|
Pleroma
Pleroma ( grc-koi, πλήρωμα, literally "fullness") generally refers to the totality of divine powers. It is used in Christian theological contexts, especially in Gnosticism. The term also appears in the Epistle to the Colossians, which is traditionally attributed to Paul the Apostle. The word is used 17 times in the New Testament. The word literally means "fullness", from the verb (, "to fill"), from ( πλήρης, "full"). Svenska Akademiens ordbok, search on the word ''Pleroma'/ref> Christianity New Testament The word itself is a relative term, capable of many shades of meaning, according to the subject with which it is joined and the antithesis to which it is contrasted. It denotes the result of the action of the verb ''pleroun;'' but ''pleroun'' is either *to fill up an empty thing (''e.g.'' ), or *to complete an incomplete thing (''e.g.'' ); and the verbal substantive in -''ma'' may express either #the objective accusative after the verb, 'the thing filled or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleroma
Pleroma ( grc-koi, πλήρωμα, literally "fullness") generally refers to the totality of divine powers. It is used in Christian theological contexts, especially in Gnosticism. The term also appears in the Epistle to the Colossians, which is traditionally attributed to Paul the Apostle. The word is used 17 times in the New Testament. The word literally means "fullness", from the verb (, "to fill"), from ( πλήρης, "full"). Svenska Akademiens ordbok, search on the word ''Pleroma'/ref> Christianity New Testament The word itself is a relative term, capable of many shades of meaning, according to the subject with which it is joined and the antithesis to which it is contrasted. It denotes the result of the action of the verb ''pleroun;'' but ''pleroun'' is either *to fill up an empty thing (''e.g.'' ), or *to complete an incomplete thing (''e.g.'' ); and the verbal substantive in -''ma'' may express either #the objective accusative after the verb, 'the thing filled or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
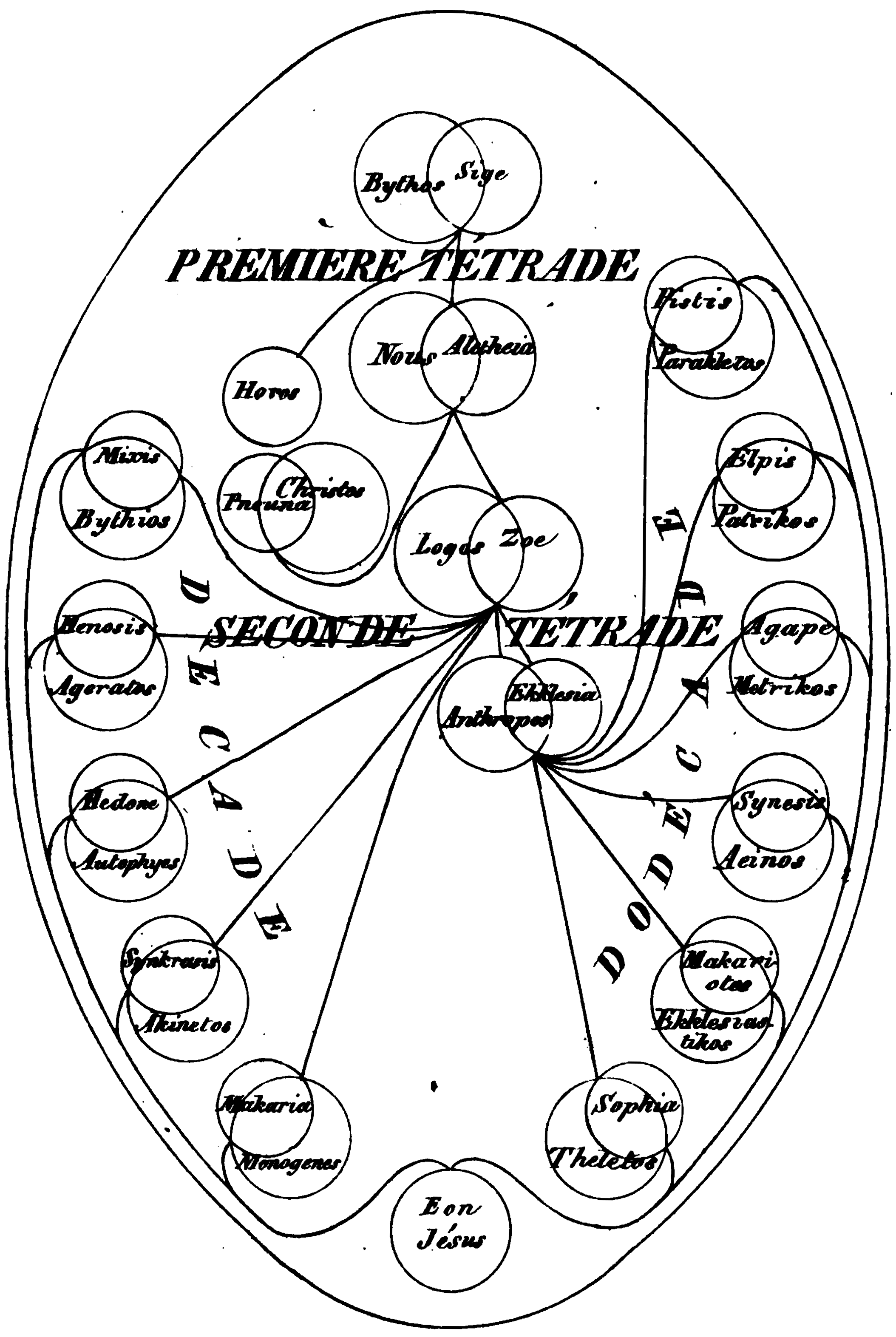
Aeon (Gnosticism)
In many Gnostic systems, various emanations of God are known by such names as One, Monad, ''Aion teleos'' (αἰών τέλεος "The Broadest Aeon"), Bythos (, "depth" or "profundity"), ''Proarkhe'' ("before the beginning", ), ''Arkhe'' ("the beginning", ), and Aeons. In different systems these emanations are differently named, classified, and described, but emanation theory is common to all forms of Gnosticism. In Basilidian Gnosis they are called sonships (υἱότητες ''huiotetes''; sing.: υἱότης ''huiotes''); according to Marcus, they are numbers and sounds; in Valentinianism they form male/female pairs called syzygies (Greek , from σύζυγοι ''syzygoi'', lit. "yokings together"). This source of all being is an Aeon, in which an inner being dwells, known as ''Ennoea'' ("thought, intent", Greek ), ''Charis'' ("grace", Greek ), or ''Sige'' ("silence", Greek ). The split perfect being conceives the second Aeon, ''Nous'' ("mind", Greek Νους), within i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentinianism
Valentinianism was one of the major Gnostic Christian movements. Founded by Valentinus in the 2nd century AD, its influence spread widely, not just within Rome but also from Northwest Africa to Egypt through to Asia Minor and Syria in the East. Later in the movement's history it broke into an Eastern and a Western school. Disciples of Valentinus continued to be active into the 4th century AD, after the Roman Emperor Theodosius I issued the Edict of Thessalonica (380 AD), which declared Nicene Christianity as the State church of the Roman Empire. The doctrine, practices and beliefs of Valentinus and the Gnostic movement that bore his name were condemned as heretical by proto-orthodox Christian leaders and scholars. Prominent Church Fathers such as Irenaeus of Lyons and Hippolytus of Rome wrote against Gnosticism. Because early church leaders encouraged the destruction of Gnostic texts, most evidence for the Valentinian theory comes from its critics and detractors, most nota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenoma
Valentinius, a mid-2nd century Gnostic thinker and preacher, was among the early Christians who attempted to align Christianity with middle Platonism. Valentinius pooled dual concepts from the Platonic world of ideal forms, or fullness (pleroma), and the lower world of phenomena, or emptiness (''kenoma'', κένωμα). Employing a third concept of cosmos, what is manifest, Valentinian initiates could exegete scripture in light of these three aspects of correlated existence. The void The ancient Greek term for emptiness or void (''kenoma''), as pertaining to Theodotus's exegesis of Gospel of John chapter 1 verse 3, is described in ''The Excerpta ex Theodoto of Clement of Alexandria'' (Casey, 1934). Hysterema Elsewhere, the usual antithesis to Pleroma is not Kenoma, but ''Hysterema'' (ὑστέρημα). As the system is reported by Hippolytus (vi. 31, p. 180) this word is used as the complement of the word Pleroma, denoting all that is not included in the meaning of the lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heracleon
Heracleon was a Gnostic who flourished about AD 175, probably in the south of Italy. He is described by Clement of Alexandria ('' Strom.'' iv. 9) as the most esteemed (δοκιμώτατος) of the school of Valentinus; and, according to Origen (''Comm. in S. Joann.'' t. ii. § 8, ''Opp.'' t. iv. p. 66), said to have been in personal contact (γνώριμος) with Valentinus himself. He is barely mentioned by Irenaeus (ii. 41) and by Tertullian (''adv. Valent.'' 4). The common source of Philaster and Pseudo-Tertullian (''i.e.'' probably the earlier treatise of Hippolytus) contained an article on Heracleon between those on Ptolemaeus and Secundus, and on Marcus and Colarbasus. In his system he appears to have regarded the divine nature as a vast abyss in whose Pleroma were Aeons of different orders and/or degrees, emanations from the source of being. Midway between the supreme God and the material world was the '' Demiourgos'', who created the latter, and under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenoma
Valentinius, a mid-2nd century Gnostic thinker and preacher, was among the early Christians who attempted to align Christianity with middle Platonism. Valentinius pooled dual concepts from the Platonic world of ideal forms, or fullness (pleroma), and the lower world of phenomena, or emptiness (''kenoma'', κένωμα). Employing a third concept of cosmos, what is manifest, Valentinian initiates could exegete scripture in light of these three aspects of correlated existence. The void The ancient Greek term for emptiness or void (''kenoma''), as pertaining to Theodotus's exegesis of Gospel of John chapter 1 verse 3, is described in ''The Excerpta ex Theodoto of Clement of Alexandria'' (Casey, 1934). Hysterema Elsewhere, the usual antithesis to Pleroma is not Kenoma, but ''Hysterema'' (ὑστέρημα). As the system is reported by Hippolytus (vi. 31, p. 180) this word is used as the complement of the word Pleroma, denoting all that is not included in the meaning of the lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnosticism
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish and early Christian sects. These various groups emphasized personal spiritual knowledge ('' gnosis'') above the orthodox teachings, traditions, and authority of religious institutions. Gnostic cosmogony generally presents a distinction between a supreme, hidden God and a malevolent lesser divinity (sometimes associated with the Yahweh of the Old Testament) who is responsible for creating the material universe. Consequently, Gnostics considered material existence flawed or evil, and held the principal element of salvation to be direct knowledge of the hidden divinity, attained via mystical or esoteric insight. Many Gnostic texts deal not in concepts of sin and repentance, but with illusion and enlightenment. Gnostic writings flourished among certain Christian groups in the Mediterranean wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplatonism
Neoplatonism is a strand of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a chain of thinkers. But there are some ideas that are common to it. For example, the monistic idea that all of reality can be derived from a single principle, "the One". Neoplatonism began with Ammonius Saccas and his student Plotinus (c. 204/5 – 271 AD) and stretched to the 6th century AD. After Plotinus there were three distinct periods in the history of neoplatonism: the work of his student Porphyry (3rd to early 4th century); that of Iamblichus (3rd to 4th century); and the period in the 5th and 6th centuries, when the Academies in Alexandria and Athens flourished. Neoplatonism had an enduring influence on the subsequent history of philosophy. In the Middle Ages, neoplatonic ideas were studied and discussed by Christian, Jewish, and Muslim thinkers. In the Islamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophylact Of Ohrid
Theophylact ( gr, Θεοφύλακτος, bg, Теофилакт; around 1055after 1107) was a Byzantine archbishop of Ohrid and commentator on the Bible. Life Theophylact was born in the mid-11th century at Euripus (Chalcis) in Euboea, at the time part of the Byzantine Empire (now Greece). He became a deacon at Constantinople, attained a high reputation as a scholar, and became the tutor of Constantine Doukas , son of the Emperor Michael VII, for whom he wrote ''The Education of Princes''. In about 1078 he moved to the Province of Bulgaria where he became the archbishop of Achrida (modern Ohrid). Ohrid was one of the capital cities of Bulgaria that had been re-conquered by the Byzantines sixty years earlier. In this demanding position in a conquered territory on the outskirts of the Byzantine Empire, he conscientiously and energetically carried out his pastoral duties over the course of the next twenty years. Although a Byzantine by upbringing and outlook, he was a diligent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godhead In Christianity
Godhead (or '' godhood'') refers to the essence or substance (''ousia'') of the Christian God, especially as existing in three persons — God the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit. at dictionary.com. Retrieved 29 November 2022. Appearance in English Bibles introduced the term ''godhede'' into English versions in two places, and, though somewhat archaic, the term survives in modern English because of its use in three places of the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
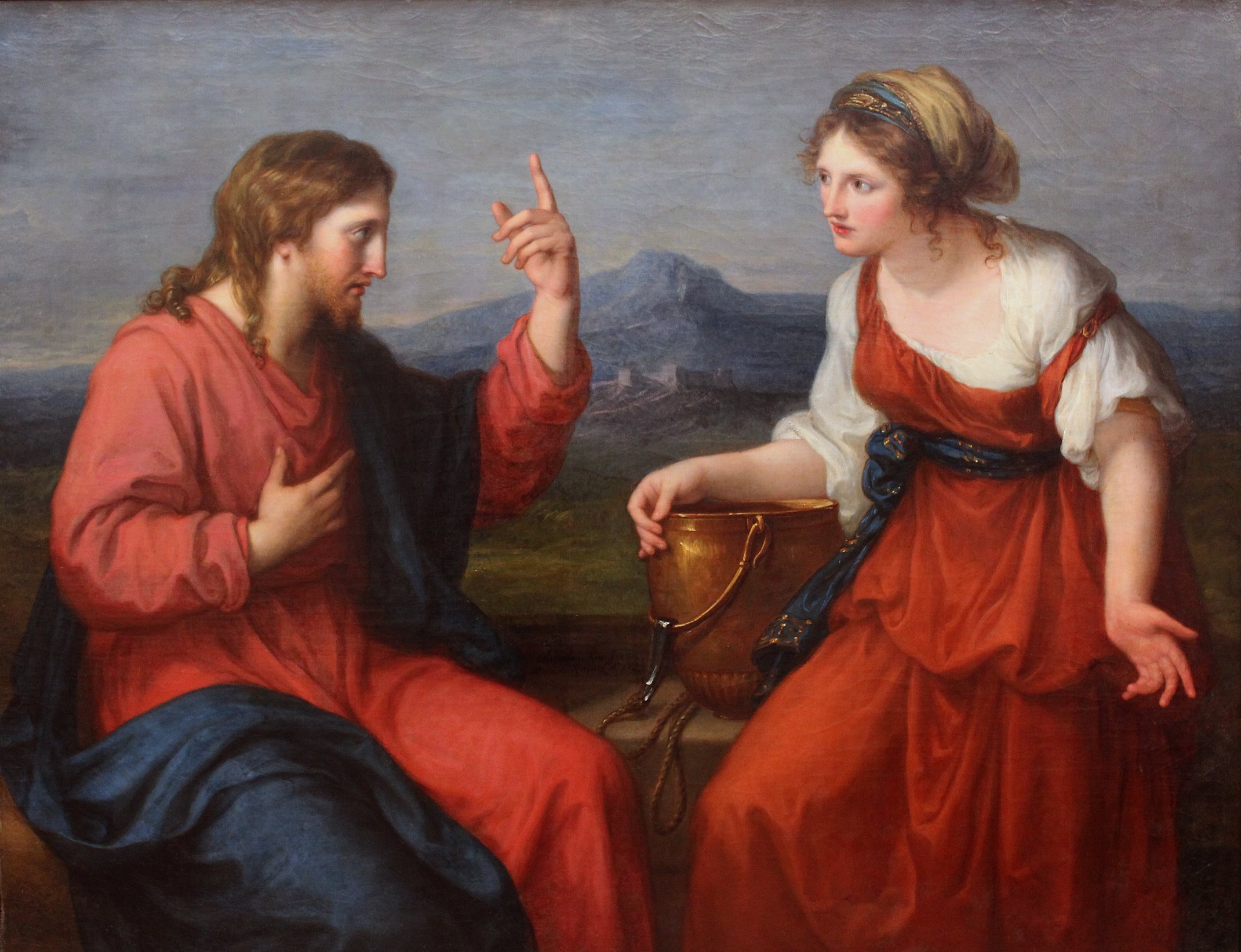
Samaritan Woman At The Well
The Samaritan woman at the well is a figure from the Gospel of John. John 4:4–42 relates her conversation with Jesus at Jacob's Well near the city of Sychar. Biblical account The woman appears in ; here is John 4:4–26: This episode takes place before the return of Jesus to Galilee. Some Jews regarded the Samaritans as foreigners and their attitude was often hostile, although they shared most beliefs, while many other Jews accepted Samaritans as either fellow Jews or as Samaritan Israelites. The two communities seem to have drifted apart in the post-exilic period. Both communities share the Pentateuch, although crucially the Samaritan Pentateuch locates the holy mountain at Mount Gerizim rather than at Mount Zion, as this incident acknowledges at John 4:20. The Gospel of John, like the Gospel of Luke, is favourable to the Samaritans throughout, and, while the Matthaean Gospel quotes Jesus at one early phase in his ministry telling his followers to not at that time evangeli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |