|
Quantum Spin Liquid
In condensed matter physics, a quantum spin liquid is a phase of matter that can be formed by interacting quantum spins in certain magnetic materials. Quantum spin liquids (QSL) are generally characterized by their long-range quantum entanglement, fractionalized excitations, and absence of ordinary magnetic order. The quantum spin liquid state was first proposed by physicist Phil Anderson in 1973 as the ground state for a system of spins on a triangular lattice that interact antiferromagnetically with their nearest neighbors, i.e. neighboring spins seek to be aligned in opposite directions. Quantum spin liquids generated further interest when in 1987 Anderson proposed a theory that described high temperature superconductivity in terms of a disordered spin-liquid state. Basic properties The simplest kind of magnetic phase is a paramagnet, where each individual spin behaves independently of the rest, just like atoms in an ideal gas. This highly disordered phase is the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensed Matter Physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the subject deals with "condensed" phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions between them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on crystal lattices of atoms, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in ultracold atomic systems. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theories to develop mathematical models. The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order And Disorder (physics)
In physics, the terms order and disorder designate the presence or absence of some symmetry or correlation in a many-particle system. In condensed matter physics, systems typically are ordered at low temperatures; upon heating, they undergo one or several phase transitions into less ordered states. Examples for such an order-disorder transition are: * the melting of ice: solid-liquid transition, loss of crystalline order; * the demagnetization of iron by heating above the Curie temperature: ferromagnetic-paramagnetic transition, loss of magnetic order. The degree of freedom that is ordered or disordered can be translational (crystalline ordering), rotational (ferroelectric ordering), or a spin state ( magnetic ordering). The order can consist either in a full crystalline space group symmetry, or in a correlation. Depending on how the correlations decay with distance, one speaks of long range order or short range order. If a disordered state is not in thermodynamic equilibriu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Susceptibility
In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility (Latin: , "receptive"; denoted ) is a measure of how much a material will become magnetized in an applied magnetic field. It is the ratio of magnetization (magnetic moment per unit volume) to the applied magnetizing field intensity . This allows a simple classification, into two categories, of most materials' responses to an applied magnetic field: an alignment with the magnetic field, , called paramagnetism, or an alignment against the field, , called diamagnetism. Magnetic susceptibility indicates whether a material is attracted into or repelled out of a magnetic field. Paramagnetic materials align with the applied field and are attracted to regions of greater magnetic field. Diamagnetic materials are anti-aligned and are pushed away, toward regions of lower magnetic fields. On top of the applied field, the magnetization of the material adds its own magnetic field, causing the field lines to concentrate in paramagnetism, or be exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
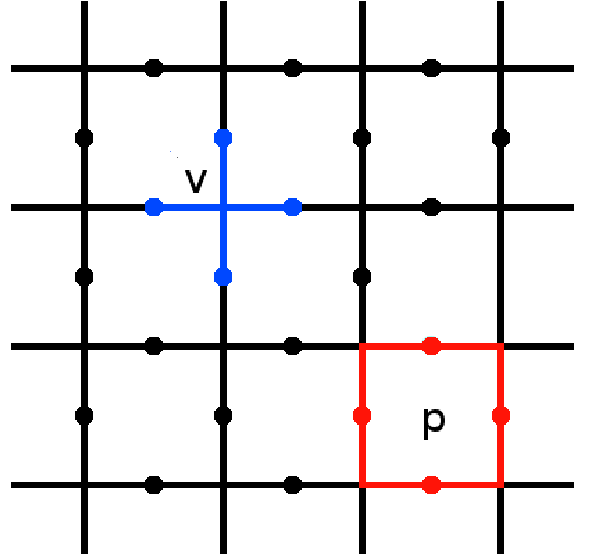
Toric Code
The toric code is a topological quantum error correcting code, and an example of a stabilizer code, defined on a two-dimensional spin lattice. It is the simplest and most well studied of the quantum double models. It is also the simplest example of topological order—''Z''2 topological order (first studied in the context of ''Z''2 spin liquid in 1991). The toric code can also be considered to be a ''Z''2 lattice gauge theory in a particular limit. It was introduced by Alexei Kitaev. The toric code gets its name from its periodic boundary conditions, giving it the shape of a torus. These conditions give the model translational invariance, which is useful for analytic study. However, some experimental realizations require open boundary conditions, allowing the system to be embedded on a 2D surface. The resulting code is typically known as the planar code. This has identical behaviour to the toric code in most, but not all, cases. Error correction and computation The toric code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z2 Topological Order
Z (or z) is the 26th and last letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual names in English are ''zed'' () and ''zee'' (), with an occasional archaic variant ''izzard'' ()."Z", ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989); ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993); "zee", ''op. cit''. Name and pronunciation In most English-speaking countries, including Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, New Zealand and the United Kingdom, the letter's name is ''zed'' , reflecting its derivation from the Greek ''zeta'' (this dates to Latin, which borrowed Y and Z from Greek), but in American English its name is ''zee'' , analogous to the names for B, C, D, etc., and deriving from a late 17th-century English dialectal form. Another English dialectal form is ''izzard'' . This dates from the mid-18th century and probably derives fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinon
Spinons are one of three quasiparticles, along with holons and orbitons, that electrons in solids are able to split into during the process of spin–charge separation, when extremely tightly confined at temperatures close to absolute zero. The electron can always be theoretically considered as a bound state of the three, with the spinon carrying the spin of the electron, the orbiton carrying the orbital location and the holon carrying the charge, but in certain conditions they can behave as independent quasiparticles. The term spinon is frequently used in discussions of experimental facts within the framework of both quantum spin liquid and strongly correlated quantum spin liquid. Overview Electrons, being of like charge, repel each other. As a result, in order to move past each other in an extremely crowded environment, they are forced to modify their behavior. Research published in July 2009 by the University of Cambridge and the University of Birmingham in England showed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinon Moving
Spinons are one of three quasiparticles, along with holons and orbitons, that electrons in solids are able to split into during the process of spin–charge separation, when extremely tightly confined at temperatures close to absolute zero. The electron can always be theoretically considered as a bound state of the three, with the spinon carrying the spin of the electron, the orbiton carrying the orbital location and the holon carrying the charge, but in certain conditions they can behave as independent quasiparticles. The term spinon is frequently used in discussions of experimental facts within the framework of both quantum spin liquid and strongly correlated quantum spin liquid. Overview Electrons, being of like charge, repel each other. As a result, in order to move past each other in an extremely crowded environment, they are forced to modify their behavior. Research published in July 2009 by the University of Cambridge and the University of Birmingham in England showed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximally Entangled State
Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon that occurs when a group of particles are generated, interact, or share spatial proximity in a way such that the quantum state of each particle of the group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, including when the particles are separated by a large distance. The topic of quantum entanglement is at the heart of the disparity between classical and quantum physics: entanglement is a primary feature of quantum mechanics not present in classical mechanics. Measurements of physical properties such as position, momentum, spin, and polarization performed on entangled particles can, in some cases, be found to be perfectly correlated. For example, if a pair of entangled particles is generated such that their total spin is known to be zero, and one particle is found to have clockwise spin on a first axis, then the spin of the other particle, measured on the same axis, is found to be anticlockwise. However, this behavior gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valence Bond Solid
Valence or valency may refer to: Science * Valence (chemistry), a measure of an element's combining power with other atoms * Degree (graph theory), also called the valency of a vertex in graph theory * Valency (linguistics), aspect of verbs relative to other parts of speech * Valence (psychology) or hedonic tone, the (emotional) value associated with an event, object or situation Places France * Valence, Charente, a commune in the Charente department * Valence, Drôme, Drôme, a commune and prefecture of the Drôme department ** University of Valence, a medieval university * Valence, Tarn-et-Garonne, a commune in the Tarn-et-Garonne department * Canton of Valence, Tarn-et-Garonne department * Arrondissement of Valence, Drôme department * Roman Catholic Diocese of Valence * Valence-d'Albigeois, in the Tarn department * Valence-en-Brie, in the Seine-et-Marne department * Valence-sur-Baïse, in the Gers department * Bourg-lès-Valence, in the Drôme department England * Rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ising Spin
The Ising model () (or Lenz-Ising model or Ising-Lenz model), named after the physicists Ernst Ising and Wilhelm Lenz, is a mathematical model of ferromagnetism in statistical mechanics. The model consists of discrete variables that represent magnetic dipole moments of atomic "spins" that can be in one of two states (+1 or −1). The spins are arranged in a graph, usually a lattice (where the local structure repeats periodically in all directions), allowing each spin to interact with its neighbors. Neighboring spins that agree have a lower energy than those that disagree; the system tends to the lowest energy but heat disturbs this tendency, thus creating the possibility of different structural phases. The model allows the identification of phase transitions as a simplified model of reality. The two-dimensional square-lattice Ising model is one of the simplest statistical models to show a phase transition. The Ising model was invented by the physicist , who gave it as a proble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometrical Frustration
In condensed matter physics, the term geometrical frustration (or in short: frustration) refers to a phenomenon where atoms tend to stick to non-trivial positions or where, on a regular crystal lattice, conflicting inter-atomic forces (each one favoring rather simple, but different structures) lead to quite complex structures. As a consequence of the frustration in the geometry or in the forces, a plenitude of distinct ground states may result at zero temperature, and usual thermal ordering may be suppressed at higher temperatures. Much studied examples are amorphous materials, glasses, or dilute magnets. The term ''frustration'', in the context of magnetic systems, has been introduced by Gerard Toulouse in 1977. Frustrated magnetic systems had been studied even before. Early work includes a study of the Ising model on a triangular lattice with nearest-neighbor spins coupled antiferromagnetically, by G. H. Wannier, published in 1950. Related features occur in magnets with ''competi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
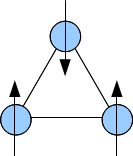
Triangular Ising Spin
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC. In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non-collinear, determine a unique triangle and simultaneously, a unique plane (i.e. a two-dimensional Euclidean space). In other words, there is only one plane that contains that triangle, and every triangle is contained in some plane. If the entire geometry is only the Euclidean plane, there is only one plane and all triangles are contained in it; however, in higher-dimensional Euclidean spaces, this is no longer true. This article is about triangles in Euclidean geometry, and in particular, the Euclidean plane, except where otherwise noted. Types of triangle The terminology for categorizing triangles is more than two thousand years old, having been defined on the very first page of Euclid's Elements. The names used for modern classification are eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |