|
Perineal Artery
The perineal artery (superficial perineal artery) arises from the internal pudendal artery, and turns upward, crossing either over or under the superficial transverse perineal muscle, and runs forward, parallel to the pubic arch, in the interspace between the bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles, both of which it supplies, and finally divides into several posterior scrotal branches which are distributed to the skin and dartos tunic of the scrotum. As it crosses the superficial transverse perineal muscle it gives off the ''transverse perineal artery'' which runs transversely on the cutaneous surface of the muscle, and anastomoses with the corresponding vessel of the opposite side and with the perineal and inferior hemorrhoidal arteries. It supplies the Transversus perinæi superficialis and the structures between the anus The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Pudendal Artery
The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia. Structure The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It is smaller in the female than in the male. Path It arises from the anterior division of internal iliac artery. It runs on the lateral pelvic wall. It exits the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen, inferior to the piriformis muscle, to enter the gluteal region. It then curves around the sacrospinous ligament to enter the perineum through the lesser sciatic foramen. It travels through the pudendal canal with the internal pudendal veins and the pudendal nerve. Branches The internal pudendal artery gives off the following branches: The deep artery of clitoris is a branch of the internal pudendal artery and supplies the clitoral crura. Another branch of the internal pudendal artery is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Perineal Artery
The perineal artery (superficial perineal artery) arises from the internal pudendal artery, and turns upward, crossing either over or under the superficial transverse perineal muscle, and runs forward, parallel to the pubic arch, in the interspace between the bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles, both of which it supplies, and finally divides into several posterior scrotal branches which are distributed to the skin and dartos tunic of the scrotum. As it crosses the superficial transverse perineal muscle it gives off the ''transverse perineal artery'' which runs transversely on the cutaneous surface of the muscle, and anastomoses with the corresponding vessel of the opposite side and with the perineal and inferior hemorrhoidal arteries. It supplies the Transversus perinæi superficialis and the structures between the anus The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Scrotal Arteries
The posterior scrotal arteries are branches of the internal pudendal artery. Function The anterior scrotal arteries supply part of the scrotum The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum co ... in men. See also * Anterior scrotal arteries References Arteries of the abdomen Scrotum {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineal Vein
Perineal may refer to: * The perineum, the region of the body between the pubic arch and the tail bone * Perineal artery, an artery supplying the perineal region * Perineal nerve, a nerve innervating the perineal region See also *Peroneal (other) *Peritoneal The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mes ... * Perennial (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulbospongiosus Muscle
The bulbospongiosus muscle (bulbocavernosus in older texts) is one of the superficial muscles of the perineum. It has a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. In males, it covers the bulb of the penis. In females, it covers the vestibular bulb. In both sexes, it is innervated by the deep or muscular branch of the perineal nerve, which is a branch of the pudendal nerve. Structure In males, the bulbospongiosus is located in the middle line of the perineum, in front of the anus. It consists of two symmetrical parts, united along the median line by a tendinous perineal raphe. It arises from the central tendinous point of the perineum and from the median perineal raphe in front. In females, there is no union, nor a tendinous perineal raphe; the parts are disjoint primarily and arise from the same central tendinous point of the perineum, which is the tendon that is formed at the point where the bulbospongiosus muscle, superficial transverse peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischiocavernosus Muscle
The ischiocavernosus muscle (erectores penis ''or'' erector clitoridis in older texts) is a muscle just below the surface of the perineum, present in both men and women. Structure It arises by tendinous and fleshy fibers from the inner surface of the tuberosity of the ischium, behind the crus penis; and from the inferior pubic rami and ischium on either side of the crus. From these points fleshy fibers succeed, and end in an aponeurosis which is inserted into the sides and under surface of the crus penis. Function In females, the ischiocavernosus muscle assists with clitoral erection. In males, it helps to stabilize the erect penis An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, a ... by compressing the crus penis and retarding the return of blood through the veins. Additional im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartos Tunic
The dartos fascia or simply dartos is a layer of connective tissue found in the penile shaft, foreskin, scrotum and labia. The penile portion is referred to as the superficial fascia of penis or the subcutaneous tissue of penis, while the scrotal part is the dartos proper. In addition to being continuous with itself between the scrotum and the penis, it is also continuous with Colles fascia of the perineum and Scarpa's fascia of the abdomen. The dartos lies just below the skin, which places it just superficial to the external spermatic fascia in the scrotum and to Buck's fascia in the penile shaft. In the scrotum, it consists mostly of smooth muscle. The tone of this smooth muscle is responsible for the wrinkled (rugose) appearance of the scrotum. In females, the same muscle fibers are less well developed and termed ''dartos muliebris,'' lying beneath the skin of the labia majora. The dartos fascia receives innervation from postganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers arriving via t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
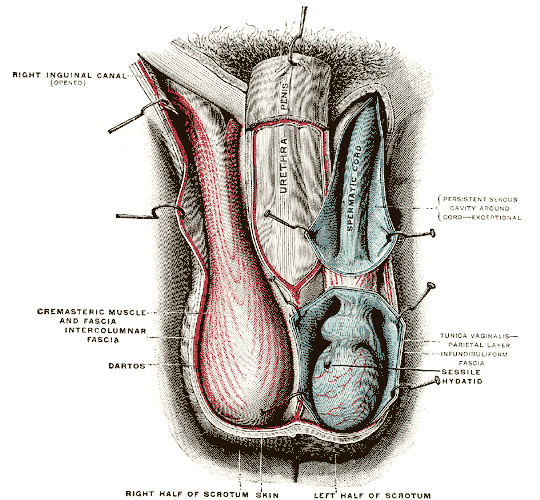
Scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. In humans and some other mammals the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of an impact. The scrotum is biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Pudendal Artery
The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia. Structure The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It is smaller in the female than in the male. Path It arises from the anterior division of internal iliac artery. It runs on the lateral pelvic wall. It exits the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen, inferior to the piriformis muscle, to enter the gluteal region. It then curves around the sacrospinous ligament to enter the perineum through the lesser sciatic foramen. It travels through the pudendal canal with the internal pudendal veins and the pudendal nerve. Branches The internal pudendal artery gives off the following branches: The deep artery of clitoris is a branch of the internal pudendal artery and supplies the clitoral crura. Another branch of the internal pudendal artery is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Transverse Perineal Muscle
The transverse perineal muscles (transversus perinei) are the superficial and the deep transverse perineal muscles. Superficial transverse perineal The superficial transverse perineal muscle (transversus superficialis perinei or Lloyd-Beanie muscle) is a narrow muscular slip, which passes more or less transversely across the perineal space in front of the anus. It arises by tendinous fibers from the inner and forepart of the ischial tuberosity and, running medially, is inserted into the central tendinous point of the perineum (perineal body), joining in this situation with the muscle of the opposite side, with the external anal sphincter muscle behind, and with the bulbospongiosus muscle in front. In some cases, the fibers of the deeper layer of the external anal sphincter cross over in front of the anus and are continued into this mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubic Arch
The pubic arch, also referred to as the ''ischiopubic arch'', is part of the pelvis. It is formed by the convergence of the inferior rami of the ischium and pubis on either side, below the pubic symphysis. The angle at which they converge is known as the subpubic angle. Function The pubic arch is one of three notches (the one in front) that separate the eminences of the lower circumference of the true pelvis. Clinical significance Subpubic angle The subpubic angle (or pubic angle) is the angle in the human body as the apex of the pubic arch, formed by the convergence of the inferior rami of the ischium and pubis on either side. The subpubic angle is important in forensic anthropology, in determining the sex of someone from skeletal remains. A subpubic angle of 50-82 degrees indicates a male; an angle of 90 degrees indicates a female.Anthony J. Bertino. Forensic Science - Fundamentals and Investigations. South-Western Cengage Learning, 2000. . Page 368 Other sources operate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Scrotal Arteries
The posterior scrotal arteries are branches of the internal pudendal artery. Function The anterior scrotal arteries supply part of the scrotum The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum co ... in men. See also * Anterior scrotal arteries References Arteries of the abdomen Scrotum {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |