|
Possessive
A possessive or ktetic form ( abbreviated or ; from la, possessivus; grc, κτητικός, translit=ktētikós) is a word or grammatical construction used to indicate a relationship of possession in a broad sense. This can include strict ownership, or a number of other types of relation to a greater or lesser degree analogous to it. Most European languages feature possessive forms associated with personal pronouns, like the English ''my'', ''mine'', ''your'', ''yours'', ''his'' and so on. There are two main ways in which these can be used (and a variety of terminologies for each): * Together with a noun, as in ''my car'', ''your sisters'', ''his boss''. Here the possessive form serves as a '' possessive determiner''. * Without an accompanying noun, as in ''mine is red'', ''I prefer yours'', ''this book is his''. A possessive used in this way is called a ''substantive possessive pronoun'', a possessive pronoun or an ''absolute pronoun''. Some languages, including English, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Possessive
A possessive or ktetic form ( abbreviated or ; from la, possessivus; grc, κτητικός, translit=ktētikós) is a word or grammatical construction used to indicate a relationship of possession in a broad sense. This can include strict ownership, or a number of other types of relation to a greater or lesser degree analogous to it. Most European languages feature possessive forms associated with personal pronouns, like the English ''my'', ''mine'', ''your'', ''yours'', ''his'' and so on. There are two main ways in which these can be used (and a variety of terminologies for each): * Together with a noun, as in ''my car'', ''your sisters'', ''his boss''. Here the possessive form serves as a '' possessive determiner''. * Without an accompanying noun, as in ''mine is red'', ''I prefer yours'', ''this book is his''. A possessive used in this way is called a ''substantive possessive pronoun'', a possessive pronoun or an ''absolute pronoun''. Some languages, including English, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
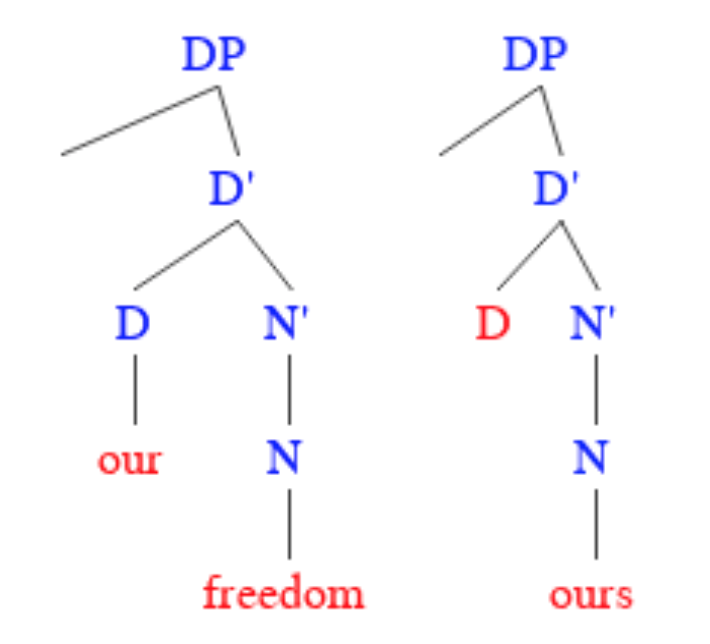
Possessive Determiner
Possessive determiners (from la, possessivus, translit=; grc, κτητικός / ktētikós - en. ktetic Lallu) are determiners which express possession. Some traditional grammars of English refer to them as possessive adjectives, though they do not have the same syntactic distribution as bona fide adjectives. Examples in English include possessive forms of the personal pronouns, namely: ''my'', ''your'', ''his'', ''her'', ''its'', ''our'' and ''their'', but excluding those forms such as ''mine'', ''yours'', ''ours'', and ''theirs'' that are used as possessive pronouns but not as determiners. Possessive determiners may also be taken to include possessive forms made from nouns, from other pronouns and from noun phrases, such as ''John's'', ''the girl's'', ''somebody's'', ''the king of Spain's'', when used to modify a following noun. In many languages, possessive determiners are subject to agreement with the noun they modify, as in the French ''mon'', ''ma'', ''mes'', respective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Possessive Affix
In linguistics, a possessive affix (from la, affixum possessivum) is an affix (usually suffix or prefix) attached to a noun to indicate its possessor, much in the manner of possessive adjectives. Possessive affixes are found in many languages of the world. The ''World Atlas of Language Structures'' lists 642 languages with possessive suffixes, possessive prefixes, or both out of a total sample of 902 languages. Possessive suffixes are found in some Austronesian, Uralic, Altaic, Semitic, and Indo-European languages. Complicated systems are found in the Uralic languages; for example, Nenets has 27 (3×3×3) different types of forms distinguish the possessor (first-, second- or third-person), the number of possessors (singular, dual or plural) and the number of objects (singular, dual or plural). That allows Nenets-speakers to express the phrase "we two's many houses" in one word. Mayan languages and Nahuan languages also have possessive prefixes. Uralic languages Finnish F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Grammar
English grammar is the set of structural rules of the English language. This includes the structure of words, phrases, clauses, Sentence (linguistics), sentences, and whole texts. This article describes a generalized, present-day Standard English – a form of speech and writing used in public discourse, including broadcasting, education, entertainment, government, and news, over a range of Register (sociolinguistics), registers, from formal to informal. Divergences from the grammar described here occur in some historical, social, cultural, and regional List of dialects of the English language, varieties of English, although these are more minor than differences in English phonology, pronunciation and lexicon, vocabulary. Modern English has largely abandoned the inflectional grammatical case, case system of Indo-European in favor of analytic language, analytic constructions. The personal pronouns retain morphological case more strongly than any other word class (a remnant of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitive Case
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can also serve purposes indicating other relationships. For example, some verbs may feature arguments in the genitive case; and the genitive case may also have adverbial uses (see adverbial genitive). Genitive construction includes the genitive case, but is a broader category. Placing a modifying noun in the genitive case is one way of indicating that it is related to a head noun, in a genitive construction. However, there are other ways to indicate a genitive construction. For example, many Afroasiatic languages place the head noun (rather than the modifying noun) in the construct state. Possessive grammatical constructions, including the possessive case, may be regarded as a subset of genitive construction. For example, the genitive const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers ( determiners, adjectives, participles, and numerals), which corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nominal groups consisting of a noun and its modifiers belong to one of a few such categories. For instance, in English, one says ''I see them'' and ''they see me'': the nominative pronouns ''I/they'' represent the perceiver and the accusative pronouns ''me/them'' represent the phenomenon perceived. Here, nominative and accusative are cases, that is, categories of pronouns corresponding to the functions they have in representation. English has largely lost its inflected case system but personal pronouns still have three cases, which are simplified forms of the nominative, accusative and genitive cases. They are used with personal pronouns: subjective case (I, you, he, she, it, we, they, who, whoever), objective case (me, you, him, her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Personal Pronouns
The English personal pronouns are a subset of English pronouns taking various forms according to number, person, case and natural gender. Modern English has very little inflection of nouns or adjectives, to the point where some authors describe it as an analytic language, but the Modern English system of personal pronouns has preserved some of the inflectional complexity of Old English and Middle English. Forms Unlike nouns, which are not inflected for case except for possession (''woman/woman's''), English personal pronouns have a number of forms, which are named according to their typical grammatical role in a sentence: * objective (accusative) case (''me'', ''us'', etc.), used as the object of a verb, complement of a preposition, and the subject of a verb in some constructions (see below). The same forms are also used as disjunctive pronouns. * subjective (nominative) case (''I'', ''we'', etc.), used as the subject of a verb (see also below). * reflexive form (''m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Pronoun
Personal pronouns are pronouns that are associated primarily with a particular grammatical person – first person (as ''I''), second person (as ''you''), or third person (as ''he'', ''she'', ''it'', ''they''). Personal pronouns may also take different forms depending on number (usually singular or plural), grammatical or natural gender, case, and formality. The term "personal" is used here purely to signify the grammatical sense; personal pronouns are not limited to people and can also refer to animals and objects (as the English personal pronoun ''it'' usually does). The re-use in some languages of one personal pronoun to indicate a second personal pronoun with formality or social distance – commonly a second person plural to signify second person singular formal – is known as the T–V distinction, from the Latin pronouns and . Examples are the majestic plural in English and the use of in place of in French. For specific details of the personal pronouns used in the Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Possession (linguistics)
In linguistics, possession is an asymmetric relationship between two constituents, the referent of one of which (the possessor) in some sense possesses (owns, has as a part, rules over, etc.) the referent of the other (the possessed). Possession may be marked in many ways, such as simple juxtaposition of nouns, possessive case, possessed case, construct state (as in Arabic, and Nêlêmwa), or adpositions ( possessive suffixes, possessive adjectives). For example, English uses a possessive clitic, '' 's''; a preposition, ''of''; and adjectives, ''my'', ''your'', ''his'', ''her'', etc. Predicates denoting possession may be formed either by using a verb such as English ''have'' or by other means, such as existential clauses (as is usual in languages such as Russian). Some languages have more than two possessive classes. In Papua New Guinea, for example, Anêm has at least 20 and Amele has 32. Alienable and inalienable There are many types of possession, but a common distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Subtypes include personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive and reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its antecedent, ''that poor man''. The name of the adjective that belongs with a "pronoun" is called a "pronominal". A pronominal is also a word or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossing Abbreviation
This article lists common abbreviations for grammatical terms that are used in linguistic interlinear glossing of oral languages in English. The list provides conventional glosses as established by standard inventories of glossing abbreviations such as the Leipzig Glossing rules, the most widely known standard. These will generally be the glosses used on Wikipedia. Synonymous glosses are listed as alternatives for reference purposes. In a few cases, long and short standard forms are listed, intended for texts where that gloss is rare or common. Conventions * Grammatical abbreviations are generally written in full or small caps to visually distinguish them from the translations of lexical words. For instance, capital or small-cap (frequently abbreviated to ) glosses a grammatical past-tense morpheme, while lower-case 'past' would be a literal translation of a word with that meaning. Similarly, (small) cap might be a locative suffix used in nominal inflections, prototypically in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish (language)
Finnish ( endonym: or ) is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland (the other being Swedish). In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. The Kven language, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian county Troms og Finnmark by a minority group of Finnish descent. Finnish is typologically agglutinative and uses almost exclusively suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numerals and verbs are inflected depending on their role in the sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, although the extensive use of inflection allows them to be ordered differently. Word order variations are often reserved for differences in information structure. Finnish ort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |