|
Pelvic Outlet
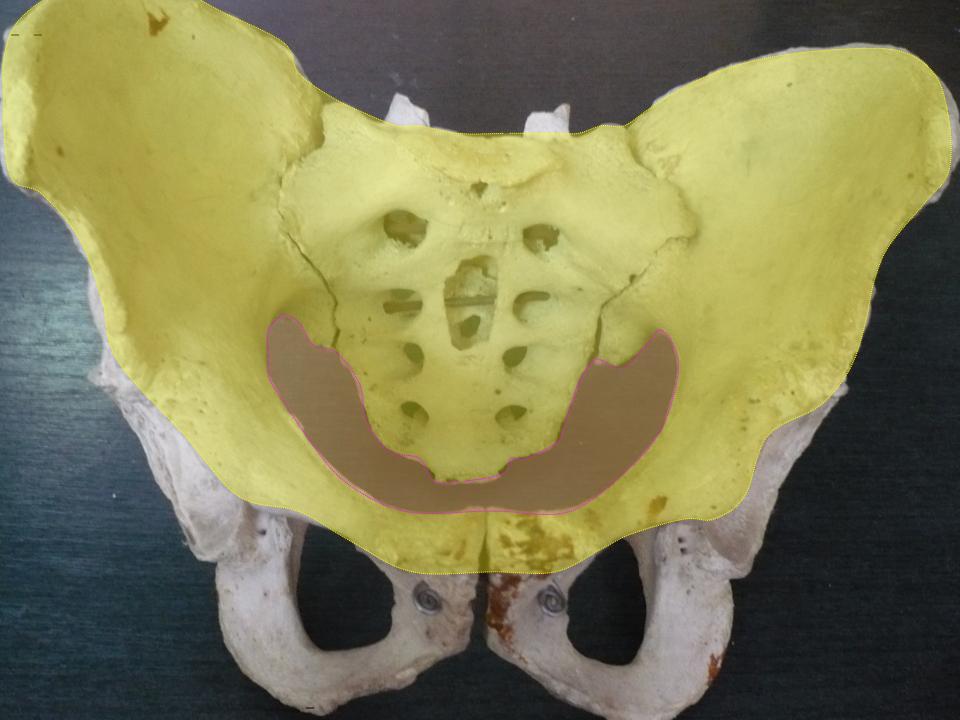
The lower circumference of the lesser pelvis is very irregular; the space enclosed by it is named the inferior aperture or pelvic outlet. It is an important component of pelvimetry. Boundaries It has the following boundaries: * anteriorly: the pubic arch * laterally: the ischial tuberosities * posterolaterally: the inferior margin of the sacrotuberous ligament * posteriorly: the anterior border of the middle of the coccyx. Notches These eminences are separated by three notches: * one in front, the pubic arch, formed by the convergence of the inferior rami of the ischium and pubis on either side. * The other notches, one on either side, are formed by the sacrum and coccyx behind, the ischium in front, and the ilium above; they are called the sciatic notches; in the natural state they are converted into foramina by the sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. In situ When the ligaments are in situ, the inferior aperture of the pelvis is lozenge-shaped, bounded as follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Pelvis
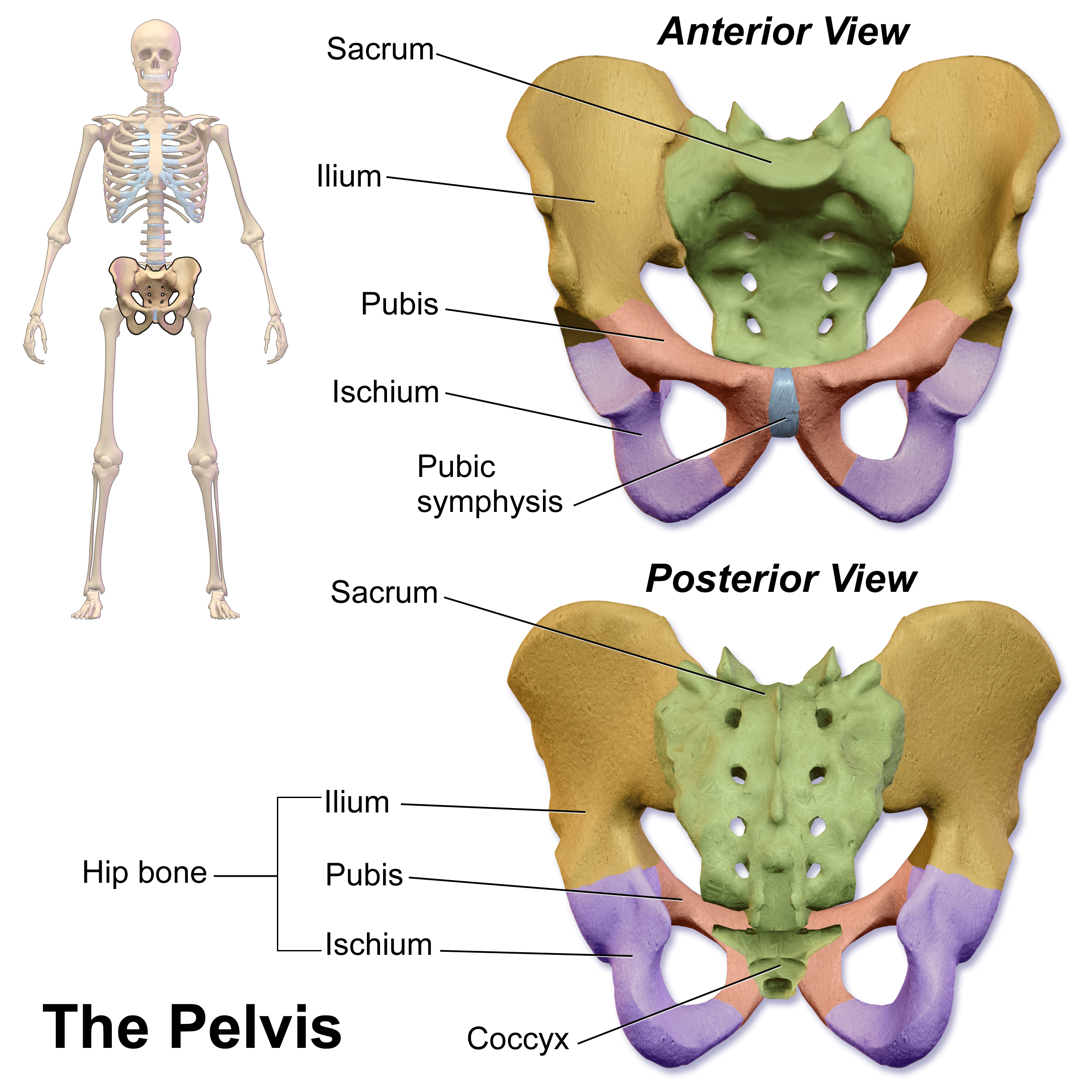
The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet (the superior opening of the pelvis). Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor. The pelvic cavity primarily contains the reproductive organs, urinary bladder, distal ureters, proximal urethra, terminal sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal. In females, the uterus, Fallopian tubes, ovaries and upper vagina occupy the area between the other viscera. The rectum is located at the back of the pelvis, in the curve of the sacrum and coccyx; the bladder is in front, behind the pubic symphysis. The pelvic cavity also contains major arteries, veins, muscles, and nerves. These structures coexist in a crowded space, and disorders of one pelvic component may impact upon another; for example, constipation may overload the rectum and compress the urinary bladder, or childbirth might damage the pudendal nerves and later lead to anal weakness. Structure The pelvis ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. plural foramina, or foramens ) is an open hole that is present in extant or extinct s. Foramina inside the body of typically allow nerves, |
Pelvic Inlet
The pelvic inlet or superior aperture of the pelvis is a planar surface which defines the boundary between the pelvic cavity and the abdominal cavity (or, according to some authors, between two parts of the pelvic cavity, called lesser pelvis and greater pelvis). It is a major target of measurements of pelvimetry. Its position and orientation relative to the skeleton of the pelvis is anatomically defined by its edge, the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim is an approximately apple-shaped line passing through the prominence of the sacrum, the arcuate and pectineal lines, and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis. Occasionally, the terms pelvic inlet and pelvic brim are used interchangeably. Boundaries The edge of the pelvic inlet (pelvic brim) is formed as follows: Diameters The diameters or conjugates of the pelvis are measured at the pelvic inlet and outlet and as oblique diameters. Two diameters may be measured from the outside of the body using a pelvimeter Additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrotuberous Ligaments
The sacrotuberous ligament (great or posterior sacrosciatic ligament) is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends. Structure It runs from the sacrum (the lower transverse sacral tubercles, the inferior margins sacrum and the upper coccyx) to the tuberosity of the ischium. It is a remnant of part of Biceps femoris muscle. The sacrotuberous ligament is attached by its broad base to the posterior superior iliac spine, the posterior sacroiliac ligaments (with which it is partly blended), to the lower transverse sacral tubercles and the lateral margins of the lower sacrum and upper coccyx. Its oblique fibres descend laterally, converging to form a thick, narrow band that widens again below and is attached to the medial margin of the ischial tuberosity. It then spreads along the ischial ramus as the falciform process, whose concave edge blends with the fascial sheath of the internal pudendal vessels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischia
Ischia ( , , ) is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It lies at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about from Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands. Roughly trapezoidal in shape, it measures approximately east to west and north to south and has about of coastline and a surface area of . It is almost entirely mountainous; the highest peak is Mount Epomeo, at . The island is very densely populated, with 62,000 residents (more than 1,300 inhabitants per square km). Ischia is also well known for its thermal water and thermal gardens used since ancient times. Its volcanic nature makes Ischia one of the largest spas in Europe. Ischia's thermal waters are alkaline. Already the first Euboic settlers (8th century BC), as evidenced by the numerous archaeological finds found in the site of Pithecusa and preserved in thArchaeological Museum of Villa Arbustoin Lacco Ameno, appreciated and used the waters of the island's thermal springs. The Greeks, in fact, used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Rami Of The Pubes
In vertebrates, the pubic region ( la, pubis) is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three main regions making up the coxal bone. The left and right pubic regions are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic region is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of fat, which is covered by the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubic region is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic region. The bodies of the left and right pubic regions join at the pubic symphysis. The rough upper edge is the pubic crest, ending laterally in the pubic tubercle. This tubercle, found roughly 3 cm from the pubic symphysis, is a distinctive feature on the lower part of the abdominal wall; important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubic Arcuate Ligament
The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is close to the clitoris. In most adults it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth. The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'. Structure The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubic bones are covered by a thin layer of hyal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lozenge (shape)
A lozenge ( ; symbol: ), often referred to as a diamond, is a form of rhombus. The definition of ''lozenge'' is not strictly fixed, and the word is sometimes used simply as a synonym () for ''rhombus''. Most often, though, lozenge refers to a thin rhombus—a rhombus with two acute and two obtuse angles, especially one with acute angles of 45°. The lozenge shape is often used in parquetry (with acute angles that are 360°/''n'' with ''n'' being an integer higher than 4, because they can be used to form a set of tiles of the same shape and size, reusable to cover the plane in various geometric patterns as the result of a tiling process called tessellation in mathematics) and as decoration on ceramics, silverware and textiles. It also features in heraldry and playing cards. Symbolism The lozenge motif dates from the Neolithic and Paleolithic period in Eastern Europe and represents a sown field and female fertility. The ancient lozenge pattern often shows up in Diamond vault ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrospinous Ligament
The sacrospinous ligament (small or anterior sacrosciatic ligament) is a thin, triangular ligament in the human pelvis. The base of the ligament is attached to the outer edge of the sacrum and coccyx, and the tip of the ligament attaches to the spine of the ischium, a bony protuberance on the human pelvis. Its fibres are intermingled with the sacrotuberous ligament. Structure The sacrotuberous ligament passes behind the sacrospinous ligament. In its entire length, the sacrospinous ligament covers the equally triangular coccygeus muscle, to which its closely connected.Gray's Anatomy 1918 Function The presence of the ligament in the greater sciatic notch creates an opening (foramen), the greater sciatic foramen, and also converts the lesser sciatic notch into the lesser sciatic foramen.Platzer (2004), p 188 The greater sciatic foramen lies above the ligament, and the lesser sciatic foramen lies below it. The pudendal vessels and nerve pass behind the sacrospinous ligament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrotuberous
The sacrotuberous ligament (great or posterior sacrosciatic ligament) is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends. Structure It runs from the sacrum (the lower transverse sacral tubercles, the inferior margins sacrum and the upper coccyx) to the tuberosity of the ischium. It is a remnant of part of Biceps femoris muscle. The sacrotuberous ligament is attached by its broad base to the posterior superior iliac spine, the posterior sacroiliac ligaments (with which it is partly blended), to the lower transverse sacral tubercles and the lateral margins of the lower sacrum and upper coccyx. Its oblique fibres descend laterally, converging to form a thick, narrow band that widens again below and is attached to the medial margin of the ischial tuberosity. It then spreads along the ischial ramus as the falciform process, whose concave edge blends with the fascial sheath of the internal pudendal vessel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciatic Notches (other)
Sciatic notch may refer to : * Greater sciatic notch * Lesser sciatic notch Below the ischial spine is a small notch, the lesser sciatic notch; it is smooth, coated in the recent state with cartilage, the surface of which presents two or three ridges corresponding to the subdivisions of the tendon of the Obturator internu ... {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
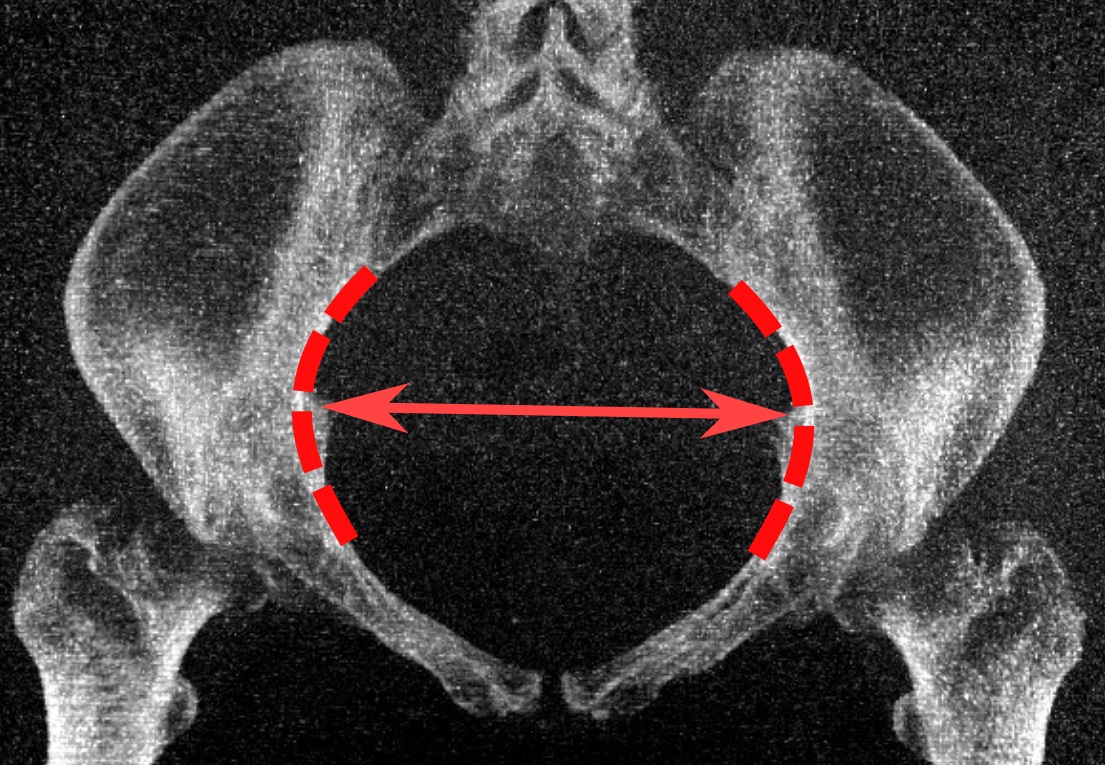
Pelvimetry
Pelvimetry is the measurement of the female pelvis. It can theoretically identify cephalo-pelvic disproportion, which is when the capacity of the pelvis is inadequate to allow the fetus to negotiate the birth canal. However, clinical evidence indicate that all pregnant women should be allowed a trial of labor regardless of pelvimetry results. Indication Theoretically, pelvimetry may identify cephalo-pelvic disproportion, which is when the capacity of the pelvis is inadequate to allow the fetus to negotiate the birth canal. However, a woman's pelvis loosens up before birth (with the help of hormones). A Cochrane review in 2017 found that there was too little evidence to show whether pelvimetry is beneficial and safe when the baby is in cephalic presentation. A review in 2003 came to the conclusion that pelvimetry does not change the management of pregnant women, and recommended that all women should be allowed a trial of labor regardless of pelvimetry results. It considered routin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |