|
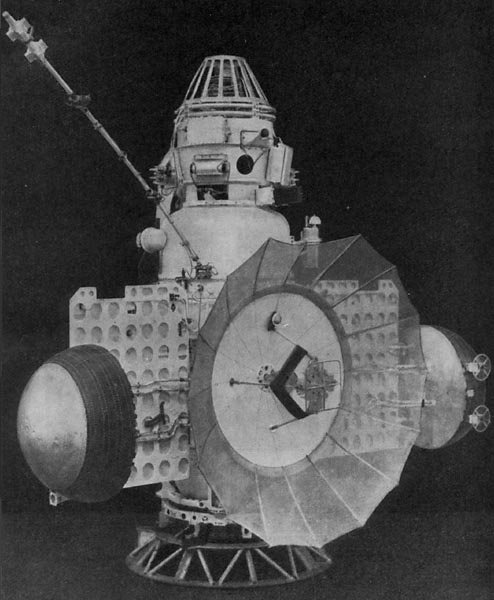
Proton Satellite
Proton (russian: протон) (' proton') was a Soviet series of four cosmic ray and elementary particle detecting satellites. Orbited 1965–68, three on test flights of the UR-500 ICBM and one on a Proton-K rocket, all four satellites completed their missions successfully, the last reentering the Earth's atmosphere in 1969. Background The Proton satellites were heavy automated laboratories launched 1965–68 to study high energy particles and cosmic rays. These satellites were built to utilize the test launches of the UR-500, a heavy two-stage ICBM designed by Vladimir Chelomey's OKB-52 to carry a 100-megaton nuclear payload. Each Proton was housed in a purpose-built third stage added to the UR-500 stack. Spacecraft design Protons 1–3 were largely identical craft massing , with scientific packages developed under the supervision of Academician Sergey Nikolayevich Vernov of Moscow State University's Scientific-Research Institute of Nuclear Physics. Experiments includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voskhod (spacecraft)
The Voskhod (, ''"Sunrise"'') was a spacecraft built by the Soviet Union's space program for human spaceflight as part of the Voskhod programme. It was a development of and a follow-on to the Vostok spacecraft. Voskhod 1 was used for a three-man flight whereas Voskhod 2 had a crew of two. They consisted of a spherical descent module (diameter ), which housed the cosmonauts, and instruments, and a conical equipment module (mass , long, wide), which contained propellant and the engine system. Voskhod was superseded by the Soyuz spacecraft in 1967. Design The Voskhod spacecraft was, essentially, a Vostok spacecraft that had a backup solid fuel retrorocket added to the top of the descent module. The ejection seat was removed for more space and two or three crew couches were added to the interior at a 90° angle to that of the Vostok crew position. There was no provision for crew escape in the event of a launch or landing emergency. Lack of space meant that the three crew members o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vostok (spacecraft)
Vostok (russian: Восток, translated as "East") was a class of single-pilot crewed spacecraft built by the Soviet Union. The first human spaceflight was accomplished with Vostok 1 on April 12, 1961, by Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin. The Vostok programme made six crewed spaceflights from 1961 through 1963. This was followed in 1964 and 1965 by two flights of Vostok spacecraft modified for up to three pilots, identified as Voskhod. By the late 1960s, these were replaced with Soyuz spacecraft, which are still used . Development The Vostok spacecraft was originally designed for use both as a camera platform (for the Soviet Union's first spy satellite program, Zenit) and as a crewed spacecraft. This dual-use design was crucial in gaining Communist Party support for the program. The basic Vostok design has remained in use for some 40 years, gradually adapted for a range of other uncrewed satellites. The descent module design was reused, in heavily modified form, by the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sputnik
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for three weeks before its three silver-zinc batteries ran out, and continued in orbit for three months until aerodynamic drag caused it to fall back into the atmosphere on 4 January 1958. It was a polished metal sphere in diameter with four external radio antennas to broadcast radio pulses. Its radio signal was easily detectable by amateur radio operators, and the 65° orbital inclination made its flight path cover virtually the entire inhabited Earth. The satellite's unanticipated success precipitated the American Sputnik crisis and triggered the Space Race, part of the Cold War. The launch was the beginning of a new era of political, military, technological and scientific developments. The word ''sputnik'' is Russian for ''satellite'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OKB-1
PAO S. P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia (russian: Ракетно-космическая корпорация «Энергия» им. С. П. Королёва, Raketno-kosmicheskaya korporatsiya "Energiya" im. S. P. Korolyova), also known as RSC Energia (, RKK "Energiya"), is a Russian manufacturer of spacecraft and space station components. The company is the prime developer and contractor of the Russian crewed spaceflight program; it also owns a majority of Sea Launch. Its name is derived from Sergei Korolev, the first chief of its design bureau, and the Russian word for energy. Overview Energia is the largest company of the Russian space industry and one of its key players. It is responsible for all operations involving human spaceflight and is the lead developer of the Soyuz and Progress spacecraft, and the lead developer of the Russian end of the International Space Station (ISS). In the mid-2000s, the company employed 22,000–30,000 people. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Korolev
Sergei Pavlovich Korolev (russian: Сергей Павлович Королёв, Sergey Pavlovich Korolyov, sʲɪrˈɡʲej ˈpavləvʲɪtɕ kərɐˈlʲɵf, Ru-Sergei Pavlovich Korolev.ogg; ukr, Сергій Павлович Корольов, Serhiy Pavlovych Korol'ov, sɛrˈɦij ˈpavlovɪtʃ koroˈlʲou̯) 14 January 1966) was a lead Soviet rocket engineer and spacecraft designer during the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union in the 1950s and 1960s. He is regarded by many as the father of practical astronautics. He was involved in the development of the R-7 Rocket, Sputnik 1, launching Laika, Sputnik 3, the first human-made object to make contact with another celestial body, Belka and Strelka, the first human being, Yuri Gagarin, into space, Voskhod 1, and the first person, Alexei Leonov, to conduct a spacewalk. Although Korolev trained as an aircraft designer, his greatest strengths proved to be in design integration, organization and strategic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond Program
Zond (russian: Зонд, lit=probe) was the name given to two distinct series of Soviet robotic spacecraft launched between 1964 and 1970. The first series, based on the 3MV planetary probe, was intended to gather information about nearby planets. The second series of test spacecraft was intended as a precursor to remote-controlled robotic circumlunar loop flights, using a stripped-down variant of Soyuz spacecraft, consisting of the service and descent modules, but lacking the orbital module. Two tortoises and other lifeforms aboard Zond 5 were the first terrestrial organisms to travel around the Moon and return to Earth. Missions based on the 3MV planetary probe The first three missions were based on the model 3MV planetary probe, intended to explore Venus and Mars. After two failures, Zond 3 was sent on a test mission, becoming the second spacecraft to photograph the far side of the Moon (after Luna 3). It then continued out to the orbit of Mars in order to test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemini 11
Gemini 11 (officially Gemini XI) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was the ninth crewed spaceflight mission of NASA's Project Gemini, which flew from September 12 to 15, 1966. It was the 17th crewed American flight and the 25th spaceflight to that time (includes X-15 flights over ). Astronauts Charles "Pete" Conrad Jr. and Richard F. Gordon Jr. performed the first direct-ascent (first orbit) rendezvous with an Agena Target Vehicle, docking with it 1 hour 34 minutes after launch; used the Agena rocket engine to achieve a record high-apogee Earth orbit; and created a small amount of artificial gravity by spinning the two spacecraft connected by a tether. Gordon also performed two extra-vehicular activities for a total of 2 hours 41 minutes. Crew Backup crew Support crew * Clifton C. Williams Jr. (Cape CAPCOM) * John W. Young (Houston CAPCOM) * Alan L. Bean (Houston CAPCOM) Mission parameters *Mass: Highest orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' ( Atlantic) before the Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Chinese explorers in the Indian Ocean during the 15th century called it the Western Oceans. In Ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attitude Control
Attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of an aerospace vehicle with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc. Controlling vehicle attitude requires sensors to measure vehicle orientation, actuators to apply the torques needed to orient the vehicle to a desired attitude, and algorithms to command the actuators based on (1) sensor measurements of the current attitude and (2) specification of a desired attitude. The integrated field that studies the combination of sensors, actuators and algorithms is called guidance, navigation and control (GNC). Aircraft attitude control An aircraft's attitude is stabilized in three directions: '' yaw'', nose left or right about an axis running up and down; ''pitch'', nose up or down about an axis running from wing to wing; and ''roll'', rotation about an axis running from nose to tail. Elevators (moving flaps on the horizontal t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)