly afterwards and finally died of consumption on May 25, 1848, at the age of 26. In 1851, White was married a second time to Mary Seely, who came f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Hickok
Henry may refer to: People *Henry (given name) * Henry (surname) * Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry Royalty * Portuguese royalty ** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal ** Henry, Count of Portugal, Henry of Burgundy, Count of Portugal (father of Portugal's first king) ** Prince Henry the Navigator, Infante of Portugal ** Infante Henrique, Duke of Coimbra (born 1949), the sixth in line to Portuguese throne * King of Germany **Henry the Fowler (876–936), first king of Germany * King of Scots (in name, at least) ** Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley (1545/6–1567), consort of Mary, queen of Scots ** Henry Benedict Stuart, the 'Cardinal Duke of York', brother of Bonnie Prince Charlie, who was hailed by Jacobites as Henry IX * Four kings of Castile: **Henry I of Castile **Henry II of Castile **Henry III of Castile **Henry IV of Castile * Five kings of France, spelt ''Henri'' in Modern French since the Renaissance to italianize the name and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foochow
Fuzhou (; , Fuzhounese: Hokchew, ''Hók-ciŭ''), alternately romanized as Foochow, is the capital and one of the largest cities in Fujian province, China. Along with the many counties of Ningde, those of Fuzhou are considered to constitute the Mindong (lit. Eastern Fujian) linguistic and cultural area. Fuzhou lies on the north (left) bank of the estuary of Fujian's largest river, the Min River. All along its northern border lies Ningde, and Ningde's Gutian County lies upriver. Its population was 7,115,370 inhabitants as of the 2010 census, of whom 4,408,076 inhabitants are urban representing around 61.95%, while rural population is at 2,707,294 representing around 38.05%. As of 31 December 2018, the total population was estimated at 7,740,000 whom 4,665,000 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of 5 urban districts plus Minhou County. In 2015, Fuzhou was ranked as the 10th fastest growing metropolitan area in the world by Brookings Institution. Fuzhou is listed as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery In The United States
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Slavery was established throughout European colonization in the Americas. From 1526, during early colonial days, it was practiced in what became Britain's colonies, including the Thirteen Colonies that formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property that could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of U.S. states until abolition. In the decades after the end of Reconstruction, many of slavery's economic and social functions were continued through segregation, sharecropping, and convict leasing. By the time of the American Revolution (1775–1783), the status of enslaved people had been institutionalized as a racial caste associated with African ancestry. During and immediately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Divinity
A Doctor of Divinity (D.D. or DDiv; la, Doctor Divinitatis) is the holder of an advanced academic degree in divinity. In the United Kingdom, it is considered an advanced doctoral degree. At the University of Oxford, doctors of divinity are ranked first in "academic precedence and standing", while at the University of Cambridge they rank ahead of all other doctors in the "order of seniority of graduates". In some countries, such as in the United States, the degree of doctor of divinity is usually an honorary degree and not a research or academic degree. Doctor of Divinity by country or church British Isles In the United Kingdom and Ireland, the degree is a higher doctorate conferred by universities upon a religious scholar of standing and distinction, usually for accomplishments beyond the Ph.D. level. Bishops of the Church of England have traditionally held Oxford, Cambridge, Dublin, or Lambeth degrees making them doctors of divinity. At the University of Oxford, doc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master's Degree
A master's degree (from Latin ) is an academic degree awarded by universities or colleges upon completion of a course of study demonstrating mastery or a high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice. A master's degree normally requires previous study at the bachelor's degree, bachelor's level, either as a separate degree or as part of an integrated course. Within the area studied, master's graduates are expected to possess advanced knowledge of a specialized body of and applied topics; high order skills in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14598130197).jpg)