|
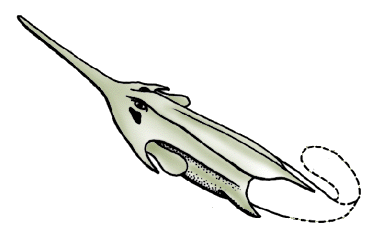
Pituriaspis
''Pituriaspis doylei'' is one of two known species of jawless fish belonging to the Class Pituriaspida, and is the better known of the two. The species lived in estuaries during the Givetian epoch of the Middle Devonian, 390 million years ago in what is now the Georgina Basin of Western Queensland, Australia. The paleontologist Gavin Young, named the fossil agnathan ''Pituriaspis doylei'' after the nicotine-containing drug pituri, as he thought he might be hallucinating upon viewing the fossil fish's bizarre form.Long, John A. ''The Rise of Fishes: 500 Million Years of Evolution''. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996. The first specimens of ''P. doylei'' were empty sandstone casts of the head shields, with none of the original bone remaining. ''P. doylei'' vaguely resembled the Osteostraci, though neither are considered to be close relatives. The headshield extends posteriorly to form a long abdominal division which probably reached the anal region. The dorsa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituriaspida
The Pituriaspida ('Pituri-shield' or 'hallucinogen-shield') are a small group of extinct armored jawless fishes with tremendous nose-like rostrums, which lived in the marine, deltaic environments of Middle Devonian Australia (about 390 Ma). They are known only by two species, '' Pituriaspis doylei'' and '' Neeyambaspis enigmatica'' found in a single sandstone location of the Georgina Basin, in Western Queensland, Australia. "Pituriaspida" is often translated as 'hallucinogenic shield.' Pituri is a hallucinogenic drug, made from the leaves of the Corkwood Tree and ''Acacia'' ash, and used by local Aborigine shamans for vision quests. The pituriaspids' discoverer, Dr Gavin Young, named '' Pituriaspis'' after the drug because, upon examining the first specimens, he suspected he was hallucinating (Long, p 59). The better studied species - '' Pituriaspis doylei'', which had a superficial resemblance to the Osteostraci, had an elongate headshield, that, coupled with its spear-lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Fish
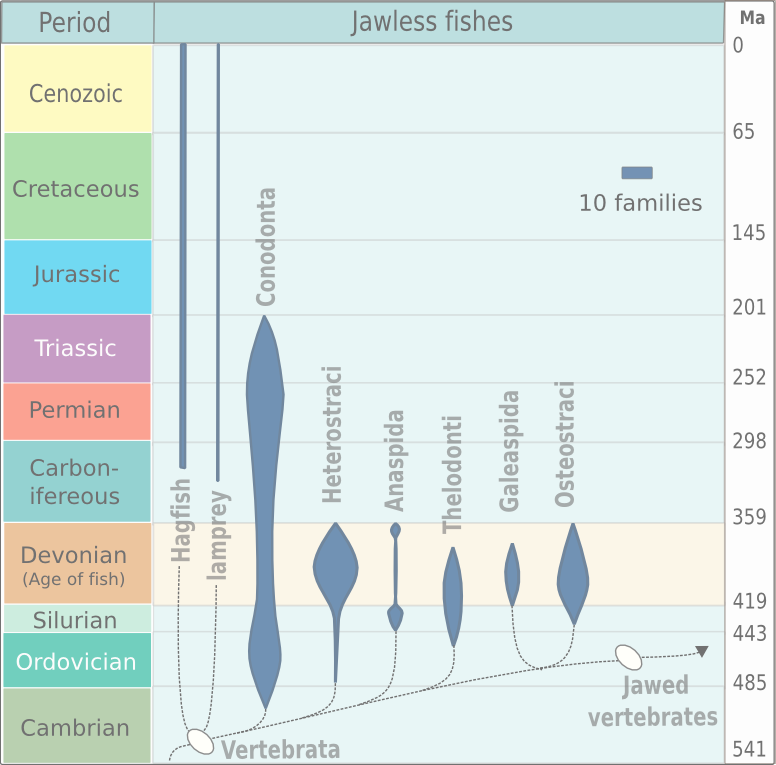
The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion. It was during this time that the early chordates developed the skull and the vertebral column, leading to the first craniates and vertebrates. The first fish lineages belong to the Agnatha, or jawless fish. Early examples include ''Haikouichthys''. During the late Cambrian, eel-like jawless fish called the conodonts, and small mostly armoured fish known as ostracoderms, first appeared. Most jawless fish are now extinct; but the extant lampreys may approximate ancient pre-jawed fish. Lampreys belong to the Cyclostomata, which includes the extant hagfish, and this group may have split early on from other agnathans. The earliest jawed vertebrates probably developed during the late Ordovician period. They are first represented in the fossil record from the Silurian by two groups of fish: the armoured fish known as placoderms, which evolved from the ostracoderms; and the Acanthodii (or spiny sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Givetian
The Givetian is one of two faunal stages in the Middle Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Eifelian Stage and followed by the Frasnian The Frasnian is one of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Givetian Stage and followed by the Famennian Stage. Major reef-building was under way during th ... Stage. It is named after the town of Givet in France. The oldest forests occurred during the late Givetian. The lower GSSP is located at Jebel Mech Irdane, Tafilalt, Morocco. Name and definition The Givetian Stage was proposed in 1879 by French geologist Jules Gosselet and was accepted for the higher stage of the Middle Devonian by the Subcommission on Devonian Stratigraphy in 1981. References Further reading * {{Geological history, p, p Middle Devonian Devonian geochronology . Devonian North America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnathostome
Gnathostomata (; from Greek: (') "jaw" + (') "mouth") are the jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all living vertebrates, including humans. In addition to opposing jaws, living gnathostomes have true teeth (a characteristic which has subsequently been lost in some), paired appendages (pectoral and pelvic fins, arms, legs, wings, etc.), the elastomeric protein of elastin, and a horizontal semicircular canal of the inner ear, along with physiological and cellular anatomical characters such as the myelin sheaths of neurons, and an adaptive immune system that has the discrete lymphoid organs of spleen and thymus, and uses V(D)J recombination to create antigen recognition sites, rather than using genetic recombination in the variable lymphocyte receptor gene. It is now assumed that Gnathostomata evolved from ancestors that already possessed a pair of both pectoral and pelvic fins. Until recently these ancestors, know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
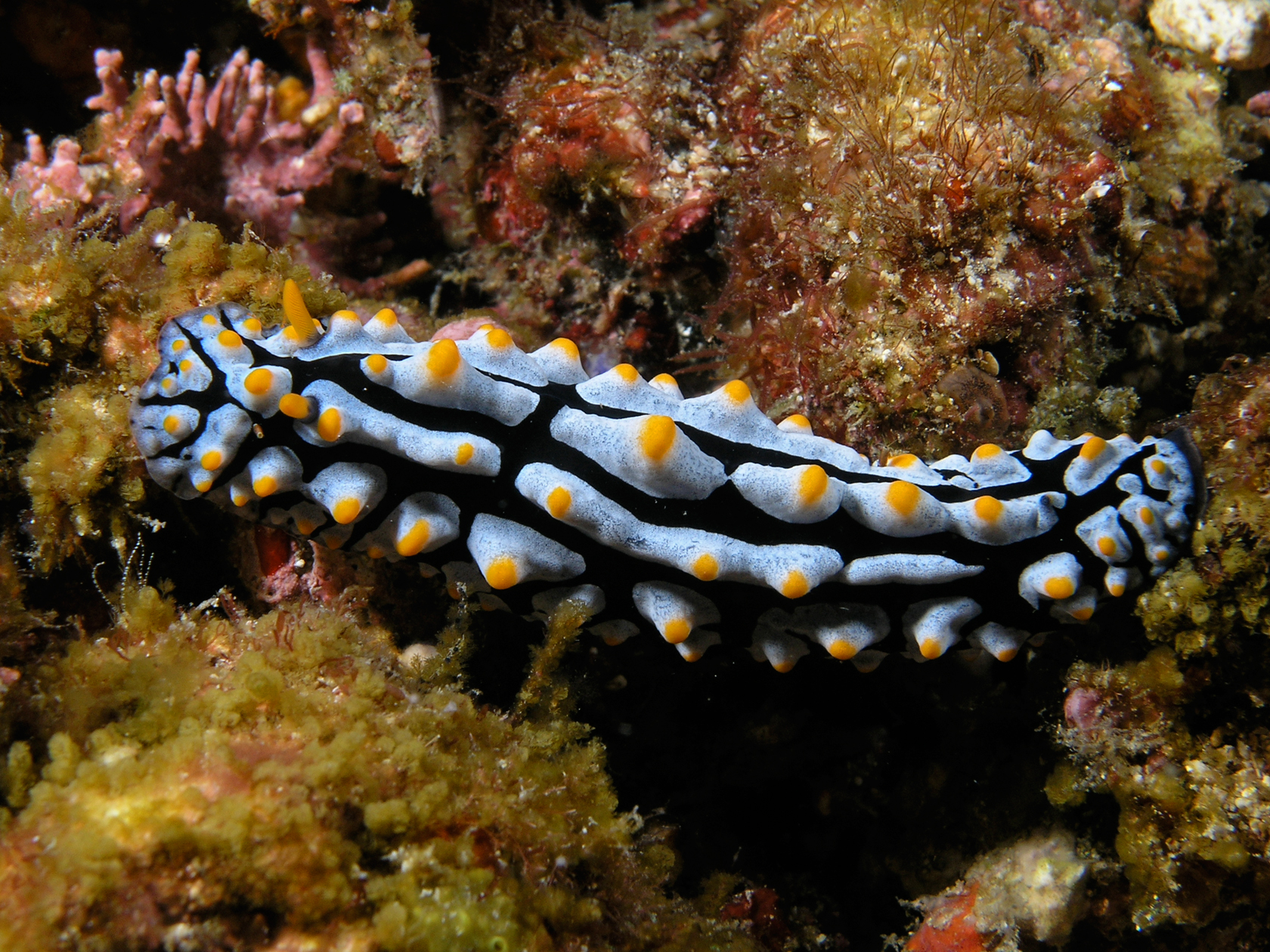
Tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal. In plants A tubercle is generally a wart-like projection, but it has slightly different meaning depending on which family of plants or animals it is used to refer to. In the case of certain orchids and cacti, it denotes a round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on the lip. They are also known as podaria (singular ''podarium''). When referring to some members of the pea family, it is used to refer to the wart-like excrescences that are found on the roots. In fungi In mycology, a tubercle is used to refer to a mass of hyphae from which a mushroom is made. In animals When it is used in relation to certain dorid nudibranchs such as '' Peltodoris nobilis'', it means the nodules on the dorsum of the animal. The tubercles in nudibranchs can present themselves in different w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as " shells". Examples of exoskeletons within animals include the arthropod exoskeleton shared by chelicerates, myriapods, crustaceans, and insects, as well as the shell of certain sponges and the mollusc shell shared by snails, clams, tusk shells, chitons and nautilus. Some animals, such as the turtle, have both an endoskeleton and an exoskeleton. Role Exoskeletons contain rigid and resistant components that fulfill a set of functional roles in many animals including protection, excretion, sensing, support, feeding and acting as a barrier against desiccation in terrestrial organisms. Exoskeletons have a role in defense from pests and predators, support and in providing an attachment fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
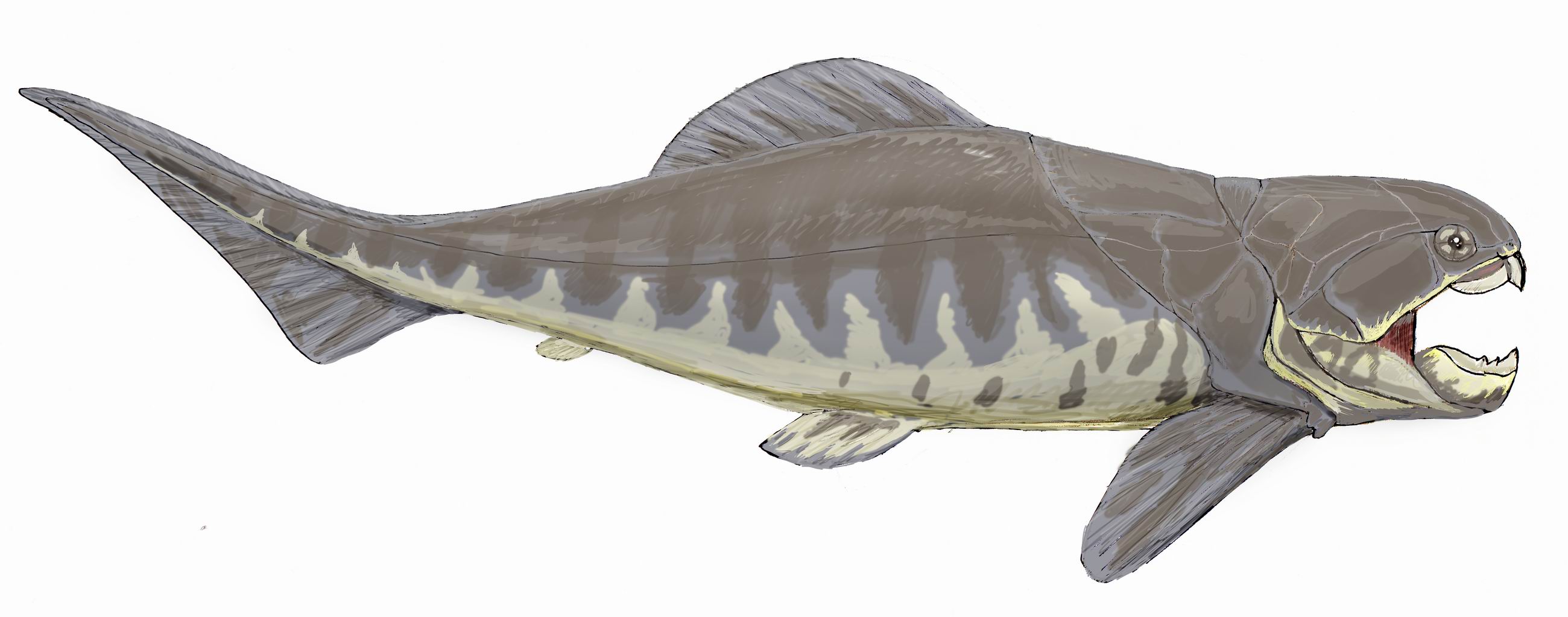
Cephalaspis
''Cephalaspis'' (from el, κεφαλή , 'head' and el, ἀσπίς , 'shield') is a possibly monotypic genus of extinct osteostracan agnathan vertebrate. It was a trout-sized detritivorous fish that lived in the early Devonian. Description Like its relatives, ''Cephalaspis'' was heavily armored, presumedly to defend against predatory placoderms and eurypterids, as well as to serve as a source of calcium for metabolic functions in calcium-poor freshwater environments. It had sensory patches along the rim and center of its head shield, which were used to sense for worms and other burrowing organisms in the mud. Diet Because its mouth was situated directly beneath its head, ''Cephalaspis'' was thought of as being a bottom-feeder, akin to a heavily armoured catfish or sturgeon. It moved its plow-like head from side to side, ''Cephalaspis'' easily stirring sand and dust into the water, along with revealing the hiding places of its prey, digging up worms or crustaceans hidden in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineal
The pineal gland, conarium, or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycles. The shape of the gland resembles a pine cone, which gives it its name. The pineal gland is located in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus join. The pineal gland is one of the neuroendocrine secretory circumventricular organs in which capillaries are mostly permeable to solutes in the blood. Nearly all vertebrate species possess a pineal gland. The most important exception is a primitive vertebrate, the hagfish. Even in the hagfish, however, there may be a "pineal equivalent" structure in the dorsal diencephalon. The lancelet ''Branchiostoma lanceolatum'', an early chordate which is a close relative to vertebrates, also lacks a recogniza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteostraci
The class Osteostraci (meaning "bony shells") is an extinct taxon of bony-armored jawless fish, termed "ostracoderms", that lived in what is now North America, Europe and Russia from the Middle Silurian to Late Devonian. Anatomically speaking, the osteostracans, especially the Devonian species, were among the most advanced of all known agnathans. This is due to the development of paired fins, and their complicated cranial anatomy. The osteostracans were more similar to lampreys than to jawed vertebrates in possessing two pairs of semicircular canals in the inner ear, as opposed to the three pairs found in the inner ears of jawed vertebrates. They are thought to be the sister-group to pituriaspids, and together, these two taxa of jawless vertebrates are the sister-group of gnathostomes. Several synapomorphies support this hypothesis, such as the presence of: sclerotic ossicles, paired pectoral fins, a dermal skeleton with three layers (a basal layer of isopedin, a middle layer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituri
Pituri, also known as mingkulpa, is a mixture of leaves and wood ash traditionally chewed as a stimulant (or, after extended use, a depressant) by Aboriginal Australians widely across the continent. Leaves are gathered from any of several species of native tobacco (''Nicotiana'') or from at least one distinct population of the species '' Duboisia hopwoodii''. Various species of ''Acacia'', '' Grevillea'' and ''Eucalyptus'' are burned to produce the ash. The term "pituri" may also refer to the plants from which the leaves are gathered or from which the ash is made. Some authors use the term to refer only to the plant ''Duboisia hopwoodii'' and its leaves and any chewing mixture containing its leaves.Silcock JL, Tischler M, Smith MA"Quantifying the Mulligan River Pituri, ''Duboisia hopwoodii'' ((F.Muell.) F.Muell.) (Solanaceae), Trade of Central Australia."''Ethnobotany Research & Applications''. 2012; 10:037-044. Retrieved 30 April 2015. History The earliest record of Aboriginal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jawless Fish
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present ( cyclostomes) and extinct (conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostomes. Recent molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that living agnathans, the cyclostomes, are monophyletic. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian, and two groups still survive today: the lampreys and the hagfish, comprising about 120 species in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebrae; before this event was inferred from molecular and developmental data, the group Craniata was created by Linnaeus (and is still sometimes used as a strictly morphological descriptor) to reference hagfish plus vertebrates. While a few s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, (gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |