|
Pecica Culture
The Prehistory of Transylvania describes what can be learned about the region known as Transylvania through archaeology, anthropology, comparative linguistics and other allied sciences. Transylvania proper is a plateau or tableland in northwest central Romania. It is bounded and defined by the Carpathian Mountains to the east and south, and the Apuseni Mountains to the west. As a diverse and relatively protected region, the area has always been rich in wildlife, and remains one of the more ecologically diverse areas in Europe. The mountains contain a large number of caves, which attracted both human and animal residents. The Bears' Cave, Peștera Urșilor, the "Bears Cave", was home to a large number of cave bears (''Ursus spelæus'') whose remains were discovered when the cave was discovered in 1975. Other caves in the area sheltered early humans. Prehistory is the longest period in the history of mankind, throughout of which writing was still unknown. In Transylvania specif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ROMANIA Fizic
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a predominantly Temperate climate, temperate-continental climate, and an area of , with a population of around 19 million. Romania is the List of European countries by area, twelfth-largest country in Europe and the List of European Union member states by population, sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Its capital and largest city is Bucharest, followed by Iași, Cluj-Napoca, Timișoara, Constanța, Craiova, Brașov, and Galați. The Danube, Europe's second-longest river, rises in Germany's Black Forest and flows in a southeasterly direction for , before emptying into Romania's Danube Delta. The Carpathian Mountains, which cross Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Before Present
Before Present (BP) years, or "years before present", is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use 1 January 1950 as the commencement date (epoch) of the age scale. The abbreviation "BP" has been interpreted retrospectively as "Before Physics", which refers to the time before nuclear weapons testing artificially altered the proportion of the carbon isotopes in the atmosphere, which scientists must now account for. In a convention that is not always observed, many sources restrict the use of BP dates to those produced with radiocarbon dating; the alternative notation RCYBP stands for the explicit "radio carbon years before present". Usage The BP scale is sometimes used for dates established by means other than radiocarbon dating, such as stratigraphy. This usage differs fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx Bone
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
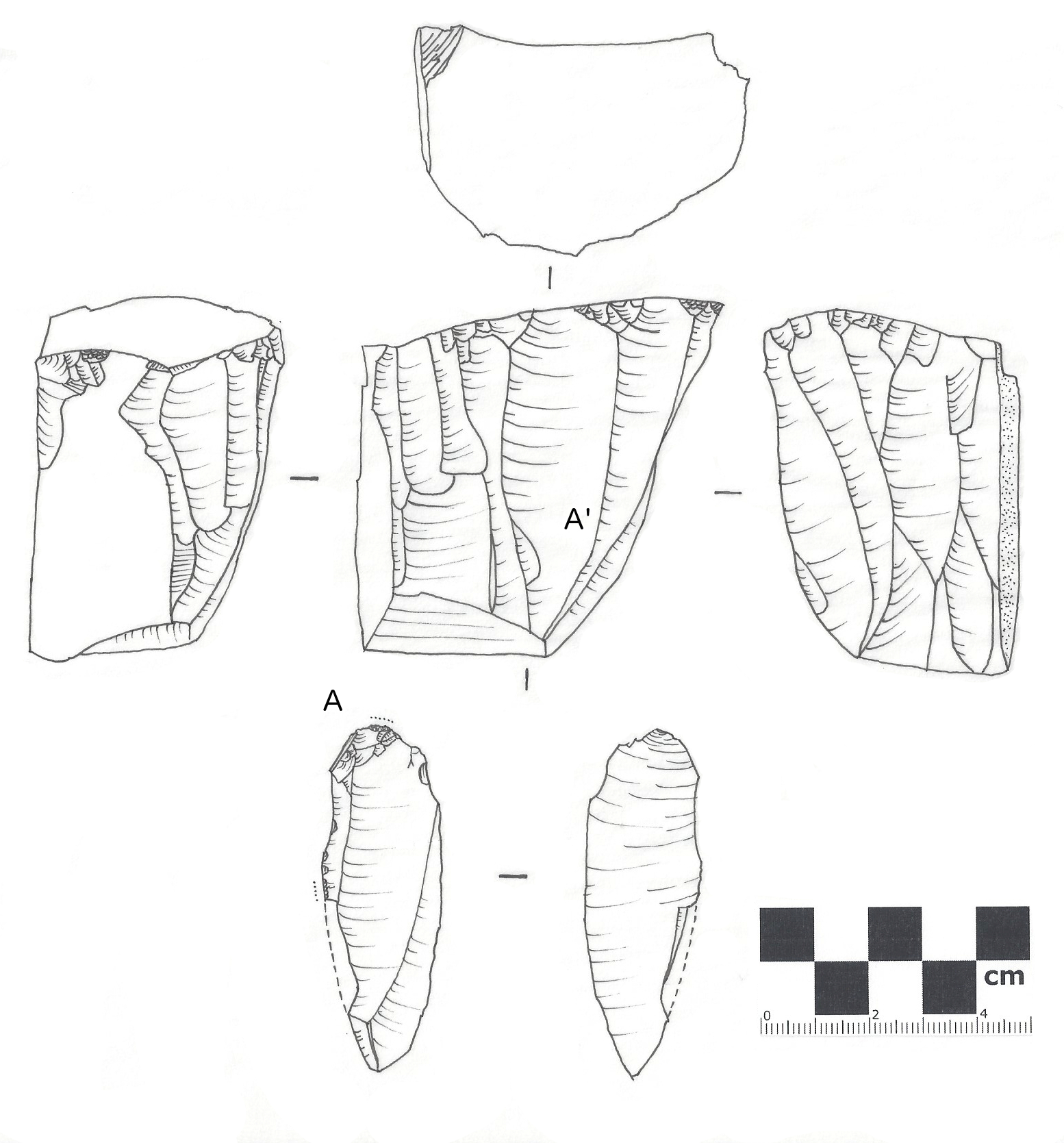
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90° ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
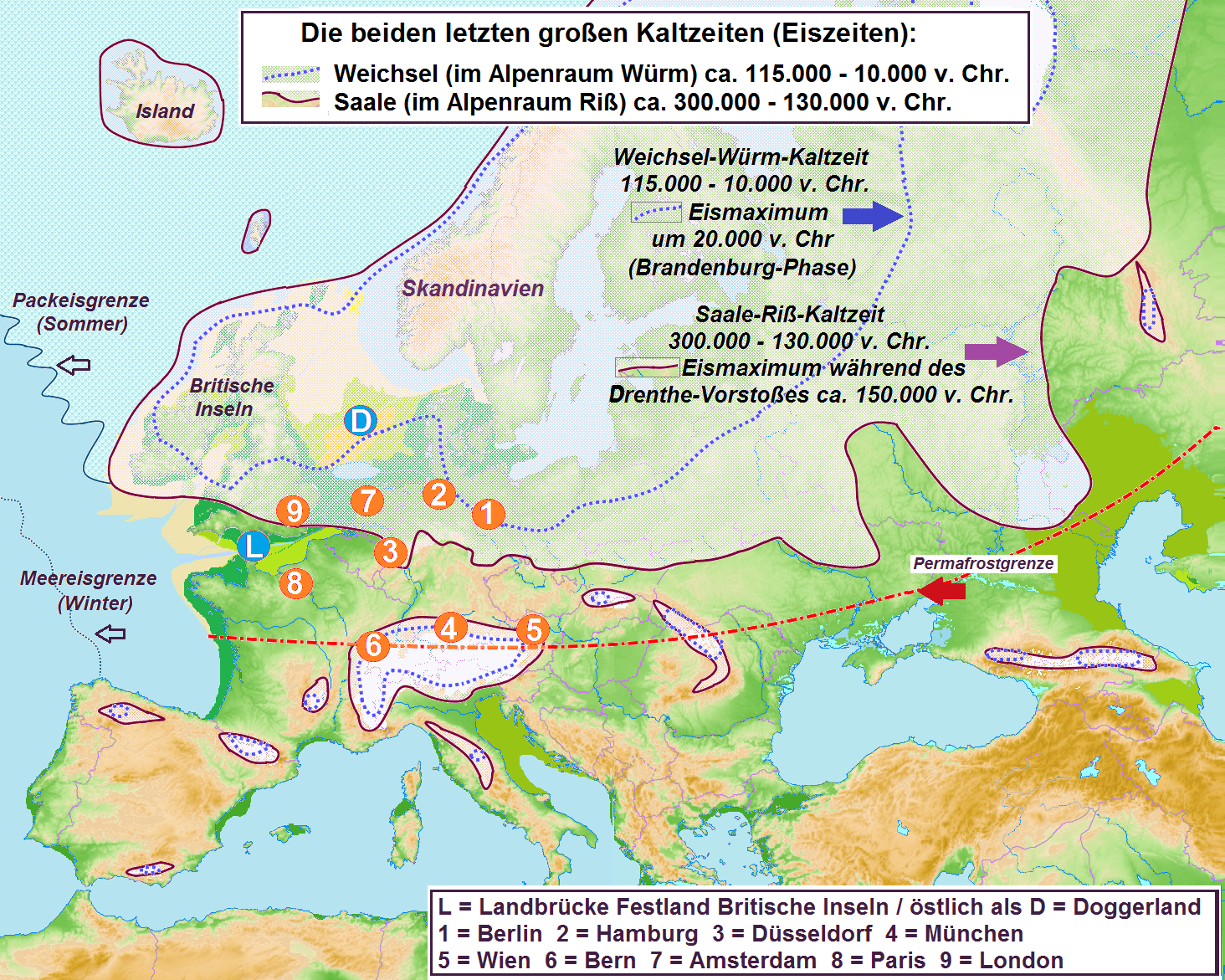
Würm Glaciation
The Würm glaciation or Würm stage (german: Würm-Kaltzeit or ''Würm-Glazial'', colloquially often also ''Würmeiszeit'' or ''Würmzeit''; cf. ice age), usually referred to in the literature as the Würm (often spelled "Wurm"), was the last glacial period in the Alpine region. It is the youngest of the major glaciations of the region that extended beyond the Alps themselves. Like most of the other ice ages of the Pleistocene epoch, it is named after a river, in this case the Würm in Bavaria, a tributary of the Amper. The Würm ice age can be dated to about 115,000 to 11,700 years ago, but sources differ about the dates, depending on whether the long transition phases between the glacials and interglacials (warmer periods) are allocated to one or other of those periods. The average annual temperatures during the Würm ice age in the Alpine Foreland were below −3 °C (today +7 °C). That has been determined from changes in the vegetation ( pollen analysis), as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riss Glaciation
The Riss glaciation, Riss Glaciation, Riss ice age, Riss Ice Age, Riss glacial or Riss Glacial (german: Riß-Kaltzeit, ', ' or (obsolete) ') is the second youngest glaciation of the Pleistocene epoch in the traditional, quadripartite glacial classification of the Alps. The literature variously dates it to between about 300,000 to 130,000 years ago and 347,000 to 128,000 years ago. It coincides with the glaciation of North Germany. The name goes back to and who named this cold period after the river in Upper Swabia in their three-volume work ' ("The Alps in the Ice Age") published between 1901 and 1909. Boundaries and division The Riss glaciation was defined by Penck and Brückner as the Lower (''Niedere'') or Younger Old Moraines and Old Terminal Moraines High Terraces (''Jüngere Altmoränen und Alt-Endmoränen-Hochterrassen''). The type locality lies near Biberach an der Riß where the end of the northeastern Rhine Glacier stood. Results gained from over a century of resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindel Glaciation
The Mindel glaciation (german: Mindel-Kaltzeit, also ''Mindel-Glazial'', ''Mindel-Komplex'' or, colloquially, ''Mindel-Eiszeit'') is the third youngest glacial stage in the Alps. Its name was coined by Albrecht Penck and Eduard Brückner, who named it after the Swabian river, the Mindel. The Mindel glacial occurred in the Middle Pleistocene; it was preceded by the Haslach-Mindel interglacial (often regarded as part of Günz) and succeeded by the Mindel-Riss interglacial ( Holstein interglacial). The Mindel glaciation is commonly correlated to the Elster glaciation of northern Europe. The more precise timing is controversial since Mindel is commonly correlated to two different marine isotope stages, MIS 12 (478–424 thousand years ago) and MIS 10 (374–337 thousand years ago). This ambiguity is much related to the correlation problem described in more detail in the article 'Elster glaciation'. See also * Timeline of glaciation *Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Günz Glaciation
Gunz, Günz or Gunz Complex is a timespan in the glacial history of the Alps. It started approximately one million years ago and ended about 370 000 years ago. Some sources put the end at 480 000 years ago. Deep sea core samples have identified approximately 5 glacial cycles of varying intensity during Gunz. History of the term The name Gunz glaciation, Gunzian glaciation or Günz glacial stage (german: Günz-Kaltzeit, also ''Günz-Glazial'', ''Günz-Komplex'' and ''Günz-Eiszeit'') goes back to Albrecht Penck and Eduard Brückner, who named this ice age after the River Günz in their multi-volume work, ''Die Alpen im Eiszeitalter'' ("The Alps in the Ice Age Period") which was published between 1901 and 1909. Its type region is the Iller-Lech Plateau. It is the oldest glaciation of the Pleistocene in the traditional, quadripartite glacial classification of the Alps. The Günz was thought to follow the Danube-Günz interglacial and was ended by the Günz-Haslach interglacial. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia. The Alpine arch generally extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 128 peaks higher than . The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountains, precipita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago. The Holocene is the current interglacial. A time with no glaciers on Earth is considered a greenhouse climate state. Quaternary Period Within the Quaternary, which started about 2.6 million years before present, there have been a number of glacials and interglacials. At least eight glacial cycles have occurred in the last 740,000 years alone. Penultimate Glacial Period The Penultimate Glacial Period (PGP) is the glacial period that occurred before the Last Glacial Period. It began about 194,000 years ago and ended 135,000 years ago, with the beginning of the Eemian interglacial. Last Glacial Period The last glacial period was the most recent glacial perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today, although a third epoch, the Anthropocene, has been proposed but is not yet officially recognised by the ICS). The Quaternary Period is typically defined by the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. Research history In 1759 Giovanni Arduino proposed that the geological strata of northern Italy could be divided into four successive formations or "orders" ( it, quattro ordini). The term "quaternary" was introduced by Jules Desn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |