|
Plant Genetic Systems
Plant Genetic Systems (PGS), since 2002 part of Bayer CropScience, is a biotech company located in Ghent, Belgium. The focus of its activities is the genetic engineering of plants. The company is best known for its work in the development of insect-resistant transgenic plants. Its origin goes back to the work of Marc Van Montagu and Jeff Schell at the University of Ghent who were among the first to assemble a practical system for genetic engineering of plants. They developed a vector system for transferring foreign genes into the plant genome, by using the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. They also found a way to make plant cells resistant to the antibiotic kanamycin by transferring a bacterial neomycin phosphotransferase gene into the plant genome. PGS was the first company (in 1985) to develop genetically engineered (tobacco) plants with insect tolerance by expressing genes encoding for insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). History The company was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. Definition The concept of biotechnology encompasses a wide range of procedures for modifying living organisms according to human purposes, going back to domestication of animals, cultivation of the plants, and "improvements" to these through breeding programs that employ artificial selection and hybridization. Modern usage also includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. The American Chemical Society defines biotechnology as the application of biological organisms, systems, or processes by various industries to learning about the science of life and the improvement of the value of materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
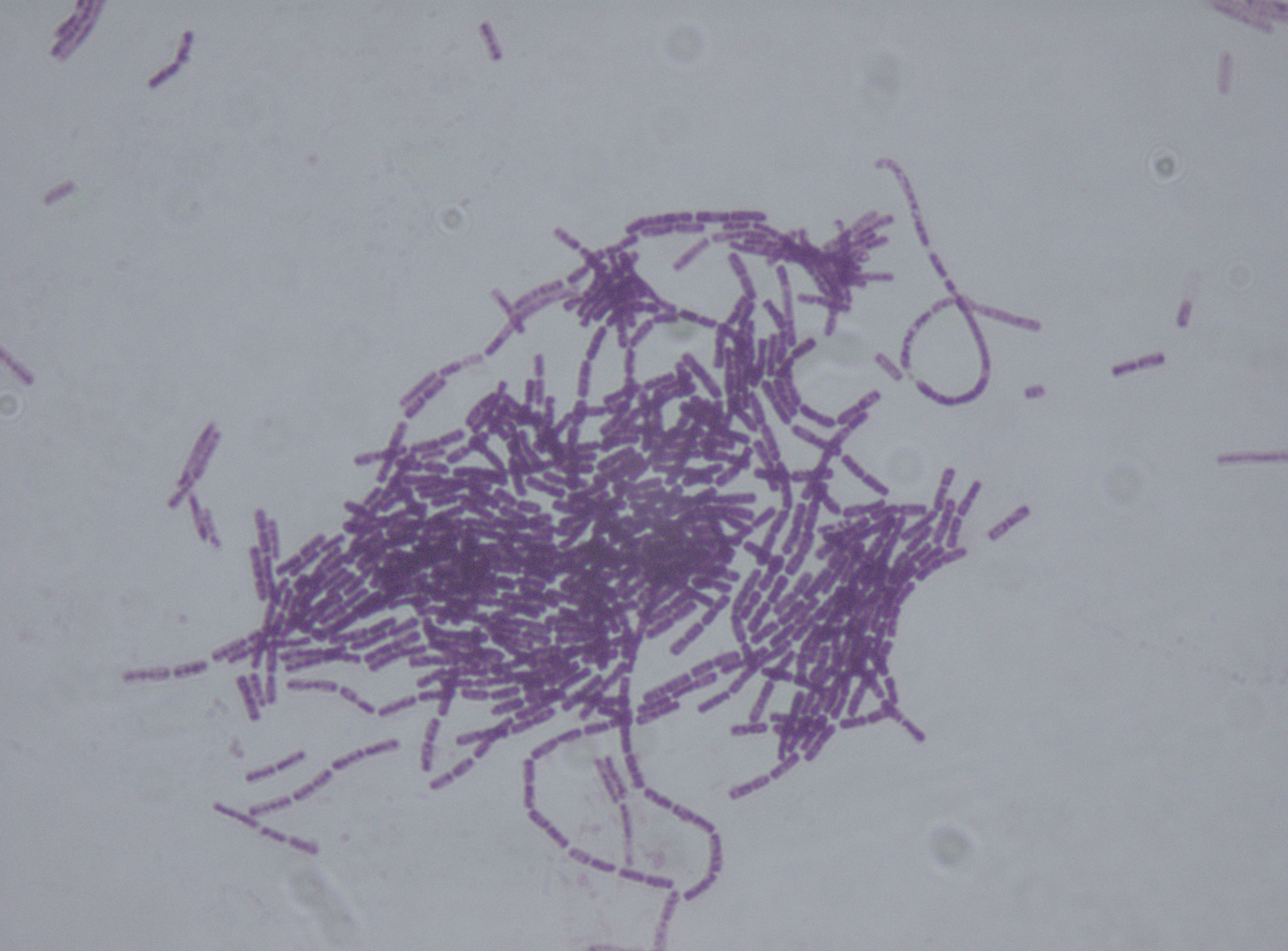
Neomycin
Neomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against gram-positive bacilli and anaerobic gram-negative bacilli. Neomycin comes in oral and topical formulations, including creams, ointments, and eyedrops. Neomycin belongs to the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics that contain two or more amino sugars connected by glycosidic bonds. Neomycin was discovered in 1949 by microbiologist Selman Waksman and his student Hubert Lechevalier at Rutgers University. Neomycin received approval for medical use in 1952. Rutgers University was granted the patent for neomycin in 1957. Discovery Neomycin was discovered in 1949 by the microbiologist Selman Waksman and his student Hubert Lechevalier at Rutgers University. It is produced naturally by the bacterium ''Streptomyces fradiae''. Synthesis requires specific nutrient conditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology Companies Established In 1982
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. Definition The concept of biotechnology encompasses a wide range of procedures for modifying living organisms according to human purposes, going back to domestication of animals, cultivation of the plants, and "improvements" to these through breeding programs that employ artificial selection and hybridization. Modern usage also includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. The American Chemical Society defines biotechnology as the application of biological organisms, systems, or processes by various industries to learning about the science of life and the improvement of the value of materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology Companies Of Belgium
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. Definition The concept of biotechnology encompasses a wide range of procedures for modifying living organisms according to human purposes, going back to domestication of animals, cultivation of the plants, and "improvements" to these through breeding programs that employ artificial selection and hybridization. Modern usage also includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. The American Chemical Society defines biotechnology as the application of biological organisms, systems, or processes by various industries to learning about the science of life and the improvement of the value of materials an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Engineering And Agriculture
Genetic may refer to: *Genetics, in biology, the science of genes, heredity, and the variation of organisms **Genetic, used as an adjective, refers to genes ***Genetic disorder, any disorder caused by a genetic mutation, whether inherited or de novo ***Genetic mutation In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ..., a change in a gene **** Heredity, genes and their mutations being passed from parents to offspring ** Genetic recombination, refers to the recombining of alleles resulting in a new molecule of DNA * Genetic relationship (linguistics), in linguistics, a relationship between two languages with a common ancestor language * Genetic algorithm, in computer science, a kind of search technique modeled on evolutionary biology See also * Genetic memory (other) {{d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Pest Control
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also involves an active human management role. It can be an important component of integrated pest management (IPM) programs. There are three basic strategies for biological pest control: classical (importation), where a natural enemy of a pest is introduced in the hope of achieving control; inductive (augmentation), in which a large population of natural enemies are administered for quick pest control; and inoculative (conservation), in which measures are taken to maintain natural enemies through regular reestablishment. Natural enemies of insect pests, also known as biological control agents, include predators, parasitoids, pathogens, and competitors. Biological control agents of plant diseases are most often referred to as antagonists. Biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marc Zabeau
Marc Zabeau (born Lier, 1949) is a Belgian scientist and businessman. Biography Marc Zabeau graduated in 1971 as a licentiate in zoology at the University of Ghent and obtained a PhD in 1974, studying the genetics of ''Escherichia coli'' in the lab of Jeff Schell. In 1976, on an NFWO scholarship as a Fulbright Hayes postdoctoral fellow, he went for two years to the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory in New York, the United States. From 1978 until 1983 he worked at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Heidelberg, Germany. during his stay in Heidelberg, he was appointed as professor of genetic engineering at the Vrije Universiteit Brussel. In 1983, he became director of research of Plant Genetic Systems in Ghent, Belgium and in 1986 director of intellectual property and business development. He founded several biotech companies, such as Helix C.V. (Ghent, 1988), KeyGene N.V. (Wageningen, 1989), GenScope Inc. (United States, 1995) and Methexis (Ghent, 1997). In 1999, he suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FlandersBio
flanders.bio, founded in 2004, is the networking organisation for the life sciences sector in Flanders and represents and supports around 350 member companies. The key strategic objectives of flanders.bio are knowledge exchange and valorisation, human capital development, internationalization of the cluster activities and visibility, familiarization of the public with products derived from the sector and the further development of a supportive environment for the members of flanders.bio. The flanders.bio network brings together companies with activities in the life sciences – companies that are for example developing biopharmaceuticals, medical technologies or agricultural or industrial biotech products. The network also welcomes research institutes, universities and providers of capital, services and technologies to the life sciences community. Since 2018, Willem Dhooge and Pascale Engelen are both co-General Managers at flanders.bio. They were preceded by Henk Joos, Ann De Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanders Interuniversity Institute Of Biotechnology
VIB is a research institute located in Flanders, Belgium. It was founded by the Flemish government in 1995, and became a full-fledged institute on 1 January 1996. The main objective of VIB is to strengthen the excellence of Flemish life sciences research and to turn the results into new economic growth. VIB spends almost 80% of its budget on research activities, while almost 12% is spent on technology transfer activities and stimulating the creation of new businesses, in addition VIB spends approximately 2% on socio-economic activities. VIB is member of EU-LIFE, an alliance of leading life sciences research centres in Europe. The institute is led by Christine Durinx and Jérôme Van Biervliet. Ajit Shetty is chairman of the board of directors. Goals VIB's mission is ''to conduct frontline biomolecular research in life sciences for the benefit of scientific progress and the benefit of society''. The strategic goals of the VIB are: # Strategic basic research # Technology transfer p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CropDesign
CropDesign is a biotech company located in Ghent, Belgium. The company develops a portfolio of agronomic traits for the global commercial seed markets. It has developed a technology platform to discover genetic traits for the improvement of corn, rice and other plants. Current Managing Director is Juergen Logemann. History CropDesign was founded in 1998 as a spin-off from the Flanders Institute of Biotechnology (VIB) and the Institute of Plant Biotechnology for Developing Countries of the University of Ghent. One of the founders of the company is Marc Van Montagu who is a Flemish pioneer in plant genetics. Another co-founder was Professor Dirk Inzé, specialist in plant cell cycle technologies. The company was financially backed until 2006 by a consortium of venture capital funds led by the GIMV. BASF Plant Science acquired the company in 2006. The company announced in May 2016 that they would cease operations by the end of the year. BASF stated at the time that they wished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhône-Poulenc
Rhône-Poulenc () was a French chemical and pharmaceutical company founded in 1928. In 1999 it merged with Hoechst AG to form Aventis. As of 2015, the pharmaceutical operations of Rhône-Poulenc are part of Sanofi and the chemicals divisions are part of Solvay group and Bayer Crop Science. History The company was founded in 1928 through the merger of Société des usines chimiques du Rhône (Society of Rhône Chemical Factories) from Lyon and Poulenc Frères (Poulenc Brothers) from Paris founded by Étienne Poulenc, a 19th-century Parisian apothecary and brought to prominence by his second and third sons Émile, father of composer Francis Poulenc, and Camille Poulenc (1864–1942). In 1950, the company synthesized chlorpromazine which it sold to Smith, Kline & French (today part of GlaxoSmithKline) who marketed the drug as Thorazine. In 1990, it merged with the pharmaceutical company Rorer to form Rhône-Poulenc Rorer. In January 1999, Rhône-Poulenc merged with Hoechst AG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as ''Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite. During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops using Bt genes, such as Bt corn. Many crystal-producing Bt strains, though, do not have insecticidal properties. The subspecies ''israelensis'' is commonly used for control o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |