|
Phosphodiesterase
A phosphodiesterase (PDE) is an enzyme that breaks a phosphodiester bond. Usually, ''phosphodiesterase'' refers to cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, which have great clinical significance and are described below. However, there are many other families of phosphodiesterases, including phospholipases C and D, autotaxin, sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, DNases, RNases, and restriction endonucleases (which all break the phosphodiester backbone of DNA or RNA), as well as numerous less-well-characterized small-molecule phosphodiesterases. The cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases comprise a group of enzymes that degrade the phosphodiester bond in the second messenger molecules cAMP and cGMP. They regulate the localization, duration, and amplitude of cyclic nucleotide signaling within subcellular domains. PDEs are therefore important regulators of signal transduction mediated by these second messenger molecules. History These multiple forms (isoforms or subtypes) of ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Weiss (scientist)
Benjamin Weiss (January 26, 1937) is an American neuropharmacologist, Emeritus Professor of Pharmacology and Physiology at Drexel University College of Medicine. He is best known for his work with cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. He was the first to propose, based on his experimental work, that selective inhibition of phosphodiesterases which are expressed differentially in all tissues, could be used as a target for drug development. His work is the basis for many marketed and developmental human drugs that selectively inhibit cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. His investigations on the modulation of adrenergic responses in the pineal gland have resulted in the formation of new concepts that may explain the phenomena of drug tolerance and drug hypersensitivity. He and his laboratory were also instrumental in the development of antisense oligonucleotides and antisense RNA as pharmacological tools to study calmodulin and dopamine receptors, and as pharmacological age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Weiss (scientist)
Benjamin Weiss (January 26, 1937) is an American neuropharmacologist, Emeritus Professor of Pharmacology and Physiology at Drexel University College of Medicine. He is best known for his work with cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. He was the first to propose, based on his experimental work, that selective inhibition of phosphodiesterases which are expressed differentially in all tissues, could be used as a target for drug development. His work is the basis for many marketed and developmental human drugs that selectively inhibit cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. His investigations on the modulation of adrenergic responses in the pineal gland have resulted in the formation of new concepts that may explain the phenomena of drug tolerance and drug hypersensitivity. He and his laboratory were also instrumental in the development of antisense oligonucleotides and antisense RNA as pharmacological tools to study calmodulin and dopamine receptors, and as pharmacological age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor
A phosphodiesterase inhibitor is a drug that blocks one or more of the five subtypes of the enzyme phosphodiesterase (PDE), thereby preventing the inactivation of the intracellular second messengers, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) by the respective PDE subtype(s). The ubiquitous presence of this enzyme means that non-specific inhibitors have a wide range of actions, the actions in the heart, and lungs being some of the first to find a therapeutic use. History The different forms or subtypes of phosphodiesterase were initially isolated from rat brains in the early 1970s and were soon afterward shown to be selectively inhibited in the brain and in other tissues by a variety of drugs. The potential for selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors as therapeutic agents was predicted as early as 1977 by Weiss and Hait. This prediction meanwhile has proved to be true in a variety of fields. Classification Nonselective PDE inhibitors Methy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase
3′,5′-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterases (EC 3.1.4.17) are a family of phosphodiesterases. Generally, these enzymes hydrolyze a nucleoside 3′,5′-cyclic phosphate to a nucleoside 5′-phosphate: :nucleoside 3′,5′-cyclic phosphate + H2O = nucleoside 5′-phosphate They thus control the cellular levels of the cyclic second messengers and the rates of their degradation. Some examples of nucleoside 3′,5′-cyclic phosphate include: * 3′,5′-cyclic AMP *3′,5′-cyclic dAMP *3′,5′-cyclic IMP * 3′,5′-cyclic GMP *3′,5′-cyclic CMP There are 11 distinct phosphodiesterase families (PDE1–PDE11) with a variety in isoforms and splicing having unique three-dimensional structure, kinetic properties, modes of regulation, intracellular localization, cellular expression, and inhibitor sensitivities. Nomenclature The systematic name for this enzyme is 3′,5′-cyclic-nucleotide 5'-nucleotidohydrolase. Other names in use include cyclic 3′,5′-mononucleoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDE1
Phosphodiesterase 1, PDE1, EC 3.1.4.1, systematic name oligonucleotide 5′-nucleotidohydrolase) is a phosphodiesterase enzyme also known as calcium- and calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase. It is one of the 11 families of phosphodiesterase (PDE1-PDE11). Phosphodiesterase 1 has three subtypes, PDE1A, PDE1B and PDE1C which divide further into various isoforms. The various isoforms exhibit different affinities for Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP and cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cGMP. Discovery The existence of the Ca2+-stimulated Phosphodiesterase 1 was first demonstrated by Cheung (1970), Kakiuchi and Yamazaki (1970) as a result of their research on bovine brain and rat brain respectively. It has since been found to be widely distributed in various mammalian Biological tissue, tissues as well as in other eukaryotes. It is now one of the most intensively studied member of the Phosphodiesterase, PDE superfamily of enzymes, which today represents 11 gene families, and the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
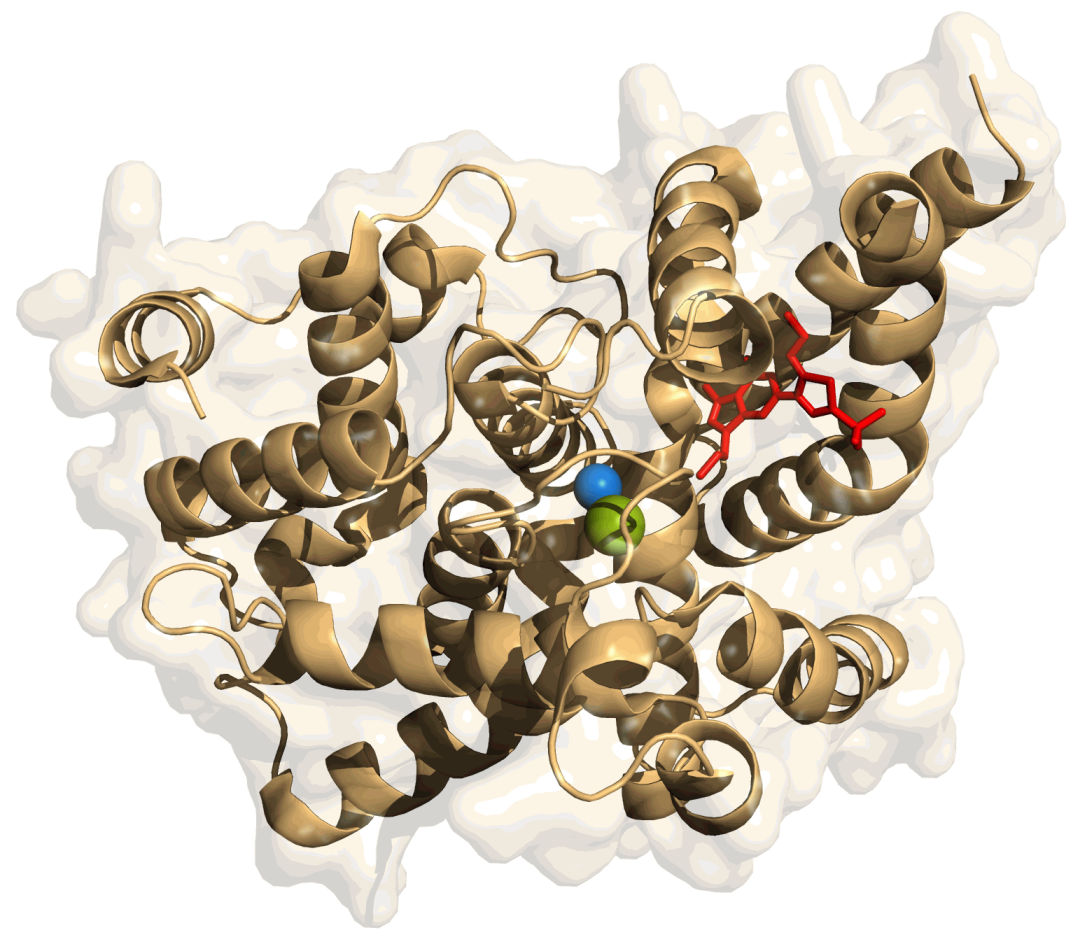
Sildenafil
Sildenafil, sold under the brand name Viagra, among others, is a medication used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary arterial hypertension. It is unclear if it is effective for treating sexual dysfunction in women. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. Onset is typically within twenty minutes and lasts for about two hours. Common side effects include headaches, heartburn, and flushed skin. Caution is advised in those with cardiovascular disease. Rare but serious side effects include a prolonged erection (priapism) that can lead to damage to the penis, vision problems, and hearing loss. Sildenafil should not be taken by people on nitrates such as nitroglycerin (glycerin trinitrate), as this may result in a serious drop in blood pressure. Sildenafil should not be taken within four hours of taking an alpha blocker. Sildenafil acts by blocking phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5), an enzyme that promotes breakdown of cGMP, which regulates blood flow in the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autotaxin
Autotaxin, also known as ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 2 (E-NPP 2), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ENPP2'' gene. Function Autotaxin (ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 2 (NPP2 or ENPP2) is a secreted enzyme important for generating the lipid signaling molecule lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Autotaxin has lyso phospholipase D activity that converts lysophosphatidylcholine into LPA. Autotaxin was originally identified as a tumor cell-motility-stimulating factor; later it was shown to be LPA (which signals through lysophospholipid receptors), the lipid product of the reaction catalyzed by autotaxin, which is responsible for its effects on cell-proliferation. The protein encoded by this gene functions as a phosphodiesterase. Autotaxin is secreted and further processed to make the biologically active form. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified. Autotaxin is able to cleave the phosphodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDE5 Inhibitor
A phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor (PDE5 inhibitor) is a vasodilating drug that works by blocking the degradative action of cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) on cyclic GMP in the smooth muscle cells lining the blood vessels supplying various tissues. These drugs dilate the corpora cavernosa of the penis, facilitating erection with sexual stimulation, and are used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). Sildenafil was the first effective oral treatment available for ED. Because PDE5 is also present in the smooth muscle of the walls of the arterioles within the lungs, two PDE5 inhibitors, sildenafil and tadalafil, are FDA-approved for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. As of 2019, the wider cardiovascular benefits of PDE5 inhibitors are being appreciated. Medical uses Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) are clinically indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Sil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDE4 Inhibitor
A phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, commonly referred to as a PDE4 inhibitor, is a drug used to block the degradative action of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). It is a member of the larger family of PDE inhibitors. The PDE4 family of enzymes are the most prevalent PDE in immune cells. They are predominantly responsible for hydrolyzing cAMP within both immune cells and cells in the central nervous system. Therapeutic utility The prototypical PDE4 inhibitor is rolipram. PDE4 inhibitors are known to possess procognitive (including long term memory-improving), wakefulness-promoting, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory effects. Consequently, PDE4 inhibitors have been investigated as treatments for a diverse group of different diseases, including central nervous system disorders such as major depressive disorder (clinical depression), anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, attention deficit- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDE3
PDE3 is a phosphodiesterase. The PDEs belong to at least eleven related gene families, which are different in their primary structure, substrate affinity, responses to effectors, and regulation mechanism. Most of the PDE families are composed of more than one gene. PDE3 is clinically significant because of its role in regulating heart muscle, vascular smooth muscle and platelet aggregation. PDE3 inhibitors have been developed as pharmaceuticals, but their use is limited by arrhythmic effects and they can increase mortality in some applications. Function PDE3 enzymes are involved in regulation of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle contractility. Molecules that inhibit PDE3 were originally investigated for the treatment of heart failure, but, because of unwanted arrhythmic side-effects, they are not studied for that indication any longer. Nonetheless, the PDE3 inhibitor milrinone is approved for use in heart failure in intravenous form. Both PDE3A and PDE3B are expressed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
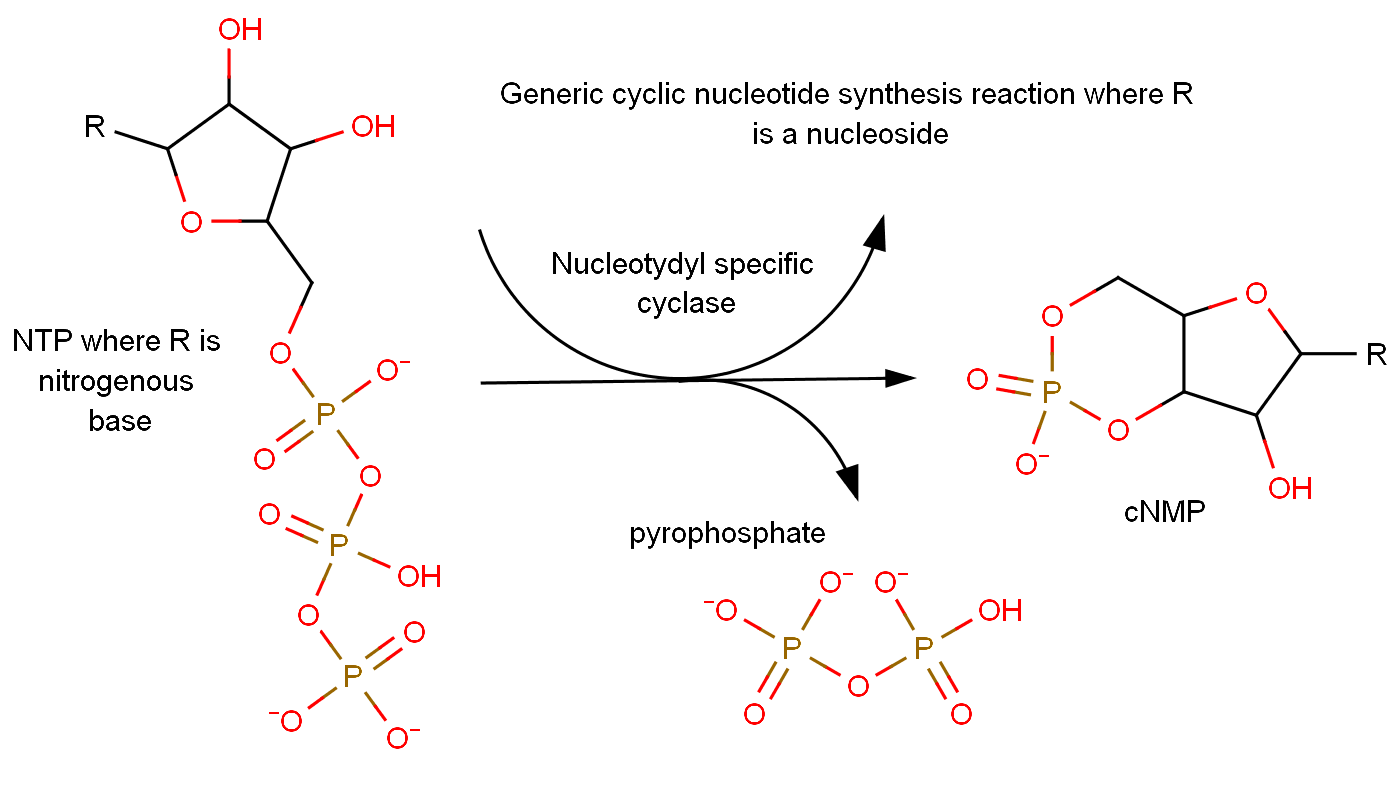
Cyclic Nucleotide
A cyclic nucleotide (cNMP) is a single-phosphate nucleotide with a cyclic bond arrangement between the sugar and phosphate groups. Like other nucleotides, cyclic nucleotides are composed of three functional groups: a sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a single phosphate group. As can be seen in the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) images, the 'cyclic' portion consists of two bonds between the phosphate group and the 3' and 5' hydroxyl groups of the sugar, very often a ribose. Their biological significance includes a broad range of protein-ligand interactions. They have been identified as secondary messengers in both hormone and ion-channel signalling in eukaryotic cells, as well as allosteric effector compounds of DNA binding proteins in prokaryotic cells. cAMP and cGMP are currently the most well documented cyclic nucleotides, however there is evidence that cCMP (cytosine) is also involved in eukaryotic cellular messaging. The ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphodiester Bond
In chemistry, a phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups () in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form two ester bonds. The "bond" involves this linkage . Discussion of phosphodiesters is dominated by their prevalence in DNA and RNA, but phosphodiesters occur in other biomolecules, e.g. acyl carrier proteins. Phosphodiester bonds make up the backbones of DNA and RNA. The phosphate is attached to the 5' carbon. The 3' carbon of one sugar is bonded to the 5' phosphate of the adjacent sugar. Specifically, the phosphodiester bond links the 3' carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the 5' carbon atom of another (hence the name, 3', 5' phosphodiester linkage). These saccharide groups are derived from deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. Phosphodiesters are negatively charged at pH 7. Repulsion between these negative charges influences the conformation of the polynucleic acids. The negative charge attracts histones, metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |