|
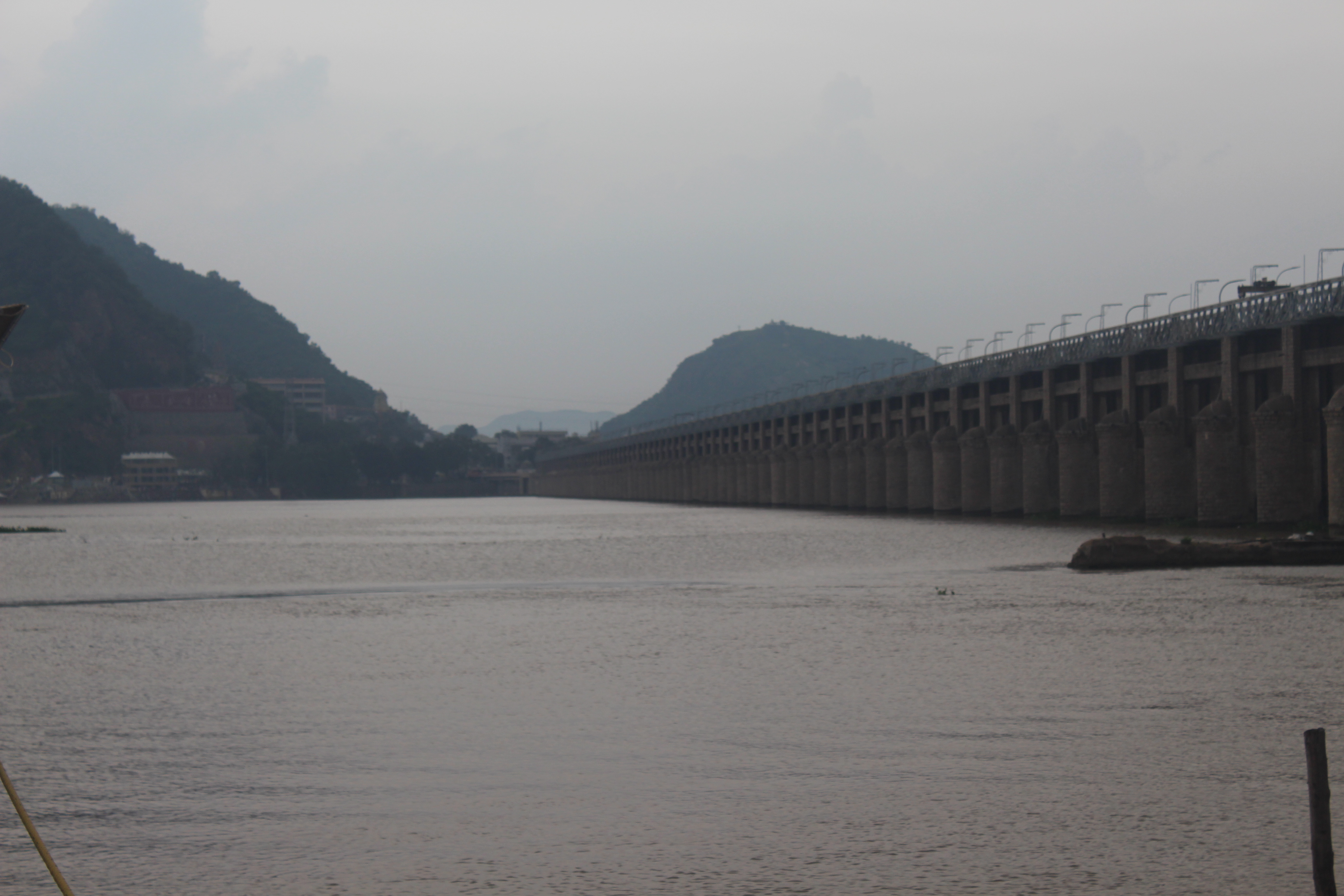
Prakasam Barrage
The Prakasam Barrage stretches 1223.5 m across the Krishna River connecting Vijayawada, NTR and Mangalagiri Tadepalle Municipal Corporation, Guntur districts in Andhra Pradesh, India. The barrage serves also as a road bridge and spans over a lake. The three canals associated with the barrage run through the city of Vijayawada, crossing it and giving it a Venetian appearance. The idea of constructing a dam across the river Krishna dates back to 1798. It began in the hands of captain Buckle and was revised in 1839 and 1841 by Captain Best and Captain Lake. After the endorsement of Major Cotton, the board of Directors of the East India Company approved it on 5 January 1850. The dam was started in 1852 and completed in 1855. It cost Rs 1.75 crore in those days and seems to have paid the then government a return of 18%. It used to irrigate 7 lakh acres. Later, the State Government constructed a bridge that was named after Tanguturi Prakasam, the first Chief Minister of Andhra (a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, interm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andhra State
Andhra State (IAST: ; ) was a state in India created in 1953 from the Telugu-speaking northern districts of Madras State. The state was made up of this two distinct cultural regions – Rayalaseema and Coastal Andhra. Andhra State did not include all Telugu-speaking areas, as it excluded some in Hyderabad State. Under the State Reorganisation Act of 1956, Andhra State was merged with the Telugu-speaking regions of Hyderabad State to form Andhra Pradesh. Creation of Andhra State In an effort to protect the interests of the Telugu people of Madras State, Potti Sreeramulu attempted to force the Madras State government to listen to public demands for the separation of Telugu-speaking districts (Rayalaseema and Coastal Andhra) from Madras State to form Andhra State. He went on a lengthy fast and only stopped when Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru made a promise to form Andhra State. Later, after witnessing no real progress towards the creation of Andhra State, he started fasting a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourist Attractions In Vijayawada
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as being limited to holiday activity only", as people "travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure and not less than 24 hours, business and other purposes". Tourism can be domestic (within the traveller's own country) or international, and international tourism has both incoming and outgoing implications on a country's balance of payments. Tourism numbers declined as a result of a strong economic slowdown (the late-2000s recession) between the second half of 2008 and the end of 2009, and in consequence of the outbreak of the 2009 H1N1 influenza virus, but slowly recovered until the COVID- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dams And Reservoirs In India
This page shows the state-wise list of dams and reservoirs in India. As of July, 2019, total number of large dams in India is 5,334. About 447 large dams are under construction in India. In terms of number of dams, India ranks third after China and the United States. Andhra Pradesh Arunachal Pradesh Chhattisgarh Bihar Goa Gujarat Gujarat has over 200 dams with reservoirs that are large enough to be of particular concern in disaster preparedness planning. These include: Haryana Himachal Pradesh Jammu and Kashmir Jharkhand Karnataka Kerala , , , , , , , , , , There are 44 rivers in Kerala, and 42 dams and reservoirs. The dams and reservoirs in Kerala include Solaiyar Dam, Kakkayam Dam, Idamalayar Dam, Peringalkuthu Dam and Kakki Reservoir. Madhya Pradesh Nevaj River Rajgarh mohanpura Dam Manipur Maharashtra Mizoram Odisha Punjab Rajasthan Sikkim Tamil Nadu Telangana Uttarakhand Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulichinthala Project
The Pulichintala Project is a multi-purpose water management project for irrigation, hydropower generation, and flood control in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. It is a crucial irrigation facility for farmers in four coastal districts: West Godavari, Krishna, Guntur, and Prakasam, covering over 13 lakh acres. It has 24 gates and a balancing reservoir with a capacity of 46 Tmcft at MSL full reservoir level (FRL). History In 1911, British engineer Col. Ellis proposed an irrigation project upstream of the Prakasam Barrage. At the time, the British government showed little interest in the proposition. Later, the Raja of Muktyala led the push for the Pulichintala Project with the help of Moturi Satyanarayana and K.L Rao. It was the first project to start under the ambitious Jalayagnam program in the year 2004. https://irrigationap.cgg.gov.in/wrd/static/approjects/KLRaoProject.html Financial tie-up happened in 2009 and commenced in 2009. On 7 December 2013, the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
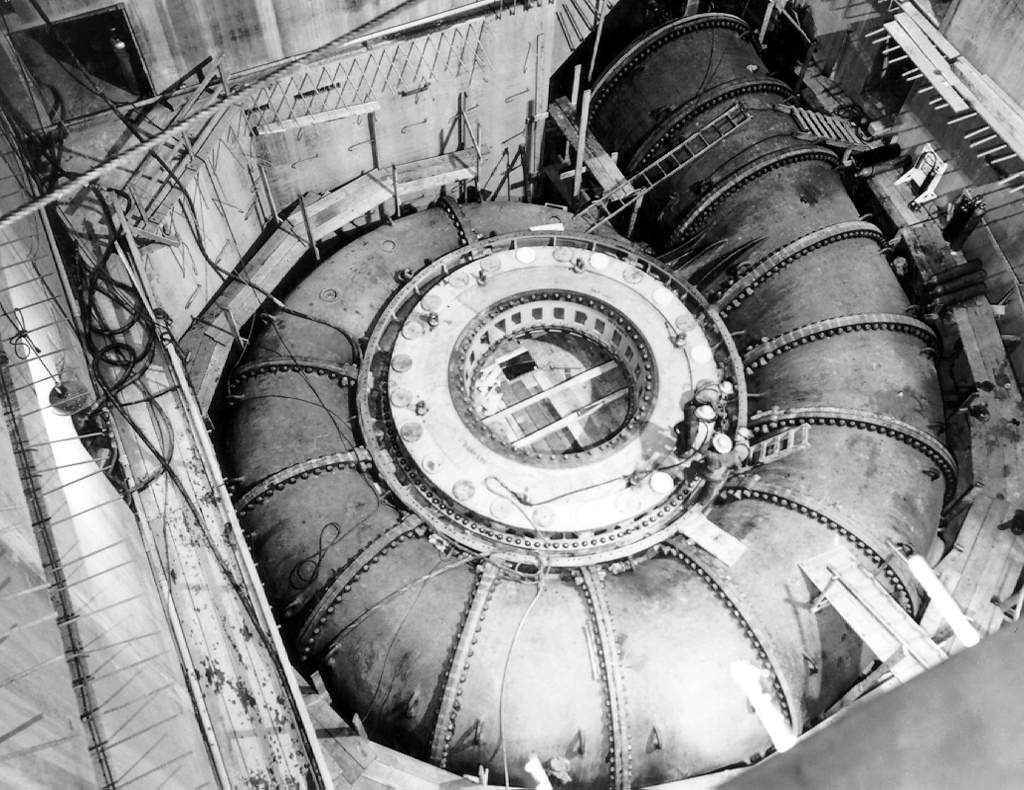
Kaplan Turbine
The Kaplan turbine is a propeller-type water turbine which has adjustable blades. It was developed in 1913 by Austrian professor Viktor Kaplan, who combined automatically adjusted propeller blades with automatically adjusted wicket gates to achieve efficiency over a wide range of flow and water level. The Kaplan turbine was an evolution of the Francis turbine. Its invention allowed efficient power production in low-head applications which was not possible with Francis turbines. The head ranges from and the output ranges from 5 to 200 MW. Runner diameters are between . Turbines rotate at a constant rate, which varies from facility to facility. That rate ranges from as low as 54.5 rpm ( Albeni Falls Dam) to 450 rpm. Kaplan turbines are now widely used throughout the world in high-flow, low-head power production. Development Viktor Kaplan, living in Brünn, Austria-Hungary (now Brno, Czechia), obtained his first patent for an adjustable blade propeller turbine in 1912. But ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagarjuna Sagar Tail Pond
Nagarjuna Sagar tail pond is a multipurpose reservoir located 21 km downstream from the Nagarjuna Sagar Dam across the Krishna River near Satrasala in Nalgonda district, India. Its gross water storage capacity is 6 Tmcft. The reservoir water spread area extends up to the toe of the Nagarjuna Sagar dam. The project was completed by July 2014. Hydro electricity generation Two units of 25 MW each hydro power generation units were commissioned in the year 2017 by APGENCO to utilize the head available across the dam from the river flood water and the water released to Prakasam Barrage requirements. Peaking power generation Presently, the 700 MW reversible hydro turbines (7 x 100 MW) located at the toe of Nagarjuna Sagar Dam are unable to operate in pumping mode due to non availability of tail pond for storing the released water during the power generation mode. With the completion of tail pond, surplus electricity from the electricity grid would be used for pumping the wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagarjuna Sagar Dam
Nagarjuna Sagar Dam is a masonry dam across the Krishna River at Nagarjuna Sagar which straddles the border between Nalgonda district in Telangana and Palnadu district in Andhra Pradesh. The dam provides irrigation water to the Nalgonda, Suryapet, Krishna, NTR, Bapatla, Eluru, Palnadu, Khammam, West Godavari, Guntur, and Prakasam districts along with electricity generation. Constructed between 1955 and 1967, the dam created a water reservoir with gross storage capacity of , its effective capacity is 6.92 cubic kms or 244.41 Tmcft. The dam is tall from its deepest foundation and long with 26 flood gates which are wide and tall. It is jointly operated by Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. Nagarjuna Sagar Dam was the earliest in a series of large infrastructure projects termed as "modern temples" initiated for achieving the Green Revolution in India. It is also one of the earliest multi-purpose irrigation and hydroelectric projects in India. History The Nizam made th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srisailam Dam
The Srisailam Dam is constructed across the Krishna River in Nagarkurnool district , Telangana and Nandyal district, Andhra Pradesh near Srisailam temple town and is the 2nd largest capacity working hydroelectric station in India. The dam was constructed in a deep gorge in the Nallamala Hills in between Kurnool and Nagarkurnool districts, above sea level. It is long, maximum height and has crest gates. It has a reservoir of . Project has an estimated live capacity to hold 178.74 Tmcft at its full reservoir level of MSL. It's gross storage capacity is 6.116 cubic kms (216 tmc ft). The minimum draw down level (MDDL) of the reservoir is at MSL from its river sluice gates and corresponding dead storage is 3.42 Tmcft. The left bank underground power station houses reversible Francis-pump turbines for pumped-storage operation (each Turbine can pump 200 cumecs) and the right bank semi under ground power station houses Francis-turbine generators. Tail pond dam/weir lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vykuntapuram Barrage
Vykuntapuram Barrage is an Indian barrage and water storage project. It is under construction on Krishna River 23 kilometers upstream of existing Prakasam Barrage with FRL 25M. It is designed to store 10 TMC of flood water coming from the Vyra and Munneru rivers. The backwater of this dam will extend beyond Pokkunuru to the toe of Pulichintala dam. Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister Nara chandrababu Naidu laid the foundation stone for this project on 13 February 2019. Features Vykuntapuram Barrage features include: Godavari Penna River link To stabilize the existing irrigated area under Nagarjuna sagar right canal, a new lift project construction was started. The project was to provide five step pumping stages and a canal to transfer 7,000 cusecs of Godavari water from Prakasam barrage back waters into the canal near Nekarikallu. The first phase was expected to utilize 73 tmcft of Godavari water. Vykuntapuram Barrage backwaters stretch beyond Pokkunuru to the toe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |