|
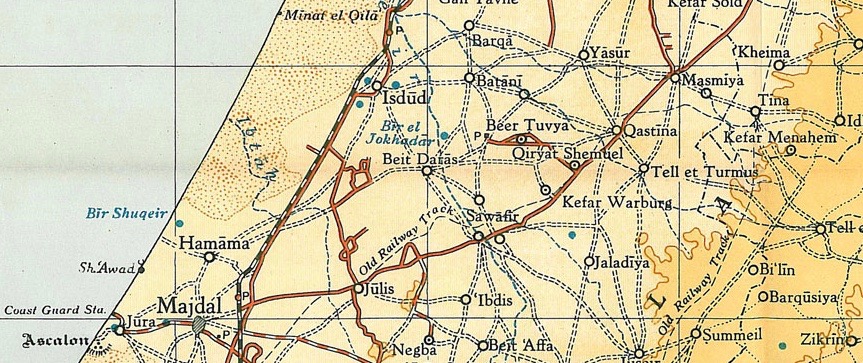
Qastina
Qastina ( ar, قسطينة) was a Palestinian village, located 38 kilometers northeast of Gaza City. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war. Location Qastina was situated on an elevated spot in a generally flat area on the coastal plain, on the highway between al-Majdal and the Jerusalem-Jaffa highway. A British military camp, Beer Tuvia, was 3 km. southwest of the village.Khalidi, 1992, pp. 130-131 History Ottoman period Qastina was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire in 1517 with the rest of Palestine, and by the 1596 tax records, it was a village in the ''nahiya'' (subdistrict) of Gaza under the '' liwa''' (district) of Gaza, with a population of 55 households and 15 bachelors, an estimated 385 persons. All the villagers were Muslim. They paid a fixed tax rate of 33,3% on a number of crops, including wheat, barley and sesame, and fruits, as well as goats, beehives and vineyards; a total of 13,100 akçe. 5/6 of the revenue went to a Muslim charitable e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiryat Malakhi
Kiryat Malakhi ( he, קִרְיַת מַלְאָכִי, also Qiryat Malakhi or Kiryat Malachi) is a city in the Southern District of Israel, from Ashkelon. In it had a population of . Its jurisdiction is 4,632 dunams (~4.6 km2). History Kiryat Malakhi, literally "City of Angels", was established in 1951 as a '' ma'abara'', or tent city, to house the masses of Jewish immigrants, who arrived during the early days of the state, many of them part of the Jewish exodus from Arab and Muslim countries. The name was chosen to honor the Jewish community of Los Angeles, which contributed much of the funding for its establishment. It was founded on the land belonging to the depopulated Palestinian village of Qastina. Kiryat Malakhi later became one of several development towns in the Negev. Moshe Katsav, later Israel's eighth president, was elected mayor in 1969 at the age of 24. His younger brother, Lior Katsav, was also mayor of Kiryat Malakhi, whilst Yosef Vanunu held the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Es-Safi
Tell es-Safi ( ar, تل الصافي, Tall aṣ-Ṣāfī, "White hill"; he, תל צפית, ''Tel Tzafit'') was an Arab Palestinian village, located on the southern banks of Wadi 'Ajjur, northwest of Hebron which had its Arab population expelled during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war on orders of Shimon Avidan, commander of the Givati Brigade. Archaeological excavations show that the site (a '' tell'' or archaeological mound) was continuously inhabited since the 5th millennium BCE. It appears on the Madaba Map as ''Saphitha'', while the Crusaders called it ''Blanche Garde''.Kallai-Kleinmann (1958), p. 155 Tsafrir (1994), p. 134 It is mentioned by Arab geographers in the 13th and 16th centuries. Under the Ottoman Empire, it was part of the district of Gaza. In modern times, the houses were built of sun-dried brick. The villagers were Muslim and cultivated cereals and orchards. Today the site, known as Tel Tzafit, is an Israeli national park incorporating archaeological remains whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arugot
Arugot ( he, עֲרוּגוֹת, , garden terraces or beds), is a moshav in southern Israel. Located near Kiryat Malakhi, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In its population was . History The moshav was founded in 1949 by Jewish immigrants from Poland and Romania on the land belonging to the depopulated Palestinian village of Qastina. Its name was taken from the Book of Ezekiel The Book of Ezekiel is the third of the Latter Prophets in the Tanakh and one of the major prophetic books, following Isaiah and Jeremiah. According to the book itself, it records six visions of the prophet Ezekiel, exiled in Babylon, during ... . References {{Be'er Tuvia Regional Council Moshavim Populated places established in 1949 Populated places in Southern District (Israel) 1949 establishments in Israel Polish-Jewish culture in Israel Romanian-Jewish culture in Israel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanjak Of Gaza
Gaza Sanjak ( ar, سنجق غزة) was a sanjak of the Damascus Eyalet, Ottoman Empire centered in Gaza. In the 16th century it was divided into ''nawahi'' (singular: ''nahiya''; third-level subdivisions): Gaza in the south and Ramla in the north. List of settlements In the 1596- daftar, the sanjak contained the following nahiyah and villages/town Gaza Nahiyah * Al-Sawafir al-Sharqiyya, Bayt Tima, Hamama,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 142 Al-Tina, Yibna, Isdud, Arab Suqrir,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 143 Deir al-Balah, Burayr, Jabalia, Beit Lahia, Al-Majdal, Askalan, Bayt 'Affa, Najd, Ni'ilya,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 144 Bayt Jirja, Hiribya, Qatra, Iraq Suwaydan, Kawkaba, Beit Jimal Monastery, Al-Batani al-Sharqi,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 145 Al-Qubayba, Al-Faluja, Bayt Daras, Al-Maghar,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 146 Hatta, Jusayr, Zikrin, Zayta, Barqa, Beit Hanoun, Dayr Sunayd, Simsim,Hütteroth and A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kfar Ahim
Kfar Ahim ( he, כְּפַר אַחִים, ''lit.'' Village of Brothers) is a moshav in south-central Israel. Located near Kiryat Malakhi, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The moshav was founded in 1949 by Jewish immigrants from Poland and Romania on the land of the depopulated Palestinian village of Qastina. It was named for two brothers who were killed during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Zvi and Efraim Guber, sons of Mordecai and Rivka Guber from the nearby moshav of Kfar Warburg. Notable natives of Kfar Ahim include Benny Gantz, Israel's former Chief of the General Staff, and Knesset member and the current Minister of Transport A ministry of transport or transportation is a ministry responsible for transportation within a country. It usually is administered by the ''minister for transport''. The term is also sometimes applied to the departments or other government ag ..., Yisrael Katz. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avigdor
Avigdor ( he, אֲבִיגְדוֹר) a small moshav in southern Israel. Located south of Kiryat Malakhi and 11 km north of Kiryat Gat and covering 3.75 km², it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In its population was . History It was founded in 1950 by veterans of the British Army and was initially named Yael, the initials of Hebrew Units for Transportation, the unit that the veterans belonged to during the war. The commander of the unit was Henry d'Avigdor-Goldsmid, the son of Sir Osmond Elim d'Avigdor-Goldsmid. Later the name was changed and now it derives its name from the Zionist Sir Osmond Elim d'Avigdor-Goldsmid, an Englishman, president of the Palestine Jewish Colonization Association between the years 1934–1939 that donated to the moshav the municipality. It was founded on the land belonging to the depopulated Palestinian village of Qastina Qastina ( ar, قسطينة) was a Palestinian village, located 38 kilometers northeas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kfar Warburg
Kfar Warburg ( he, כְּפַר וַרְבּוּרְג, ''lit.'' Warburg Village) is a large moshav in south-central Israel. Located near Kiryat Malakhi with 98 farms covering an area of 6,000 dunams, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The moshav was founded on 31 October 1939 by members of the "Menachem" organisation. It was named after Felix M. Warburg, one of the leaders of the Jewish community in the United States and a founder of the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee. It was founded on land that had traditionally belonged to the depopulated Palestinian village of Qastina. In the early 1950s, after the population of Kfar Warburg doubled, a culture hall with a 880-seat auditorium was built at the crossroads of the village's three main roads. Plays by the Habima and Cameri theaters were performed there almost every week. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaza Subdistrict, Mandatory Palestine
The Gaza Subdistrict ( ar, قضاء غزة, he, נפת עזה) was one of the subdistricts of Mandatory Palestine. It was situated in the southern Mediterranean coastline of the British Mandate of Palestine. After the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, the district disintegrated, with Israel controlling the northern and eastern portions while Egypt held control of the southern and central parts – which became the Gaza Strip, under Egyptian military between 1948 and 1967, Israeli military rule between 1967 and 2005, part of the Palestinian National Authority (with some aspects of retained Israeli rule until the 2005 withdrawal) after the Oslo Accords until 2007, and is currently ruled by the Hamas as a de facto separate entity from the Palestinian National Authority. The parts which Israel held since 1948 were merged into Israeli administrative districts, their connection with Gaza severed. Borders * Beersheba Subdistrict (Southeast) * Ramle Subdistrict (Northeast) * Hebron Subdist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ritualism, Asceticism#Islam, asceticism and esotericism. It has been variously defined as "Islamic mysticism",Martin Lings, ''What is Sufism?'' (Lahore: Suhail Academy, 2005; first imp. 1983, second imp. 1999), p.15 "the mystical expression of Islamic faith", "the inward dimension of Islam", "the phenomenon of mysticism within Islam", the "main manifestation and the most important and central crystallization" of mystical practice in Islam, and "the interiorization and intensification of Islamic faith and practice". Practitioners of Sufism are referred to as "Sufis" (from , ), and historically typically belonged to "orders" known as (pl. ) – congregations formed around a grand who would be the last in a Silsilah, chain of successive teac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahiya
A nāḥiyah ( ar, , plural ''nawāḥī'' ), also nahiya or nahia, is a regional or local type of administrative division that usually consists of a number of villages or sometimes smaller towns. In Tajikistan, it is a second-level division while in Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, Jordan, Xinjiang, and the former Ottoman Empire, where it was also called a '' bucak'', it is a third-level or lower division. It can constitute a division of a '' qadaa'', '' mintaqah'' or other such district-type of division and is sometimes translated as " subdistrict". Ottoman Empire The nahiye ( ota, ناحیه) was an administrative territorial entity of the Ottoman Empire, smaller than a . The head was a (governor) who was appointed by the Pasha. The was a subdivision of a Selçuk Akşin Somel. "Kazâ". ''The A to Z of the Ottoman Empire''. Volume 152 of A to Z Guides. Rowman & Littlefield, 2010. p. 151. and corresponded roughly to a city with its surrounding villages. s, in turn, were divided int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Masmiyya Al-Kabira
Al-Masmiyya al-Kabira ( ar, المسمية الكبيرة) was a Palestinian village in the Gaza Subdistrict, located northeast of Gaza. With a land area of 20,687 dunams, the village site (135 dunams) was situated on an elevation of along the coastal plain. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. Before the war, it had a population of 2,520 in 1945.Khalidi, 1992, p.125. History Remains from the Roman and Byzantine eras have been found here, including a coin made under Emperor Mauritius Tiberius (596–597 CE).Mamalya, 2021El-Masmiyya el-Kabira/ref> Remains, including pottery and glass were found from the Umayyad and Abbasid periods, with local glass-industry operation here in the Abbasid era. The settlement continued during Ayyubid and Mamluk times, with the wealth of pottery and glass found here indicating a strong economy. An undated column-base, with a Nine men's morris pattern incised has also been found here. Ottoman era Al-Masmiyya was mentione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waqf
A waqf ( ar, وَقْف; ), also known as hubous () or '' mortmain'' property is an inalienable charitable endowment under Islamic law. It typically involves donating a building, plot of land or other assets for Muslim religious or charitable purposes with no intention of reclaiming the assets. A charitable trust may hold the donated assets. The person making such dedication is known as a ''waqif'' (a donor). In Ottoman Turkish law, and later under the British Mandate of Palestine, a ''waqf'' was defined as usufruct state land (or property) from which the state revenues are assured to pious foundations. Although the ''waqf'' system depended on several hadiths and presented elements similar to practices from pre-Islamic cultures, it seems that the specific full-fledged Islamic legal form of endowment called ''waqf'' dates from the 9th century AD (see below). Terminology In Sunni jurisprudence, ''waqf'', also spelled ''wakf'' ( ar, وَقْف; plural , ''awqāf''; tr, v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |