|
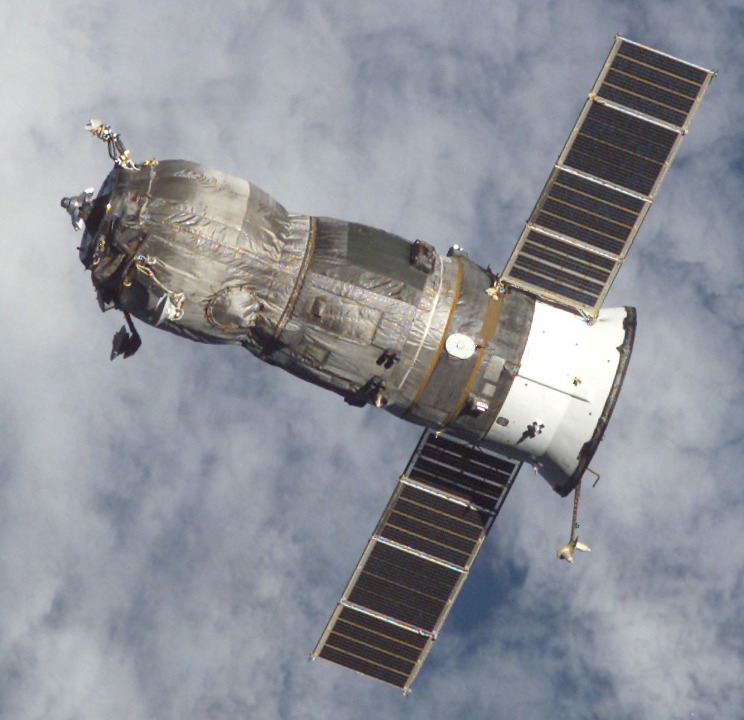
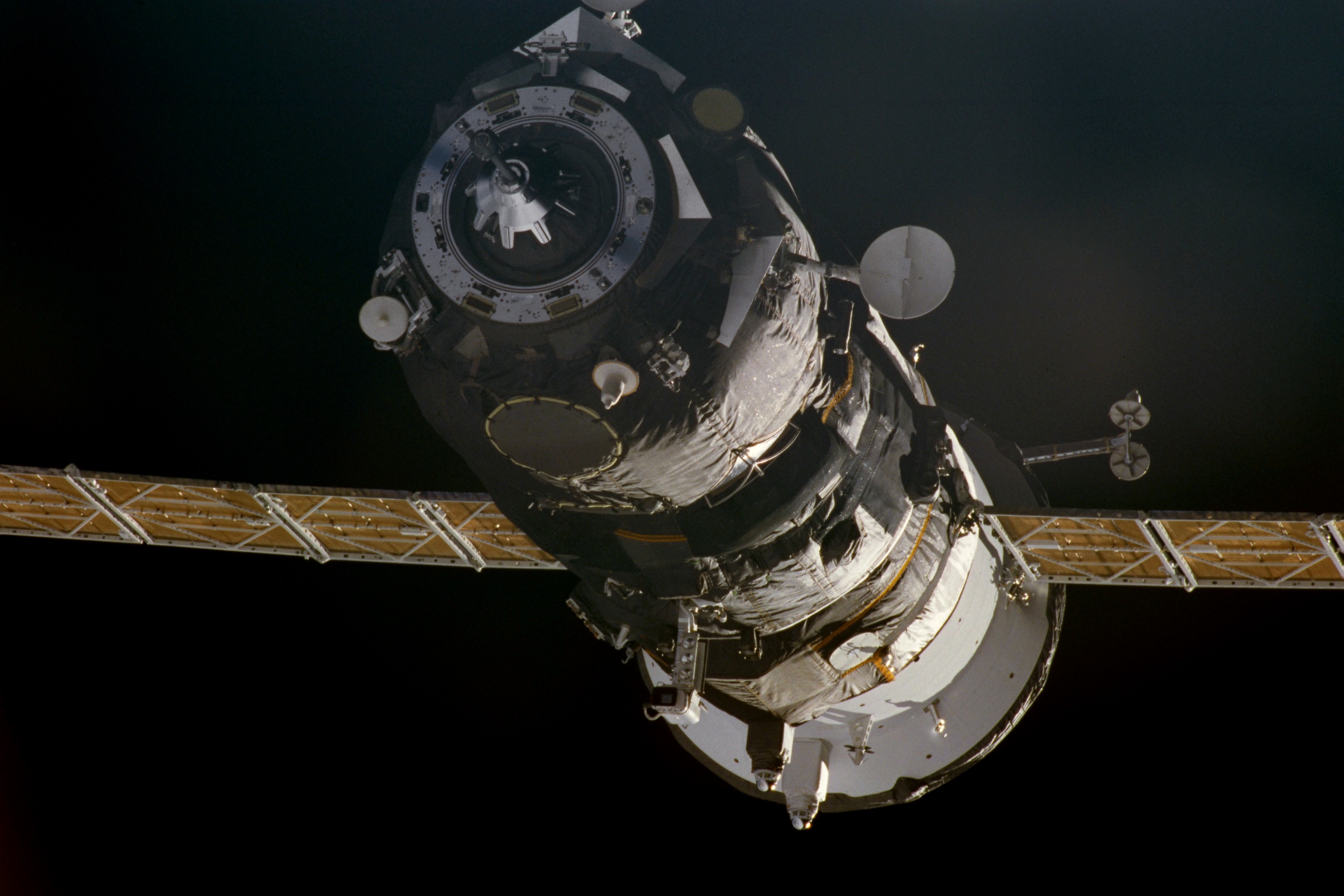
Progress-M
Progress-M (russian: Прогресс-М, GRAU indices 11F615A55 and 11F615A60), also known as Progress 7K-TGM, is a Russian, previously Soviet spacecraft which is used to resupply space stations. It is a variant of the Progress spacecraft, originally built in the late 1980s as a modernised version of the Progress 7K-TG spacecraft, using new systems developed for the Soyuz-T and Soyuz-TM spacecraft. The 11F61560 variant incorporated further modernisation, with digital flight control systems replacing the earlier analogue ones. The older 11F615A55 spacecraft outlived the newer 11F615A60. The final Progress-M, Progress-M-UM, was launched on 24 November 2021. The first forty three Progress-M spacecraft were used to resupply Mir, with subsequent spacecraft flying to the International Space Station. , eighty seven spacecraft have been launched, with sixty seven using the older model, and twenty using the newer version. Launches of the 11F615A60 are continuing. One 11F615A60, Prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress (spacecraft)
The Progress (russian: Прогресс) is a Russian expendable cargo spacecraft. Its purpose is to deliver the supplies needed to sustain a human presence in orbit. While it does not carry a crew, it can be boarded by astronauts when docked to a space station, hence it is classified as ''crewed'' by its manufacturer. Progress is derived from the crewed Soyuz spacecraft and launches on the same launch vehicle, a Soyuz rocket. Progress has supported space stations as early as Salyut 6 and as recently as the International Space Station (ISS). Each year there are between three and four Progress flights to the ISS. A Progress remains docked until shortly before being replaced with a new one or a Soyuz (which will use the same docking port). Then it is filled with waste, disconnected, and de-orbited, at which point it burns up in the atmosphere. Due to the variation in Progress vehicles flown to the ISS, NASA uses its own nomenclature where "ISS 1P" means the first Progress spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress-M1
Progress-M1 (russian: Прогресс-М1, GRAU indices 11F615A55 and 11F615A70), also known as Progress 7K-TGM1, is a Russian spacecraft which is used to resupply space stations. It is a variant of the Progress spacecraft, derived from the Progress-M, but modified to carry more UDMH and N2O4 propellant for refuelling the International Space Station instead of other cargoes such as water. A Progress M1 11F615A55 spacecraft could carry up to of propellant in eight mid-section refuelling tanks, compared to the that a Progress-M of the same generation could carry. This propellant can be transferred to the Space Station's own propulsion system through fluid connectors in the docking ring, or it can alternatively be used by the Progress' thrusters to boost the station altitude or to change its orientation, or attitude, in space. In addition to propellant, the spacecraft can also carry up to (6 cubic meters volume) of supplies in its forward pressurized cargo module (including a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
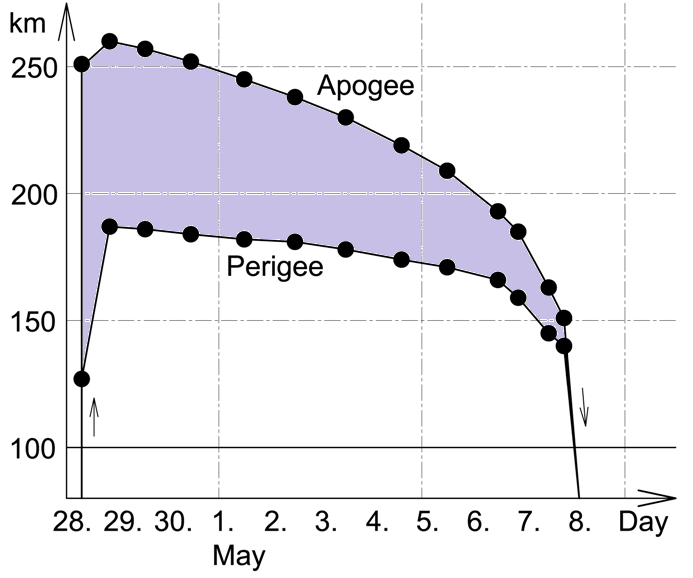
Progress M-UM
Progress M-UM (), was a specially modified Progress M 11F615A55, Russian production No.303, developed by Roscosmos to deliver the ''Prichal'' module to the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) of the International Space Station (ISS). It was launched on 24 November 2021 at 13:06:35 UTC, along with a Progress M propulsion compartment and has the pressurised cargo module removed to accommodate ''Prichal''. This was the 171st flight of a Progress spacecraft. It was the final flight of a Progress M and the first launch of a Progress spacecraft on a Soyuz 2.1b. Development On 15 January 2011, RKK Energia announced that its Scientific and Technical Council (NTS) had reviewed and approved the preliminary design of the Node Module and associated hardware, including a special version of the Progress cargo ship designated the Progress M-UM spacecraft-module, intended for the delivery of the Node Module to the station. The space payload section for the Progress M-UM was dubbed KGCh. The So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-01M
Progress M-01M (russian: Прогресс М-01М, italic=yes), identified by NASA as Progress 31P, was a Progress spacecraft used to resupply the International Space Station. It was the first flight of the Progress-M 11F615A60, which featured a TsVM-101 digital flight computer and MBITS digital telemetry system, in place of the earlier analogue systems. It was the first Progress-M 11F615A60 spacecraft, and had the serial number 401. Launch It was launched at 12:38 UTC on 26 November 2008 from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, atop a Soyuz-U carrier rocket. Following a four-day free flight, it docked with '' Pirs'' module of the ISS at 12:28 UTC on 30 November 2008. Antenna problem Immediately after launch, an antenna used by the spacecraft's Kurs docking system failed to deploy. The antenna was successfully deployed about three hours later after flight controllers resent the deployment command, however the spacecraft was docked using the backup TORU system, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-14
Progress M-14 (), was a Russian uncrewed Progress cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1992 to resupply the Mir space station. The spacecraft was modified to transport the first VDU propulsion unit to Mir. Progress M-14 also carried the sixth VBK-Raduga capsule, which was recovered after the flight. Launch Progress M-14 launched on 15 August 1992 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. It used a Soyuz-U2 rocket. Docking Progress M-14 docked with Mir on 18 August 1992 at 00:20:48 GMT. See also *1992 in spaceflight *List of Progress flights A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union ... * List of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir References {{Orbital launches in 1992 Progress (spacecraft) missions 1992 in spaceflight Spacecraft launched in 1992 1992 in Russia< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-38
Progress M-38 () was a Russian unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in March 1998 to resupply the Mir space station. Launch Progress M-38 launched on 14 March 1998 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki .... It used a Soyuz-U rocket. Docking Progress M-38 docked with the aft port of the Kvant-1 module of Mir on 17 March 1998 at 00:31:17 UTC, and was undocked on 15 May 1998 at 18:43:54 UTC. Decay It remained in orbit until 15 May 1998, when it was deorbited. The deorbit burn occurred at 21:39:00 UTC, with the mission ending at 22:26 UTC. See also * 1998 in spaceflight * List of Progress missions * List of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir References Progress (spacecraft) missions 1998 in Kazakhstan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-12M
Progress M-12M (russian: Прогресс М-12М, italic=yes), identified by NASA as Progress 44P, was an uncrewed Progress spacecraft that was lost in a launch failure on 24 August 2011, at the start of a mission to resupply the International Space Station. It was the twelfth modernised Progress-M spacecraft to be launched. Manufactured by RKK Energia, the spacecraft was to have been operated by the Russian Federal Space Agency. Planned mission Progress M-12M's planned mission had included resupplying ISS with 2670 kg of supplies, including oxygen, food and fuel. The planned mission also included three reboosts to the ISS. Progress M-12M was due to dock with the aft port of the Zvezda module of the International Space Station at around 14:40 UTC on 26 August 2011, just over two days after launch. It would have remained docked for six months, before undocking on 5 March 2012. Cargo Progress M-12M was carrying of cargo to the International Space Station. This included of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-1
Progress M-1 (russian: Прогресс М-1, italic=yes), was a Soviet uncrewed cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1989 to resupply the Mir space station. The eighteenth of sixty four Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it was the first Progress-M spacecraft to be launched, and had the serial number 201. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the Mir EO-5 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres. At the time of docking, Mir was uncrewed, and remained so until the arrival of the Mir EO-5 crew two weeks later. Launch Progress M-1 was launched at 03:09:32 UTC on 23 August 1989, atop a Soyuz-U2 carrier rocket flying from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. It docked with the forward port of Mir Core Module at 05:19:02 UTC on 25 August 1989. During the time it was docked, Mir was in an orbit of around . Progress M-1 remained docked with Mir for three months be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-29M
Progress M-29M (russian: Прогресс М-29М, italic=yes), identified by NASA as Progress 61P was a Progress spaceflight by Roskosmos to resupply the International Space Station (ISS) in 2015. It was launched on 1 October 2015, to deliver cargo to the ISS. Progress M-29M is the final vehicle in Progress-M series, which was succeeded by the modified variant known as Progress-MS later in 2015. Launch Progress M-29M was launched on 1 October 2015 at 16:49:40 UTC from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Docking Progress M-29M docked with the Zvezda docking compartment on 1 October 2015 at 22:52 UTC. The spacecraft undocked from the station on 30 March 2016 at 14:14 UTC. Cargo The Progress M-29M spacecraft carried 2369 kg of cargo and supplies to the International Space Station. The spacecraft delivered food, fuel and supplies, including 350 kg of propellant, 50 kg of oxygen and air, 420 kg of water, and 1549 kg of spare parts, supplies and experiment hardware for the six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress 7K-TG
Progress 7K-TG (russian: Прогресс 7К-ТГ, italic=yes, GRAU index 11F615A15), was a Soviet uncrewed spacecraft used to resupply space stations in low Earth orbit. Forty three flew, delivering cargo to Salyut 6, Salyut 7, and Mir. It was the first version of the Progress spacecraft to fly, and spawned later derivatives including the Progress-M which replaced it, and the later Progress-M1. The Progress 7K-TG spacecraft was derived from the crewed Soyuz 7K-T ferry spacecraft, which had been designed for the Salyut programme. The descent module of the Soyuz spacecraft was replaced with a new section designated ''Otsek Komponentov Dozapravki'', or OKD. This contained fuel tanks and pumps used for refuelling the space station that it docked with. Like the Soyuz 7K-T, the Progress was not equipped with solar panels, and instead relied on batteries for power. Early spacecraft had a design life of 33 days, including three in free flight, and the rest docked with a space stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energia (corporation)
PAO S. P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia (russian: Ракетно-космическая корпорация «Энергия» им. С. П. Королёва, Raketno-kosmicheskaya korporatsiya "Energiya" im. S. P. Korolyova), also known as RSC Energia (, RKK "Energiya"), is a Russian manufacturer of spacecraft and space station components. The company is the prime developer and contractor of the Russian crewed spaceflight program; it also owns a majority of Sea Launch. Its name is derived from Sergei Korolev, the first chief of its design bureau, and the Russian word for energy. Overview Energia is the largest company of the Russian space industry and one of its key players. It is responsible for all operations involving human spaceflight and is the lead developer of the Soyuz and Progress spacecraft, and the lead developer of the Russian end of the International Space Station (ISS). In the mid-2000s, the company employed 22,000–30,000 people. The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-27M
Progress M-27M (russian: Прогресс М-27М, italic=yes), identified by NASA as Progress 59P, was a Progress spacecraft used by Roscosmos in an unsuccessful attempt to resupply the International Space Station (ISS) in 2015. Launch Progress M-27M was the 27th Progress-M 11F615A60 spacecraft, with the serial number 427. It was built by RKK Energia and was operated by the Roscosmos. This was the second time the upgraded Soyuz-2.1a rocket was used for an ISS mission launch. The spacecraft was launched on 28 April 2015 at 07:09:50 UTC from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Progress M-27M was launched with a planned six-hour rendezvous profile to the ISS. During the launch the spacecraft achieved low Earth orbit, but a malfunction occurred near the end of the upper stage burn shortly before the separation of the Progress spacecraft, generating a debris field and leaving the spacecraft spinning and unable to be fully controlled. The spacecraft was deemed to be a total l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |