|
Pulsatilla Rhodopaea
The genus ''Pulsatilla'' contains about 40 species of herbaceous perennial plants native to meadows and prairies of North America, Europe, and Asia. Common names include pasque flower (or pasqueflower), wind flower, prairie crocus, Easter flower, and meadow anemone. Several species are valued ornamentals because of their finely-dissected leaves, solitary bell-shaped flowers, and plumed seed heads. The showy part of the flower consists of sepals, not petals. The common name ''pasque flower'' refers to its flowering period in the spring during Passover (in ''pāsaḥ''). Taxonomy The genus ''Pulsatilla'' was first formally named in 1754 by the English botanist Philip Miller. The type species is ''Pulsatilla vulgaris'', the European pasque flower. The genus is placed in the tribe Anemoneae within the family Ranunculaceae. The tribe has been shown repeatedly to be monophyletic in molecular phylogenetic studies, but the number of genera recognized within the tribe and their relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsatilla Vulgaris
''Pulsatilla vulgaris'', the pasqueflower, is a species of flowering plant belonging to the buttercup family (Ranunculaceae), found locally on calcareous grassland in Europe, and widely cultivated in gardens. It was considered part of the genus '' Anemone'', to which it is closely related. Several sources still list ''Anemone pulsatilla'' as the accepted name, with ''Pulsatilla vulgaris'' as a synonym. Other variations of its common name include European pasqueflower and common pasqueflower. The name may also be split in two - pasque flower. Description This herbaceous perennial plant develops upright rhizomes, which function as food-storage organs. Its leaves and stems are long, soft, silver-grey and hairy. It grows to high and when it is fruit-bearing up to . The roots go deep into the soil. The finely-dissected leaves are arranged in a rosette and appear with the bell-shaped flower in early spring. The purple flowers are followed by distinctive silky seed-heads which can p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyly
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria: # the grouping contains its own most recent common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population), i.e. excludes non-descendants of that common ancestor # the grouping contains all the descendants of that common ancestor, without exception Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic'' grouping meets 1. but not 2., thus consisting of the descendants of a common ancestor, excepting one or more monophyletic subgroups. A ''polyphyletic'' grouping meets neither criterion, and instead serves to characterize convergent relationships of biological features rather than genetic relationships – for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, or aquatic insects. As such, these characteristic features of a polyphyletic grouping are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsatilla Albana
The genus ''Pulsatilla'' contains about 40 species of herbaceous perennial plants native to meadows and prairies of North America, Europe, and Asia. Common names include pasque flower (or pasqueflower), wind flower, prairie crocus, Easter flower, and meadow anemone. Several species are valued ornamentals because of their finely-dissected leaves, solitary bell-shaped flowers, and plumed seed heads. The showy part of the flower consists of sepals, not petals. The common name ''pasque flower'' refers to its flowering period in the spring during Passover (in ''pāsaḥ''). Taxonomy The genus ''Pulsatilla'' was first formally named in 1754 by the English botanist Philip Miller. The type species is ''Pulsatilla vulgaris'', the European pasque flower. The genus is placed in the tribe Anemoneae within the family Ranunculaceae. The tribe has been shown repeatedly to be monophyletic in molecular phylogenetic studies, but the number of genera recognized within the tribe and their relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemone Vernalis, Near Plagne Soleil, La Plagne Tarentaise, 2017
''Anemone'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae. Plants of the genus are commonly called windflowers. They are native to the temperate and subtropical regions of all regions except Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica. The genus is closely related to several other genera including ''Anemonoides'', '' Anemonastrum'', '' Hepatica'', and ''Pulsatilla''. Some botanists include these genera within ''Anemone''. Description ''Anemone'' are perennials that have basal leaves with long leaf-stems that can be upright or prostrate. Leaves are simple or compound with lobed, parted, or undivided leaf blades. The leaf margins are toothed or entire. Flowers with 4–27 sepals are produced singly, in cymes of 2–9 flowers, or in umbels, above a cluster of leaf- or sepal-like bracts. Sepals may be any color. The pistils have one ovule. The flowers have nectaries, but petals are missing in the majority of species. The fruits are ovoid to obovoid shaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsatilla Nuttalliana Manitoba May 2019
The genus ''Pulsatilla'' contains about 40 species of herbaceous perennial plants native to meadows and prairies of North America, Europe, and Asia. Common names include pasque flower (or pasqueflower), wind flower, prairie crocus, Easter flower, and meadow anemone. Several species are valued ornamentals because of their finely-dissected leaves, solitary bell-shaped flowers, and plumed seed heads. The showy part of the flower consists of sepals, not petals. The common name ''pasque flower'' refers to its flowering period in the spring during Passover (in ''pāsaḥ''). Taxonomy The genus ''Pulsatilla'' was first formally named in 1754 by the English botanist Philip Miller. The type species is ''Pulsatilla vulgaris'', the European pasque flower. The genus is placed in the tribe Anemoneae within the family Ranunculaceae. The tribe has been shown repeatedly to be monophyletic in molecular phylogenetic studies, but the number of genera recognized within the tribe and their relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Pasque Flower - An Easter Rarity, Natural History Museum
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Of The World Online
Plants of the World Online (POWO) is an online taxonomic database published by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. History Following the Convention on Biological Diversity, the Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew launched Plants of the World Online in March 2017 with the goal of creating an exhaustive online database of all seed-bearing plants worldwide. (Govaerts wrongly speaks of "Convention for Botanical Diversity (CBD)). The initial focus was on tropical African flora, particularly flora ''Zambesiaca'', flora of West and East Tropical Africa. Since March 2024, the website has displayed AI-generated predictions of the extinction risk for each plant. Description The database uses the same taxonomical source as the International Plant Names Index, which is the World Checklist of Vascular Plants (WCVP). The database contains information on the world's flora gathered from 250 years of botanical research. It aims to make available data from projects that no longer have an online ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
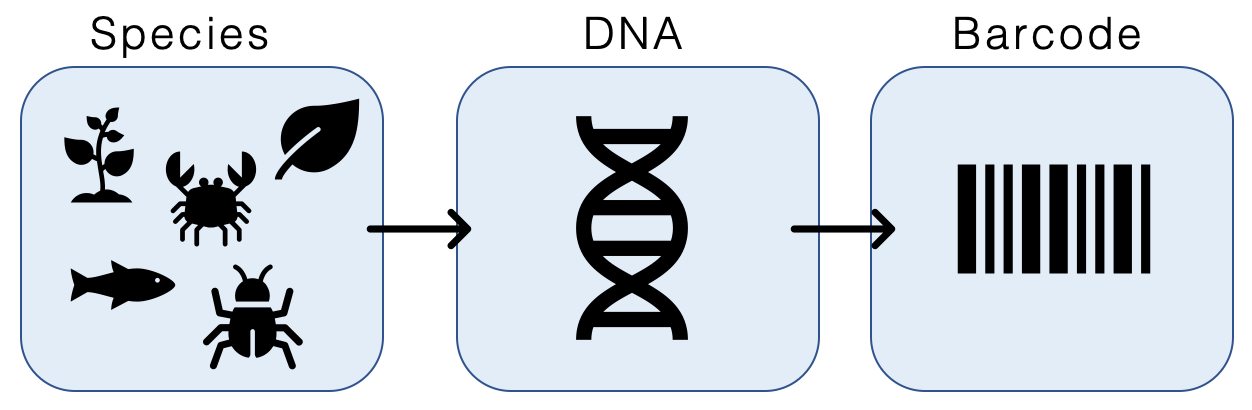
DNA Barcoding
DNA barcoding is a method of species identification using a short section of DNA from a specific gene or genes. The premise of DNA barcoding is that by comparison with a reference library of such DNA sections (also called " sequences"), an individual sequence can be used to uniquely identify an organism to species, just as a supermarket scanner uses the familiar black stripes of the UPC barcode to identify an item in its stock against its reference database. These "barcodes" are sometimes used in an effort to identify unknown species or parts of an organism, simply to catalog as many taxa as possible, or to compare with traditional taxonomy in an effort to determine species boundaries. Different gene regions are used to identify the different organismal groups using barcoding. The most commonly used barcode region for animals and some protists is a portion of the cytochrome ''c'' oxidase I (COI or COX1) gene, found in mitochondrial DNA. Other genes suitable for DNA barcoding a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigma (botany)
The stigma (: stigmas or stigmata) is the receptive tip of a Gynoecium#Carpels, carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. Description The stigma, together with the Style (botany), style and ovary (botany), ovary (typically called the stigma-style-ovary system) comprises the pistil, which is part of the gynoecium or female reproductive organ of a plant. The stigma itself forms the distal portion of the style, or stylodia, and is composed of , the cells of which are receptive to pollen. These may be restricted to the apex of the style or, especially in wind pollinated species, cover a wide surface. The stigma receives pollen and it is on the stigma that the pollen grain germination, germinates. Often sticky, the stigma is adapted in various ways to catch and trap pollen with various hairs, flaps, or sculpturings. The pollen may be captured from the air (wind-borne pollen, anemophily), from visiting insects or other animals (Pollination syndrome#Biotic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |