|
Pareiasauromorpha
Pareiasauromorpha is a group of parareptilian amniotes from the Permian. It includes genera found all over the world, with many genera from Asia and South Africa. The clade was first used as a group by Linda A. Tsuji in 2011, in order to group the family Nycteroleteridae (nycteroleters) and the superfamily Pareiasauroidea (pareiasaurs). Pareiasauromorpha is considered to be a monophyletic node, the sister group to procolophonoids. Classification ''Pareiasauromorpha'' was first used to define a group of parareptilians in 2011 by Linda A. Tsuji. The next year, Tsuji and her colleagues used Pareiasauromorpha as a node inside Procolophonia. In their 2012 publication, Tsuji ''et al.'' defined it as a monophyletic node containing "nycteroleters" (the family Nycteroleteridae) and "pareiasaurs" (in the superfamily Pareiasauroidea). Nycteroleteridae Nycteroleteridae is a family, commonly called "nycteroleters", classified in Pareiasauromorpha. The group includes the genera '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procolophonia
The Procolophonia are a suborder of herbivorous reptiles that lived from the Middle Permian till the end of the Triassic period. They were originally included as a suborder of the Cotylosauria (later renamed Captorhinida Carroll 1988) but are now considered a clade of Parareptilia. They are closely related to other generally lizard-like Permian reptiles such as the Millerettidae, Bolosauridae, Acleistorhinidae, and Lanthanosuchidae, all of which are included under the Anapsida or "Parareptiles" (as opposed to the Eureptilia). Classification There are two main groups of Procolophonia, the small, lizard-like Procolophonoidea, and the Pareiasauroidea, which include the large, armoured Pareiasauridae. According to the traditional classification of Carroll 1988 as well as recent phylogenetic analyses, smaller groups like Rhipaeosauridae (now a synonym of Nycteroleteridae) and Sclerosauridae are classified with the pareiasaurs and with the procolophonids, respectively. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasauroidea
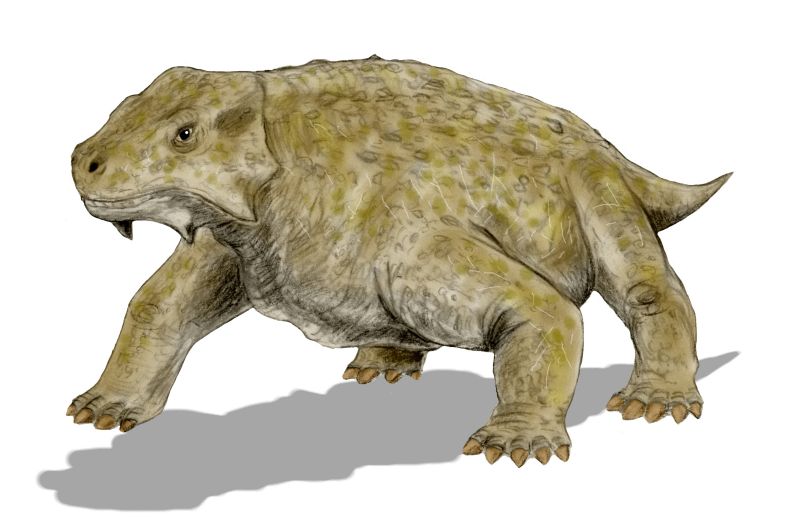
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, reaching sizes equivalent to those of contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct at the end of the Permian during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, and may have weighed up to . They were stocky, with short tails, small heads, robust limbs, and broad feet. The cow-sized species ''Bunostegos'', which lived 260 million years ago, is the earliest known example of a tetrapod with a fully erect posture as its legs were positioned directly under its body. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms that were set into the skin. Their heavy skulls wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaurus
''Pareiasaurus'' is an extinct genus of pareiasauromorph reptile from the Permian period. It was a typical member of its family, the pareiasaurids, which take their name from this genus. Fossils have been found in the Beaufort Group. Description ''Pareiasaurus'' is a large quadruped, about long, with elephantine legs, walking in a typically reptilian posture. The skull is broad and the snout short. Its skull had several spine- and wart-like protrusions. ''Pareiasauruss leaf-shaped teeth, ideal for biting through tough plant fibers, indicate it was a herbivore. Even the palate The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separ ... had teeth. Species ''P. nasicornis'' (Haughton and Boonstra, 1929) is from the ''Tropidostoma'' Zone, Karoo basin, South Africa. This early form is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokosaurus
''Macroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile which existed in Oklahoma and Russia during the upper Permian period. It was a quite generalized primitive reptile, in many ways resembling their amphibian ancestors. It was first named by paleontologists Tverdochlebova and Ivachnenko in 1984. According to classification by Michel Laurin and Robert R. Reisz, the genus is a parareptile, belonging to the same branch as Millerettidae, Procolophonidae and other generalized anapsid reptiles. The type species is ''Macroleter poezicus'' from Upper Permian of Russia. ''Macroleter'' had an 8 cm skull, and an overall length of 75 cm. It was generally lizard-like in build with a rather flat and broad skull. The teeth were small and pointy, indication it predominantly hunted insects and other small invertebrates. ''Seymouria agilis'' (Olson, 1980) that is known from only one specimen (holotype UCMP 143 277) was originally thought to be a reptile-like amphibian a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parareptilia
Parareptilia ("at the side of reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids (reptiles), typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds). Parareptiles first arose near the end of the Carboniferous period and achieved their highest diversity during the Permian period. Several ecological innovations were first accomplished by parareptiles among reptiles. These include the first reptiles to return to marine ecosystems (mesosaurs), the first bipedal reptiles (bolosaurids such as '' Eudibamus''), the first reptiles with advanced hearing systems ( nycteroleterids and others), and the first large herbivorous reptiles (the pareiasaurs). The only parareptiles to survive into the Triassic period were the procolophonoids, a group of small generalists, omnivores, and herbivores. The largest family of procolophonoids, the procolophonids, rediversified in the Triassic, but subsequently declined and became extinct by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroleter
''Macroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile which existed in Oklahoma and Russia during the upper Permian period. It was a quite generalized primitive reptile, in many ways resembling their amphibian ancestors. It was first named by paleontologists Tverdochlebova and Ivachnenko in 1984. According to classification by Michel Laurin and Robert R. Reisz, the genus is a parareptile, belonging to the same branch as Millerettidae, Procolophonidae and other generalized anapsid reptiles. The type species is ''Macroleter poezicus'' from Upper Permian of Russia. ''Macroleter'' had an 8 cm skull, and an overall length of 75 cm. It was generally lizard-like in build with a rather flat and broad skull. The teeth were small and pointy, indication it predominantly hunted insects and other small invertebrates. ''Seymouria agilis'' (Olson, 1980) that is known from only one specimen (holotype UCMP 143 277) was originally thought to be a reptile-like amphibian a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhipaeosaurus
''Rhipaeosaurus'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile known from an articulated skeleton from the mid Middle Permian of European Russia. It contained a single species, ''Rhipaeosaurus tricuspidens''. A bayesian analysis suggests that it is more closely related to pareiasaurs than to the other nycteroleterids, due to skull and tooth features. For this reason, "Nycteroleteridae" may be a grade rather than a clade, unless redefined to exclude ''Rhipaeosaurus''. Description ''Rhipaeosaurus'' is around a meter long, larger than any other "nycteroleterids" and closer in size to later pareiasaurs. Postcranial remains were similar to ''Macroleter'', though the limbs were more robust and the ankle bones were unfused. The teeth were flattened and tricuspid (possessing three cusps), seemingly intermediate in form between the one- or two-cusped teeth of earlier nycteroleterids and the multi-cusped teeth of pareiasaurs. Many components of the partial skull and skeleton (wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nycteroleter
''Nycteroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile known from the Middle Permian of European Russia. Fossils were first found in the Mezen River, near to Arkhangelsk. Within the Nycteroleteridae, it is considered most closely related to '' Emeroleter.'' However, its legs were shorter than those of ''Emeroleter'' and its skull was flatter. ''Nycteroleter'' was insectivorous, and may have been nocturnal. It was a small animal, less than a metre long. Classification ''Nycteroleter'' is classified as a primitive procolophonian, related to the Pareisauridae. It is not certain whether the nycteroleterids formed a monophyletic or polyphyletic group, as '' Rhipaeosaurus'' seems to be more similar to pareisaurids than to other nycteroleterids. Previously, it was uncertain whether nycteroleterids were parareptiles Parareptilia ("at the side of reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids ( reptiles), typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emeroleter
''Emeroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile known from the early Late Permian Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, ... of European Russia. It was a long-legged lizard-like small animal with a length about 30 cm. References Permian reptiles of Europe Pareiasauromorphs Fossil taxa described in 1997 Prehistoric reptile genera {{paleo-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
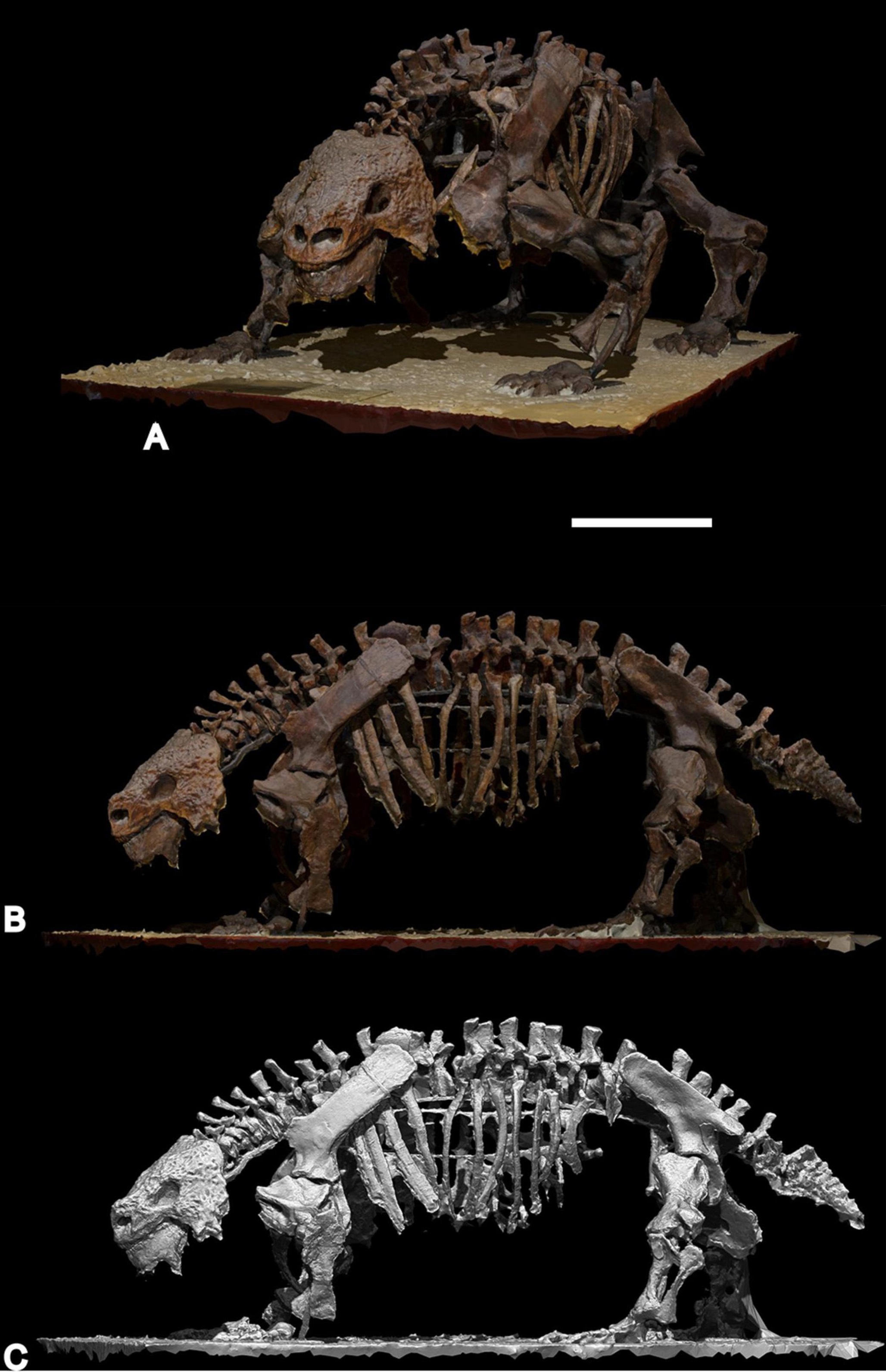
Bradysaurus Baini
''Bradysaurus'' was a large, early and common pareiasaur, the fossils of which are known from the ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone (Capitanian age) of the South African Karoo. Along with the similarly large dinocephalia, the bradysaurs constituted the herbivorous megafauna of the late Middle Permian Period. In life they were probably slow, clumsy and inoffensive animals, that had evolved a covering of armoured scutes to protect them against their predators, the gorgonopsians. Description ''Bradysaurus'' was in length and half a tonne to a tonne in weight. The skull was large (about 42 to 48 centimeters long), broad and rounded at the front. It was coarsely sculptured and knobby, with the sutures between the bones not clearly visible. The marginal teeth were high-crowned, with only a few cusps, which is a primitive characteristic. The feet were short and broad, the phalangeal count being 2,3,3,3,2 on the fore-foot and 2,3,3,4,3 on the hind. The whole body is prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradysaurus
''Bradysaurus'' was a large, early and common pareiasaur, the fossils of which are known from the ''Tapinocephalus'' Assemblage Zone (Capitanian age) of the South African Karoo. Along with the similarly large dinocephalia, the bradysaurs constituted the herbivorous megafauna of the late Middle Permian Period. In life they were probably slow, clumsy and inoffensive animals, that had evolved a covering of armoured scutes to protect them against their predators, the gorgonopsians. Description ''Bradysaurus'' was in length and half a tonne to a tonne in weight. The skull was large (about 42 to 48 centimeters long), broad and rounded at the front. It was coarsely sculptured and knobby, with the sutures between the bones not clearly visible. The marginal teeth were high-crowned, with only a few cusps, which is a primitive characteristic. The feet were short and broad, the phalangeal count being 2,3,3,3,2 on the fore-foot and 2,3,3,4,3 on the hind. The whole body is prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scutosaurus
''Scutosaurus'' ("shield lizard") is an extinct genus of pareiasaur parareptiles. Its genus name refers to large plates of armor scattered across its body. It was a large anapsid reptile that, unlike most reptiles, held its legs underneath its body to support its great weight. Fossils have been found in the Sokolki Assemblage Zone of the Malokinelskaya Formation in European Russia, close to the Ural Mountains, dating to the late Permian (Lopingian) between 264 and 252 million years ago. Research history The first fossils were uncovered by Russian paleontologist Vladimir Prokhorovich Amalitskii while documenting plant and animal species in the Upper Permian sediments in the Northern Dvina River, Arkhangelsk District, Northern European Russia. Amalitskii had discovered the site in 1899, and he and his wife Anne Amalitskii continued to oversee excavation until 1914, recovering numerous nearly complete and articulated (in their natural position) skeletons belonging to a men ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |