|
Patbap
Red bean rice, called ''patbap'' () in Korean, ''sekihan'' () in Japanese, and ''hóngdòu fàn'' () in Chinese, is an East Asian rice dish consisting of rice cooked with red beans. East Asian varieties China Hóngdòu fàn (红豆饭) is a traditional Chinese dish found in some regions of China. It is particularly common in Jiangsu province and eaten during the Winter Clothes Day. A legend from the Dafeng area of Yancheng, Jiangsu says that people eat a bowl of glutinous rice mixed with red beans on the Winter Clothes Day in Jiangsu to commemorate a shepherd boy who was slain by a landlord.《图解民俗大全-精编美绘版》(2012-5-1)."关心先人的送寒衣"( P230---P23Accessed 20 Dec. 2016 It is said that a long time ago, an adorable shepherd boy was born into a poor family. His parents could not support him, so he made a living by shepherding for a landlord.《节气时令吃什么》(2013-11-01)."十月初一——寒衣"( P18Accessed 20 Dec. 2016 One day, his c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sekihan (2017-10-15)
Red bean rice, called ''patbap'' () in Korean, ''sekihan'' () in Japanese, and ''hóngdòu fàn'' () in Chinese, is an East Asian rice dish consisting of rice cooked with red beans. East Asian varieties China Hóngdòu fàn (红豆饭) is a traditional Chinese dish found in some regions of China. It is particularly common in Jiangsu province and eaten during the Winter Clothes Day. A legend from the Dafeng area of Yancheng, Jiangsu says that people eat a bowl of glutinous rice mixed with red beans on the Winter Clothes Day in Jiangsu to commemorate a shepherd boy who was slain by a landlord.《图解民俗大全-精编美绘版》(2012-5-1)."关心先人的送寒衣"( P230---P23Accessed 20 Dec. 2016 It is said that a long time ago, an adorable shepherd boy was born into a poor family. His parents could not support him, so he made a living by shepherding for a landlord.《节气时令吃什么》(2013-11-01)."十月初一——寒衣"( P18Accessed 20 Dec. 2016 One day, his c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kongbap
''Kongbap'' is a Korean dish consisting of white or brown rice cooked together with one or more varieties of soybeans. ''Kongbap'' may be made from scratch by combining and cooking together dried rice and soybeans (usually black soybeans), although outside Korea the word "kongbap" is commercially used in premixed multi-grain packages in dried form. In Korea, multigrain rice consisting of grains other than soybeans are called ''japgok-bap'' (mixed cereal rice). The Korean word ''kong'' (bean) alone usually refers to soybeans and is contrasted with other words like ''pat'' meaning adzuki beans, and as such ''kongbap'' (bean rice) would not also be applied to ''patbap'' (red bean rice). Rice cooked with beans other than soybeans, such as French beans (''gangnangkong'' in Korean) or peas (''wandu'' in Korean), are usually named using the specific bean name, as in ''gangnang-kong-bap'' (French bean rice) or ''wandu-kong-bap'' (pea rice). ''Kongbap'' in culture Although it is generally a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asian Cuisine
This is a list of Asian cuisines, by region. A cuisine is a characteristic style of cooking practices and traditions, usually associated with a specific culture or region. Asia, being the largest, most populous and culturally diverse continent, has a great diversity of cuisines associated with its different regions. Central Asian cuisine * Central Asian cuisine includes food from Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan. ** Bukharan Jewish cuisine - cuisine of the Bukharan Jews with great influence from Uzbek cuisine. ** Kazakh cuisine – cuisine of Kazakhstan. Traditional Kazakh cuisine revolves around mutton and horse meat, as well as various milk products. For hundreds of years, Kazakhs were herders who raised fat-tailed sheep, Bactrian camels, and horses, relying on these animals for transportation, clothing, and food. *** Kazakh wine ** Kyrgyz cuisine – originating in Kyrgyzstan, is similar in many respects to that of its neighbors, par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landlord
A landlord is the owner of a house, apartment, condominium, land, or real estate which is rented or leased to an individual or business, who is called a tenant (also a ''lessee'' or ''renter''). When a juristic person is in this position, the term landlord is used. Other terms include lessor and owner. The term landlady may be used for the female owners. The manager of a pub in the United Kingdom, strictly speaking a licensed victualler, is referred to as the landlord/landlady. In political economy it refers to the owner of natural resources alone (e.g., land, not buildings) from which an economic rent is the income received. History The concept of a landlord may be traced back to the feudal system of manoralism ( seignorialism), where a landed estate is owned by a Lord of the Manor ( mesne lords), usually members of the lower nobility which came to form the rank of knights in the high medieval period, holding their fief via subinfeudation, but in some cases the land m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gomashio
Gomashio (hiragana: ごま塩; also spelled ''gomasio'') is a dry condiment, similar to ''furikake'', made from unhulled and . It is often used in Japanese cuisine, such as a topping for ''sekihan''. It is also sometimes sprinkled over plain rice or ''onigiri''. Some commercially sold gomashio also has sugar mixed in with the salt. The sesame seeds used to make ''gomashio'' may be either tan or black in color. They are toasted before being mixed with the salt. Occasionally the salt is also toasted. The ratio of sesame seeds to salt varies according to taste and diet, generally ranging between 5:1 (5 parts sesame seeds to 1 part salt) and 15:1. ''Gomashio'' is often homemade, though it is also commercially available in glass or plastic containers. ''Gomashio'' is also a part of the macrobiotic diet, where it is used as a healthier alternative to ordinary salt. Generally, the ''gomashio'' used in macrobiotic cuisine will contain less salt than traditional Japanese ''gomashio'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bento
A is the Japanese iteration of a single-portion take-out or home-packed meal, often for lunch. Outside Japan, it is common in other East and Southeast Asian culinary styles, especially within Chinese, Korean, Singaporean cuisines and more, as rice is a common staple food in the region. The term ''bento'' is derived from the Chinese term ''biandang'' (, ), which means "convenient" or "convenience". A traditional ''bento'' may contain rice or noodles with fish or meat, often with pickled and cooked vegetables in a box."Bento: Changing New York's Lunch Culture," ''Chopsticks NY,'' vol. 27, July 2009, p. 10-11. Containers range from mass-produced disposables to hand-crafted lacquerware. Often various dividers are used to separate ingredients or dishes, especially those with strong flavors, to avoid them affecting the taste of the rest of the meal. A typical divider is green plastic grass, also known as the 'sushi grass'. This also works to slow the growth of bacteria. ''Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
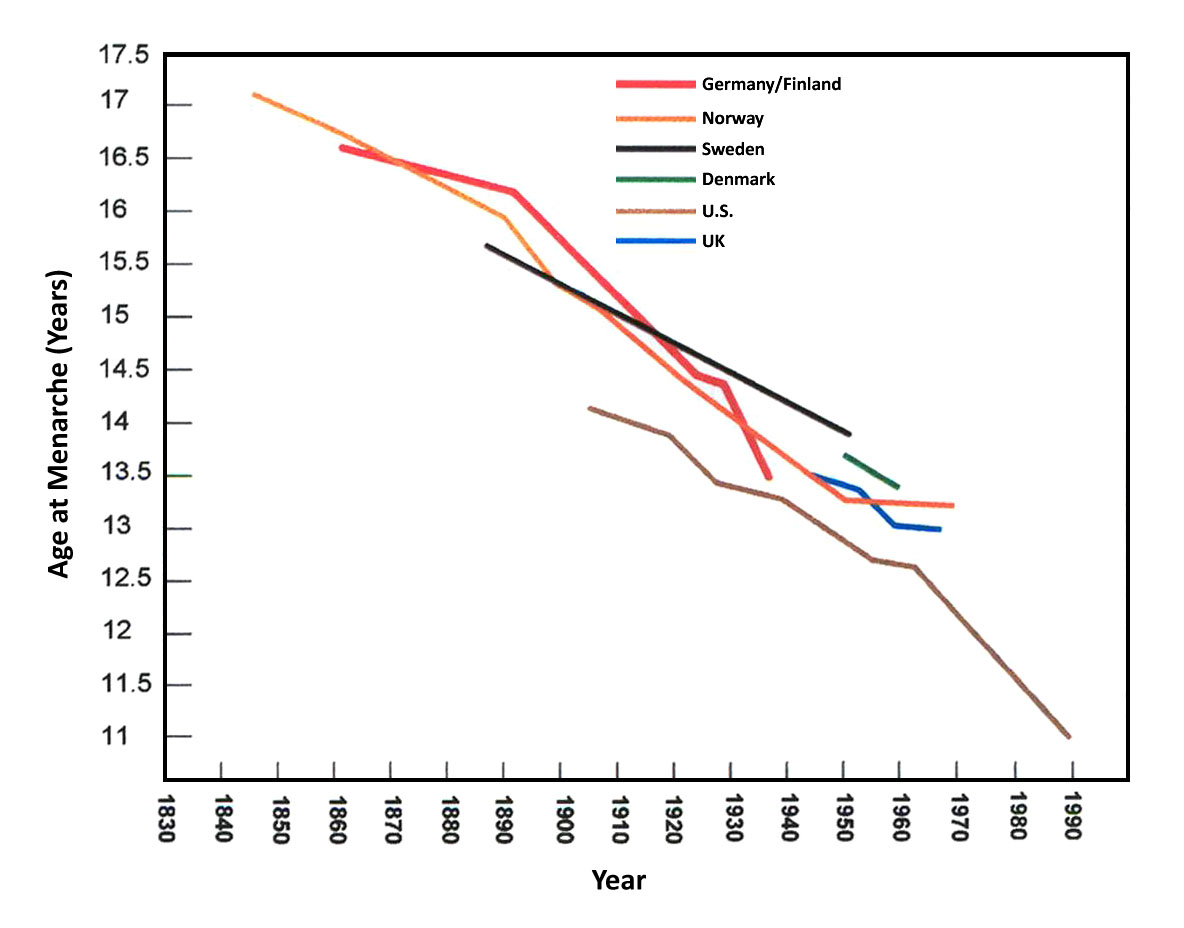
Menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility. Girls experience menarche at different ages. Having menarche occur between the ages of 9–16 in the west is considered normal.US National Health Statistics Report September 2020 Canadian psychological researcher Niva Piran claims that menarche or the perceived average age of puberty is used in many cultures to separate girls from activity with boys, and to begin confinement as a woman and future wife. The timing of menarche is influenced by female , as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shichi-Go-San
is a traditional Japanese rite of passage and festival day for three- and seven-year-old girls, five-year-old and sometimes three-year-old boys, held annually on November 15 to celebrate the growth and well-being of young children. As it is not a national holiday, it is generally observed on the nearest weekend. History is said to have originated in the Heian period amongst court nobles who would celebrate the passage of their children into middle childhood, but it is also suggested that the idea was originated from the Muromachi period due to high infant mortality. The ages 3, 5 and 7 are consistent with East Asian numerology, which holds that odd numbers are lucky. The practice was set to the fifteenth of the month during the Kamakura period. Its meaning is to celebrate the survival of children, as infant and child mortality rates were higher in previous centuries. Over time, this tradition passed to the samurai class who added a number of rituals. The first of these c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tannin
Tannins (or tannoids) are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids. The term ''tannin'' (from Anglo-Norman ''tanner'', from Medieval Latin ''tannāre'', from ''tannum'', oak bark) refers to the use of oak and other bark in tanning animal hides into leather. By extension, the term ''tannin'' is widely applied to any large polyphenolic compound containing sufficient hydroxyls and other suitable groups (such as carboxyls) to form strong complexes with various macromolecules. The tannin compounds are widely distributed in many species of plants, where they play a role in protection from predation (acting as pesticides) and might help in regulating plant growth. The astringency from the tannins is what causes the dry and puckery feeling in the mouth following the consumption of unripened fruit, red wine or tea. Likewise, the destruction or modification of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sticky Rice
Glutinous rice (''Oryza sativa var. glutinosa''; also called sticky rice, sweet rice or waxy rice) is a type of rice grown mainly in Southeast and East Asia, and the northeastern regions of South Asia, which has opaque grains, very low amylose content, and is especially sticky when cooked. It is widely consumed across Asia. It is called glutinous ( la, glūtinōsus) in the sense of being glue-like or sticky, and not in the sense of containing gluten (which it does not). While often called ''sticky rice'', it differs from non-glutinous strains of japonica rice which also become sticky to some degree when cooked. There are numerous cultivars of glutinous rice, which include ''japonica'', ''indica'' and ''tropical japonica'' strains. History In China, glutinous rice has been grown for at least 2,000 years. However, researchers believe that glutinous rice distribution appears to have been culturally influenced and closely associated with the early southward migration and distribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), Ningxia (NW) and Inner Mongolia (N). Shaanxi covers an area of over with about 37 million people, the 16th highest in China. Xi'an – which includes the sites of the former Chinese capitals Fenghao and Chang'an – is the provincial capital as well as the largest city in Northwest China and also one of the oldest cities in China and the oldest of the Four Great Ancient Capitals, being the capital for the Western Zhou, Western Han, Jin, Sui and Tang dynasties. Xianyang, which served as the Qin dynasty capital, is just north across Wei River. The other prefecture-level cities into which the province is divided are Ankang, Baoji, Hanzhong, Shangluo, Tongchuan, Weinan, Yan'an and Yulin. The province is geographicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqing and Chengdu, as well as the most populous city in Northwest China. Its total population was 12,952,907 as of the 2020 census. The total urban population was 9.28 million. Since the 1980s, as part of the economic growth of inland China especially for the central and northwest regions, Xi'an has re-emerged as a cultural, industrial, political and educational centre of the entire central-northwest region, with many facilities for research and development. Xi'an currently holds sub-provincial status, administering 11 districts and 2 counties. In 2020, Xi'an was ranked as a Beta- (global second tier) city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network, and, according to the country's own ranking, ranked 17th. Xi'an is also one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)
