|
Psychoticism
Psychoticism is one of the three traits used by the psychologist Hans Eysenck in his P–E–N model ( psychoticism, extraversion and neuroticism) model of personality. Nature Psychoticism is conceptually similar to the ''constraint'' factor in Tellegen's three-factor model of personality. Psychoticism may be divided into narrower traits such as impulsivity and sensation-seeking. These may in turn be further subdivided into even more specific traits. For example, impulsivity may be divided into narrow impulsivity (unthinking responsivity), risk taking, non-planning, and liveliness. Sensation seeking has also been analysed into a number of separate facets. Eysenck argued that there might be a correlation between psychoticism and creativity.Eysenck, Hans J. (1993). Creativity and Personality: Suggestions for a Theory. ''Psychological Inquiry''. 4(3), 147–178. Critics Critics of the trait have suggested that the trait is too heterogeneous to be taken as a single trait. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trait Theory
In psychology, trait theory (also called dispositional theory) is an approach to the study of human personality. Trait theorists are primarily interested in the measurement of ''traits'', which can be defined as habitual patterns of behaviour, thought, and emotion. According to this perspective, traits are aspects of personality that are relatively stable over time, differ across individuals (e.g. some people are outgoing whereas others are not), are relatively consistent over situations, and influence behaviour. Traits are in contrast to states, which are more transitory dispositions. In some theories and systems, traits are something a person either has or does not have, but in many others traits are dimensions such as extraversion vs. introversion, with each person rating somewhere along this spectrum. There are two approaches to define traits: as internal causal properties or as purely descriptive summaries. The internal causal definition states that traits influence our be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizotypy
In psychology, schizotypy is a theoretical concept that posits a continuum of personality characteristics and experiences, ranging from normal dissociative, imaginative states to extreme states of mind related to psychosis, especially schizophrenia. The continuum of personality proposed in schizotypy is in contrast to a categorical view of psychosis, wherein psychosis is considered a particular (usually pathological) state of mind, which the person either has or does not have. Development of the concept The categorical view of psychosis is most associated with Emil Kraepelin, who created criteria for the medical diagnosis and classification of different forms of psychotic illness. Particularly, he made the distinction between dementia praecox (now called schizophrenia), manic depressive insanity and non-psychotic states. Modern diagnostic systems used in psychiatry (such as the DSM) maintain this categorical view. In contrast, psychiatrist Eugen Bleuler did not believe there w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Eysenck
Hans Jürgen Eysenck (; 4 March 1916 – 4 September 1997) was a German-born British psychologist who spent his professional career in Great Britain. He is best remembered for his work on intelligence and personality, although he worked on other issues in psychology. At the time of his death, Eysenck was the most frequently cited living psychologist in the peer-reviewed scientific journal literature. Eysenck's research purported to show that certain personality types had an elevated risk of cancer and heart disease. Scholars have identified errors and suspected data manipulation in Eysenck's work, and large replications have failed to confirm the relationships that he purported to find. An enquiry on behalf of King's College London found the papers by Eysenck to be "incompatible with modern clinical science". In 2019, 26 of his papers (all coauthored with Ronald Grossarth-Maticek) were considered "unsafe" by an enquiry on behalf of King's College London. Fourteen of his paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
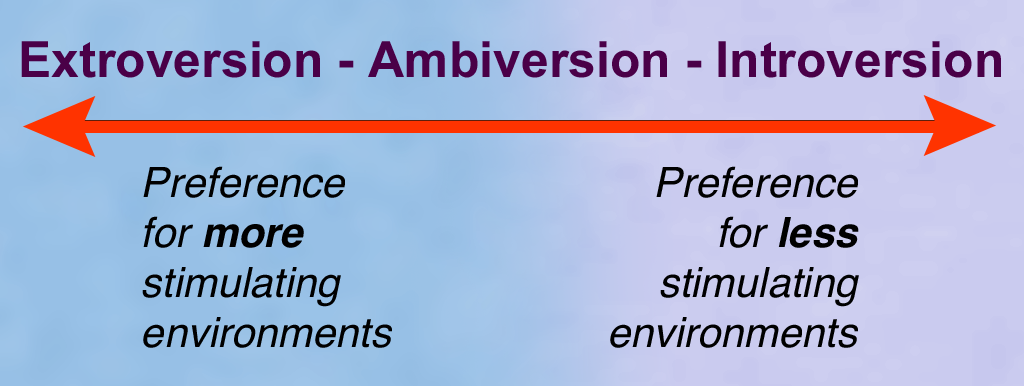
Extraversion
The traits of extraversion (also spelled extroversion Retrieved 2018-02-21.) and introversion are a central dimension in some human personality theories. The terms ''introversion'' and ''extraversion'' were introduced into psychology by Carl Jung,Jung, C. G. (1921) ''Psychologische Typen'', Rascher Verlag, Zurich – translation H.G. Baynes, 1923. although both the popular understanding and current psychological usage vary. Extraversion tends to be manifested in outgoing, talkative, energetic behavior, whereas introversion is manifested in more reflective and reserved behavior. Jung defined introversion as an "attitude-type characterised by orientation in life through subjective psychic contents", and extraversion as "an attitude-type characterised by concentration of interest on the external object". Extraversion and introversion are typically viewed as a single continuum, so to be higher in one necessitates being lower in the other. Jung provides a different perspective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creativity
Creativity is a phenomenon whereby something new and valuable is formed. The created item may be intangible (such as an idea, a scientific theory, a musical composition, or a joke) or a physical object (such as an invention, a printed Literature, literary work, or a painting). Scholarly interest in creativity is found in a number of disciplines, primarily psychology, business studies, and cognitive science. However, it can also be found in education, the humanities (philosophy, the arts) and theology, social sciences (sociology, linguistics, economics), engineering, technology and mathematics. These disciplines cover the relations between creativity and general intelligence, personality type, mental and neural processes, mental health, artificial intelligence; the potential for fostering creativity through education, training, leadership and organizational practices; the factors that determine how creativity is evaluated and perceived; the fostering of creativity for national eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraversion
The traits of extraversion (also spelled extroversion Retrieved 2018-02-21.) and introversion are a central dimension in some human personality theories. The terms ''introversion'' and ''extraversion'' were introduced into psychology by Carl Jung,Jung, C. G. (1921) ''Psychologische Typen'', Rascher Verlag, Zurich – translation H.G. Baynes, 1923. although both the popular understanding and current psychological usage vary. Extraversion tends to be manifested in outgoing, talkative, energetic behavior, whereas introversion is manifested in more reflective and reserved behavior. Jung defined introversion as an "attitude-type characterised by orientation in life through subjective psychic contents", and extraversion as "an attitude-type characterised by concentration of interest on the external object". Extraversion and introversion are typically viewed as a single continuum, so to be higher in one necessitates being lower in the other. Jung provides a different perspective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior that is inappropriate for a given situation. There may also be sleep problems, social withdrawal, lack of motivation, and difficulties carrying out daily activities. Psychosis can have serious adverse outcomes. As with many psychiatric phenomena, psychosis has several different causes. These include mental illness, such as schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, sensory deprivation and in rare cases, major depression (psychotic depression). Other causes include: trauma, sleep deprivation, some medical conditions, certain medications, and drugs such as cannabis, hallucinogens, and stimulants. One type, known as postpartum psychosis, can occur after giving birth. The neurotransmitter dopamine is believed to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensation-seeking
Sensation seeking is a personality trait defined by the search for experiences and feelings, that are "varied, novel, complex and intense", and by the readiness to "take physical, social, legal, and financial risks for the sake of such experiences." Risk is not an essential part of the trait, as many activities associated with it are not risky. However, risk may be ignored, tolerated, or minimized and may even be considered to add to the excitement of the activity. The concept was developed by Marvin Zuckerman of the University of Delaware. In order to assess this trait he created a personality test called the Sensation Seeking Scale. This test assesses individual differences in terms of sensory stimulation preferences. So there are people who prefer a strong stimulation and display a behavior that manifests a greater desire for sensations and there are those who prefer a low sensory stimulation. The scale is a questionnaire designed to measure how much stimulation a person requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensation Seeking
Sensation seeking is a personality trait defined by the search for experiences and feelings, that are "varied, novel, complex and intense", and by the readiness to "take physical, social, legal, and financial risks for the sake of such experiences." Risk is not an essential part of the trait, as many activities associated with it are not risky. However, risk may be ignored, tolerated, or minimized and may even be considered to add to the excitement of the activity. The concept was developed by Marvin Zuckerman of the University of Delaware. In order to assess this trait he created a personality test called the Sensation Seeking Scale. This test assesses individual differences in terms of sensory stimulation preferences. So there are people who prefer a strong stimulation and display a behavior that manifests a greater desire for sensations and there are those who prefer a low sensory stimulation. The scale is a questionnaire designed to measure how much stimulation a person requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychopathy
Psychopathy, sometimes considered synonymous with sociopathy, is characterized by persistent antisocial behavior, impaired empathy and remorse, and bold, disinhibited, and egotistical traits. Different conceptions of psychopathy have been used throughout history that are only partly overlapping and may sometimes be contradictory. Hervey M. Cleckley, an American psychiatrist, influenced the initial diagnostic criteria for antisocial personality reaction/disturbance in the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (''DSM''), as did American psychologist George E. Partridge. The ''DSM'' and '' International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD) subsequently introduced the diagnoses of antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) and dissocial personality disorder (DPD) respectively, stating that these diagnoses have been referred to (or include what is referred to) as psychopathy or sociopathy. The creation of ASPD and DPD was driven by the fact that many of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad'', "near", and '' ren'', "kidney") is more commonly used in the United Kingdom, whereas "norepinephrine" (from Ancient Greek ἐπῐ́ (''epí''), "upon", and νεφρός (''nephrós''), "kidney") is usually preferred in the United States. "Norepinephrine" is also the international nonproprietary name given to the drug. Regardless of which name is used for the substance itself, parts of the body that produce or are affected by it are referred to as noradrenergic. The general function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in the so-called fight-or-flight response. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroticism
In the study of psychology, neuroticism has been considered a fundamental personality trait. For example, in the Big Five approach to personality trait theory, individuals with high scores for neuroticism are more likely than average to be moody and to experience such feelings as anxiety, worry, fear, anger, frustration, envy, jealousy, guilt, depressed mood, and loneliness. Such people are thought to respond worse to stressors and are more likely to interpret ordinary situations, such as minor frustrations, as appearing hopelessly difficult. People with high scores on the neuroticism index are thought to be at risk of developing common mental disorders ( mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and substance use disorders have been studied), and the sorts of symptoms traditionally referred to as "neuroses". Definition Neuroticism is a trait in many models within personality theory, but there is significant disagreement on its definition. It is sometimes defined as a tendency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |