|
Positive Psychology In The Workplace
Positive psychology is defined as a method of building on what is good and what is already working instead of attempting to stimulate improvement by focusing on the weak links in an individual, a group, or in this case, a company. Implementing positive psychology in the workplace means creating an environment that is more enjoyable, productive, and values individual employees. This also means creating a work schedule that does not lead to emotional and physical distress. Overview Positive psychology in the workplace focuses on shifting attention away from negative aspects such as workplace violence, stress, burnout, and job insecurity; it shifts attention to positive and hopeful attributes, resilience, confidence, and a productive work culture that emphasizes professional success and human success. Through the employment of positive psychology, a working environment to promote positive affect in its employees can be created. Fun should not be looked at as something that cannot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affect (psychology)
Affect, in psychology, refers to the underlying experience of feeling, emotion or mood. History The modern conception of affect developed in the 19th century with Wilhelm Wundt. The word comes from the German ''Gefühl'', meaning "feeling." A number of experiments have been conducted in the study of social and psychological affective preferences (i.e., what people like or dislike). Specific research has been done on preferences, attitudes, impression formation, and decision-making. This research contrasts findings with recognition memory (old-new judgments), allowing researchers to demonstrate reliable distinctions between the two. Affect-based judgments and cognitive processes have been examined with noted differences indicated, and some argue affect and cognition are under the control of separate and partially independent systems that can influence each other in a variety of ways (Zajonc, 1980). Both affect and cognition may constitute independent sources of effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
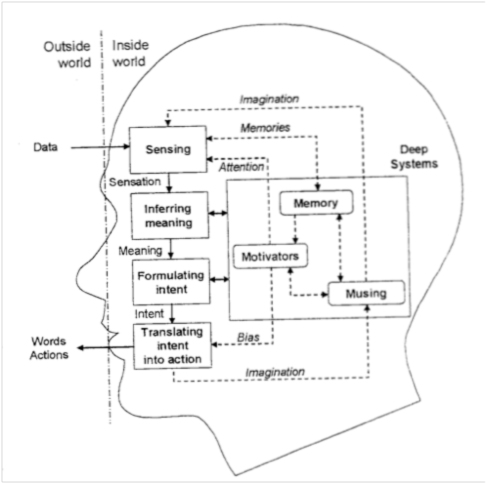
Motivation
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-directed behavior. It is often held that different mental states compete with each other and that only the strongest state determines behavior. This means that we can be motivated to do something without actually doing it. The paradigmatic mental state providing motivation is desire. But various other states, such as beliefs about what one ought to do or intentions, may also provide motivation. Motivation is derived from the word 'motive', which denotes a person's needs, desires, wants, or urges. It is the process of motivating individuals to take action in order to achieve a goal. The psychological elements fueling people's behavior in the context of job goals might include a desire for money. Various competing theories have been proposed c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Booster Breaks In The Workplace
''Booster Breaks: Improving Employee Health One Break at a Time'' is a 2010 book. Booster breaks are defined as: "organized, routine work breaks intended to improve physical and psychological health, enhance job satisfaction, and sustain or increase work productivity."Taylor WC. Transforming work breaks to promote health. ''American Journal of Preventive Medicine'', 2005; 29: 461–465.Taylor WC, Shegog R, Chen V, et al. The Booster Break program: description and feasibility test of a worksite physical activity daily practice. ''WORK: A Journal of Prevention, Assessment, and Rehabilitation'', 2010; 37:433–443.Taylor WC, Pepkin KL. ''Booster Breaks: Improving employee health one break at a time''. Houston, TX: Karrick Press, 2010.Taylor WC. Booster Breaks: an easy-to-implement workplace policy designed to improve employee health, increase productivity, and lower health care costs. ''Journal of Workplace Behavioral Health'', 2011; 26: 70–84.Taylor WC, King KE, Shegog R, et al. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work Engagement
Work engagement is the "harnessing of organization member's selves to their work roles: in engagement, people employ and express themselves physically, cognitively, emotionally and mentally during role performances". Three aspects of work motivation are cognitive, emotional and physical engagement. There are two schools of thought with regard to the definition of work engagement. On the one hand Maslach and Leiter assume that a continuum exists with burnout and engagement as two opposite poles. The second school of thought operationalizes engagement in its own right as the positive antithesis of burnout. According to this approach, work engagement is defined as a positive, fulfilling, work-related state of mind that is characterized by vigor, dedication, and absorption. Vigor is characterized by high levels of energy and mental resilience while working, the willingness to invest effort in one's work, and persistence even in the face of difficulties; dedication by being strongly invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employee Engagement
Employee engagement is a fundamental concept in the effort to understand and describe, both qualitatively and quantitatively, the nature of the relationship between an organization and its employees. An "engaged employee" is defined as one who is fully absorbed by and enthusiastic about their work and so takes positive action to further the organization's reputation and interests. An engaged employee has a positive attitude towards the organization and its values. In contrast, a disengaged employee may range from someone doing the bare minimum at work (aka 'coasting'), up to an employee who is actively damaging the company's work output and reputation. An organization with "high" employee engagement might therefore be expected to outperform those with "low" employee engagement. Employee engagement first appeared as a concept in management theory in the 1990s, becoming widespread in management practice in the 2000s, but it remains contested. It stands in an unspecified relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Psychology
Positive psychology is the scientific study of what makes life most worth living, focusing on both individual and societal well-being. It studies "positive subjective experience, positive individual traits, and positive institutions...it aims to improve quality of life." It is a field of study that has been growing steadily throughout the years as individuals and researchers look for common ground on better well-being. Positive psychology began as a new domain of psychology in 1998 when Martin Seligman chose it as the theme for his term as president of the American Psychological Association. It is a reaction against past practices, which have tended to focus on mental illness and emphasized maladaptive behavior and negative thinking. It builds on the humanistic movement by Abraham Maslow, Rollo May, James Bugental, and Carl Rogers, which encourages an emphasis on happiness, well-being, and positivity, thus creating the foundation for what is now known as positive psychol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupational Safety And Health
Occupational safety and health (OSH), also commonly referred to as occupational health and safety (OHS), occupational health, or occupational safety, is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work (i.e. in an occupation). These terms also refer to the goals of this field, so their use in the sense of this article was originally an abbreviation of ''occupational safety and health program/department'' etc. The goal of an occupational safety and health program is to foster a safe and healthy occupational environment. OSH also protects all the general public who may be affected by the occupational environment.Fanning, Fred E. (2003). Basic Safety Administration: A Handbook for the New Safety Specialist, Chicago: American Society of Safety Engineers Globally, more than 2.78 million people die annually as a result of workplace-related accidents or diseases, corresponding to one death every fifteen seconds. There are an additional 374 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flourishing
Flourishing is "when people experience positive emotions, positive psychological functioning and positive social functioning, most of the time," living "within an optimal range of human functioning." It is a descriptor and measure of positive mental health and overall life well-being, and includes multiple components and concepts, such as cultivating strengths, subjective well-being, "goodness, generativity, growth, and resilience." Flourishing is the opposite of both pathology and languishing, which are described as living a life that feels hollow and empty. It is a central concept in positive psychology, developed by Corey Keyes and Barbara Fredrickson. __TOC__ Theory Definition Flourishing is a "descriptor of positive mental health." According to Fredrickson and Losada, flourishing is living According to the Mental Health Foundation of New Zealand, flourishing According to Keyes, mental health does not imply an absence of mental illness. Rather, mental health is a "sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helping Behavior
Helping behavior refers to voluntary actions intended to help the others, with reward regarded or disregarded. It is a type of prosocial behavior (voluntary action intended to help or benefit another individual or group of individuals, such as sharing, comforting, rescuing and helping). Altruism is distinguished from helping behavior. Altruism refers to prosocial behaviors that are carried out without expectation of obtaining external reward (concrete reward or social reward) or internal reward (self-reward). An example of altruism would be anonymously donating to charity. Perspectives on helping behavior Kin selection theory Kin selection theory explains altruism in an evolutionary perspective. Since natural selection aids in screening out species without abilities to adapt the challenging environment, preservation of good traits and superior genes are important for survival of future generations (i.e. inclusive fitness). Kin selection refers to the tendency to perform behaviors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compliance (psychology)
Compliance is a response—specifically, a submission—made in reaction to a request. The request may be explicit (e.g., foot-in-the-door technique) or implicit (e.g., advertising). The target may or may not recognize that they are being urged to act in a particular way.Cialdini, R. B, & Goldstein, N. J. (2004) "Social influence: Compliance and conformity.” Annual Review of Psychology, 55: 591–621. Social psychology is centered on the idea of social influence. Defined as the effect that the words, actions, or mere presence of other people (real or imagined) have on our thoughts, feelings, attitudes, or behavior; social influence is the driving force behind compliance. It is important that psychologists and ordinary people alike recognize that social influence extends beyond our behavior—to our thoughts, feelings, and beliefs—and that it takes on many forms. Persuasion and the gaining of compliance are particularly significant types of social influence since they utilize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizational Citizenship Behavior
In industrial and organizational psychology, organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) is a person's voluntary commitment within an organization or company that is not part of his or her contractual tasks. Organizational citizenship behavior has been studied since the late 1970s. Over the past three decades, interest in these behaviors has increased substantially. Organizational behavior has been linked to overall organizational effectiveness, thus these types of employee behaviors have important consequences in the workplace. Dennis Organ is generally considered the father of OCB. Organ expanded upon Katz's (1964) original work. Definition of the concept Organ (1988) defines OCB as "individual behavior that is discretionary, not directly or explicitly recognized by the formal reward system, and that in the aggregate promotes the effective functioning of the organization". Organ, D. W. (1988). Organizational Citizenship behavior: The good soldier syndrome. Lexington, MA: Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Happiness At Work
Despite a large body of positive psychological research into the relationship between happiness and productivity,Carr, A.: "Positive Psychology: The Science of Happiness and Human Strengths" Hove, Brunner-Routledge 2004Isen, A.; Positive Affect and Decision-making. In M. Lewis and J. Haviland Jones (eds), "Handbook of Emotions" (2nd edition), pp. 417–436. New York, Guilford Press 2000 happiness at work has traditionally been seen as a potential by-product of positive outcomes at work, rather than a pathway to business success. Happiness in the workplace is usually dependent on the work environment. During the past two decades, maintaining a level of happiness at work has become more significant and relevant due to the intensification of work caused by economic uncertainty and increase in competition. Nowadays, happiness is viewed by a growing number of scholars and senior executives as one of the major sources of positive outcomes in the workplace.Boehm, J K. & S. Lyubomirsky'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

cropped.jpg)