|
Putrescine
Putrescine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(NH2)2. It is a colorless solid that melts near room temperature. It is classified as a diamine. Together with cadaverine, it is largely responsible for the foul odor of putrefying flesh, but also contributes to other unpleasant odors. Production Putrescine is produced on an industrial scale by the hydrogenation of succinonitrile. Biotechnological production of putrescine from renewable feedstock has been investigated. A metabolically engineered strain of ''Escherichia coli'' that produces putrescine at high concentrations in glucose mineral salts medium has been described. Biochemistry Spermidine synthase uses putrescine and ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine (decarboxylated ''S''-adenosyl methionine) to produce spermidine. Spermidine in turn is combined with another ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine and gets converted to spermine. Putrescine is synthesized in small quantities by healthy living cells by the action of ornithi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermidine Synthase
Spermidine synthase is an enzyme () that catalyzes the transfer of the propylamine group from ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine to putrescine in the biosynthesis of spermidine. The systematic name is S-adenosyl 3-(methylthio)propylamine:putrescine 3-aminopropyltransferase and it belongs to the group of aminopropyl transferases. It does not need any cofactors. Most spermidine synthases exist in solution as dimers. Specificity With exception of the spermidine synthases from ''Thermotoga maritimum'' and from ''Escherichia coli'', which accept different kinds of polyamines, all enzymes are highly specific for putrescine. No known spermidine synthase can use ''S''-adenosyl methionine. This is prevented by a conserved aspartatyl residue in the active site, which is thought to repel the carboxyl moiety of ''S''-adenosyl methionine. The putrescine-N-methyl transferase whose substrates are putrescine and ''S''-adenosyl methionine and which is evolutionary related to the spermidine synthase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermine
Spermine is a polyamine involved in cellular metabolism that is found in all eukaryotic cells. The precursor for synthesis of spermine is the amino acid ornithine. It is an essential growth factor in some bacteria as well. It is found as a polycation at physiological pH. Spermine is associated with nucleic acids and is thought to stabilize helical structure, particularly in viruses. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek first described crystals of spermine phosphate in human semen in 1678. The name ''spermin'' was first used by the German chemists Ladenburg and Abel in 1888, and the correct structure of spermine was not finally established until 1926, simultaneously in England (by Dudley, Rosenheim, and Starling) and Germany (by Wrede et al.). Spermine is the chemical primarily responsible for the characteristic odor of semen. Derivative A derivative of spermine, N1, N12-bis(ethyl)spermine (also known as BESm) was investigated in the late 1980s along with similar polyamine analo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyamine Synthesis
A polyamine is an organic compound having more than two amino groups. Alkyl polyamines occur naturally, but some are synthetic. Alkylpolyamines are colorless, hygroscopic, and water soluble. Near neutral pH, they exist as the ammonium derivatives. Most aromatic polyamines are crystalline solids at room temperature. Natural polyamines Low-molecular-weight linear polyamines are found in all forms of life. The principal examples are the triamine spermidine and the tetraamine spermine. They are structurally and biosynthetically related to the diamines putrescine and cadaverine. Polyamine metabolism is regulated by the activity of the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (ODC). Polyamines are found in high concentrations in the mammalian brain. File:Spermidine-2D-skeletal.svg, spermidine File:Spermine.svg, spermine Synthetic polyamines Several synthetic polyamines are used in chemical industry and the research laboratory. They are mainly of interest as additives to motor oil and as co- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithine Decarboxylase
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (, ODC) catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine (a product of the urea cycle) to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis. In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids and forms a homodimer. Reaction mechanism Lysine 69 on ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) binds the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate to form a Schiff base. Ornithine displaces the lysine to form a Schiff base attached to orthonine, which decarboxylates to form a quinoid intermediate. This intermediate rearranges to form a Schiff base attached to putrescine, which is attacked by lysine to release putrescine product and reform PLP-bound ODC. This is the first step and the rate-limiting step in humans for the production of polyamines, compounds required for cell division. Structure image:Ornithine Decarboxylase Publication View.png, 270px, 3D crystal structure of ornithine decarboxylase.; ; rendered viPyMOL The active form of ornithine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadaverine
Cadaverine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)5(NH2)2. Classified as diamine, it is a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. It is present in small quantities in living organisms but is often associated with the putrefaction of animal tissue. Production Cadaverine is produced by decarboxylation of lysine.Wolfgang Legrum: ''Riechstoffe, zwischen Gestank und Duft'', Vieweg + Teubner Verlag (2011) S. 65, It can be synthesized by many methods including the hydrogenation of glutaronitrile and the reactions of 1,5-dichloropentane. History Putrescine and cadaverine were first described in 1885 by the Berlin physician Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919). Receptors In zebrafish, the trace amine-associated receptor 13c (or TAAR13c) has been identified as a high-affinity receptor for cadaverine. In humans, molecular modelling and docking experiments have shown that cadaverine fits into the binding pocket of the human TAAR6 and TAAR8. Clinical significance Elevated le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadaverine
Cadaverine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)5(NH2)2. Classified as diamine, it is a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. It is present in small quantities in living organisms but is often associated with the putrefaction of animal tissue. Production Cadaverine is produced by decarboxylation of lysine.Wolfgang Legrum: ''Riechstoffe, zwischen Gestank und Duft'', Vieweg + Teubner Verlag (2011) S. 65, It can be synthesized by many methods including the hydrogenation of glutaronitrile and the reactions of 1,5-dichloropentane. History Putrescine and cadaverine were first described in 1885 by the Berlin physician Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919). Receptors In zebrafish, the trace amine-associated receptor 13c (or TAAR13c) has been identified as a high-affinity receptor for cadaverine. In humans, molecular modelling and docking experiments have shown that cadaverine fits into the binding pocket of the human TAAR6 and TAAR8. Clinical significance Elevated le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermidine
Spermidine is a polyamine compound () found in ribosomes and living tissues and having various metabolic functions within organisms. It was originally isolated from semen. Function Spermidine is an aliphatic polyamine. Spermidine synthase (SPDS) catalyzes its formation from putrescine. It is a precursor to other polyamines, such as spermine and its structural isomer thermospermine. Spermidine synchronizes an array of biological processes, (such as Ca2+, Na+, K+ -ATPase) thus maintaining membrane potential and controlling intracellular pH and volume. Spermidine regulates biological processes, such as Ca2+ influx by glutamatergic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDA receptor), which has been associated with nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and cGMP/PKG pathway activation and a decrease of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in cerebral cortex synaptosomes. Spermidine is a longevity agent in mammals due to various mechanisms of action, which are just beginning to be understood. Autophagy i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nylon 46
Nylon 46 (nylon 4-6, nylon 4/6 or nylon 4,6, PA46, Polyamide 46) is a high heat resistant polyamide or nylon. DSM is the only commercial supplier of this resin, which markets under the trade name Stanyl. Nylon 46 is an aliphatic polyamide formed by the polycondensation of two monomers, one containing 4 carbon atoms, 1,4-diaminobutane (putrescine), and the other 6 carbon atoms, adipic acid, which give nylon 46 its name. It has a higher melting point than nylon 6 or nylon 66 and mainly used in applications which must withstand high temperatures. Nylon 46 withstands high loads and stresses at high temperatures and exposure to aggressive environments, and is therefore suitable for under-the-bonnet applications. Typical applications are to be found in the engine and transmission, engine-management, air-inlet, brake, air cooling and electronic systems. Many automotive components have also been produced in nylon 46, because of its excellent creep resistance, toughness and good wear charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
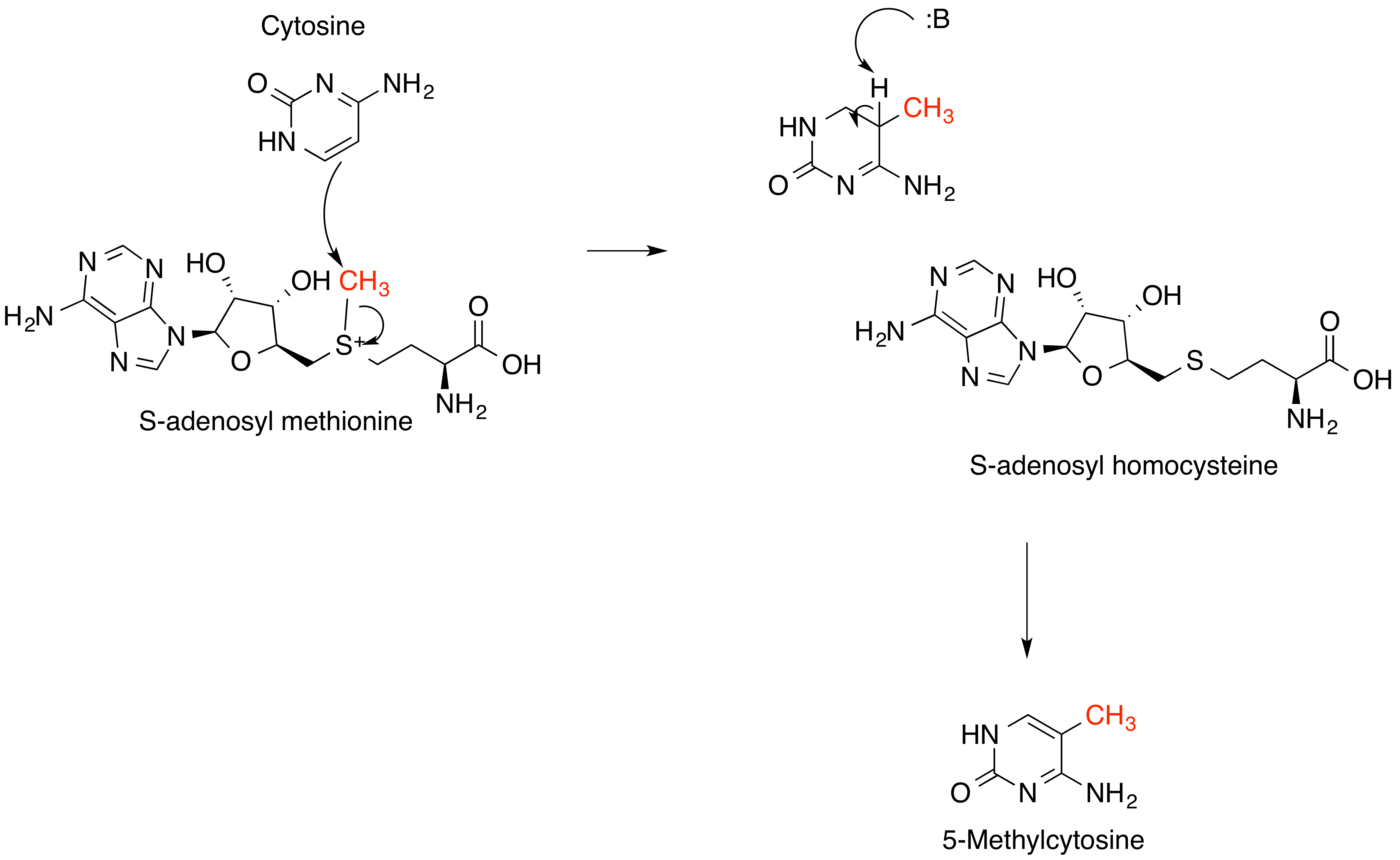
S-Adenosyl Methionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952. In bacteria, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates genes involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis. In eukaryotic cells, SAM serves as a regulator of a variety of processes including DNA, tRNA, and rRNA methylation; immune response; amino acid metabolism; transsulfuration; and more. In plants, SAM is crucial to the biosynthesis of ethylene, an important plant hormone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinonitrile
Succinonitrile, also butanedinitrile, is a nitrile, with the formula of C2H4(CN)2. It is a colorless waxy solid which melts at 58 °C. Succinonitrile is produced by the addition of hydrogen cyanide to acrylonitrile (hydrocyanation): :CH2=CHCN + HCN → NCCH2CH2CN Hydrogenation of succinonitrile yields putrescine (1,4-diaminobutane). See also * Malononitrile - A di-nitrile with 3 carbon atoms * Glutaronitrile - A di-nitrile with 5 carbon atoms * Adiponitrile Adiponitrile is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH2)4(CN)2. This viscous, colourless dinitrile is an important precursor to the polymer nylon 66. In 2005, about one million tonnes of adiponitrile were produced.M. T. Musser, "Adipi ... - A di-nitrile with 6 carbon atoms References External links WebBook page for C4H4N2 Alkanedinitriles {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Putrefaction
Putrefaction is the fifth stage of death, following pallor mortis, algor mortis, rigor mortis, and livor mortis. This process references the breaking down of a body of an animal, such as a human, post-mortem. In broad terms, it can be viewed as the decomposition of proteins, and the eventual breakdown of the cohesiveness between tissues, and the liquefaction of most organs. This is caused by the decomposition of organic matter by bacterial or fungal digestion, which causes the release of gases that infiltrate the body's tissues, and leads to the deterioration of the tissues and organs. The approximate time it takes putrefaction to occur is dependent on various factors. Internal factors that affect the rate of putrefaction include the age at which death has occurred, the overall structure and condition of the body, the cause of death, and external injuries arising before or after death. External factors include environmental temperature, moisture and air exposure, clothing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamine
A diamine is an amine with exactly two amino groups. Diamines are used as monomers to prepare polyamides, polyimides, and polyureas. The term ''diamine'' refers mostly to primary diamines, as those are the most reactive. In terms of quantities produced, 1,6-diaminohexane (a precursor to Nylon 6-6) is most important, followed by ethylenediamine. Vicinal diamines (1,2-diamines) are a structural motif in many biological compounds and are used as ligands in coordination chemistry. Aliphatic diamines Linear * 1 carbon: methylenediamine (diaminomethane) of theoretical interest only * 2 carbons: ethylenediamine (1,2-diaminoethane). Related derivatives include the N-alkylated compounds, 1,1-dimethylethylenediamine, 1,2-dimethylethylenediamine, ethambutol, tetrakis(dimethylamino)ethylene, TMEDA. File:Ethylene_diamine.png, Ethylenediamine * 3 carbons: 1,3-diaminopropane (propane-1,3-diamine) * 4 carbons: putrescine (butane-1,4-diamine) * 5 carbons: cadaverine (pentane-1,5-diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |