|
Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act
The Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA, ) is a United States Act passed as part of the National Energy Act. It was meant to promote energy conservation (reduce demand) and promote greater use of domestic energy and renewable energy (increase supply). The law was created in response to the 1973 energy crisis, and one year in advance of a second energy crisis. Upon entering the White House, President Jimmy Carter made energy policy a top priority. The law started the energy industry on the road to restructuring. Law PURPA was originally passed with the intention of conserving electric energy, increasing efficiency in facilities and resources used by utility companies, making retail rates for electric consumers more fair, speeding up the creation of hydroelectric energy production at small dams, and conserving natural gas. The main vehicle that the PURPA law used to try and accomplish these goals was by creating a new class of electric generating facilities called “ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws. Conservation may also refer to: Environment and natural resources * Nature conservation, the protection and management of the environment and natural resources **Wetland conservation, protecting and preserving areas where water exists at or near the Earth's surface, such as swamps, marshes and bogs. * Conservation biology, the science of protection and management of biodiversity * Conservation movement, political, environmental, or social movement that seeks to protect natural resources, including biodiversity and habitat * Conservation organization, an organization dedicated to protection and management of the environment or natural resources * Wildlife conservation, the practice of protecting wild species and their habitats in order to prevent species from going extinct * ''Conservation'' (magazine), published by the Society for Conservation Biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
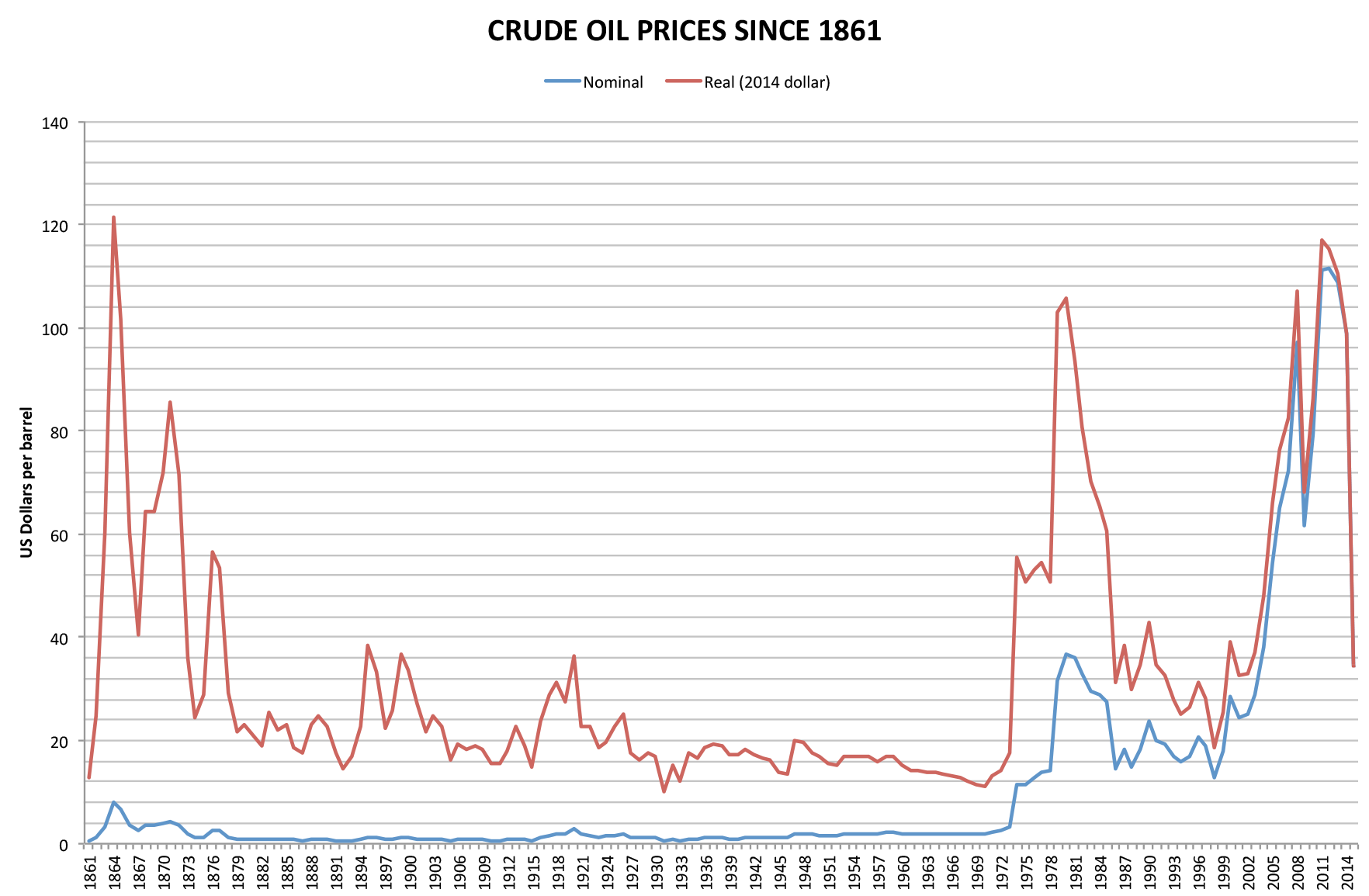
1973 Energy Crisis
In October 1973, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) announced that it was implementing a total oil embargo against countries that had supported Israel at any point during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, which began after Egypt and Syria launched a large-scale surprise attack in an ultimately unsuccessful attempt to recover the territories that they had lost to Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War. In an effort that was led by Faisal of Saudi Arabia, the initial countries that OAPEC targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the United States. This list was later expanded to include Portugal, Rhodesia, and South Africa. In March 1974, OAPEC lifted the embargo, but the price of oil had risen by nearly 300%: from US to nearly US globally. Prices in the United States were significantly higher than the global average. After it was implemented, the embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on the gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Market
In economics, a free market is an economic market (economics), system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of Forms of government, government or any other external authority. Proponents of the free market as a normative ideal contrast it with a regulated market, in which a government intervenes in supply and demand by means of various methods such as taxes or regulations. In an idealized free market economy, prices for goods and services are set solely by the bids and offers of the participants. Scholars contrast the concept of a free market with the concept of a Coordinated market economy, coordinated market in fields of study such as political economy, new institutional economics, economic sociology, and political science. All of these fields emphasize the importance in currently existing market systems of rule-making institutions external to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Power Transmission
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a ''transmission network''. This is distinct from the local wiring between high-voltage substations and customers, which is typically referred to as electric power distribution. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the electrical grid. Efficient long-distance transmission of electric power requires high voltages. This reduces the losses produced by strong currents. Transmission lines use either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). The voltage level is changed with transformers. The voltage is stepped up for transmission, then reduced for local distribution. A wide area synchronous grid, known as an ''interconnection'' in North America, directly connects generators delivering AC power with the same rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States Rights
In American political discourse, states' rights are political powers held for the state governments rather than the federal government according to the United States Constitution, reflecting especially the enumerated powers of Congress and the Tenth Amendment. The enumerated powers that are listed in the Constitution include exclusive federal powers, as well as concurrent powers that are shared with the states, and all of those powers are contrasted with the reserved powers—also called states' rights—that only the states possess. Since the 1940s, the term "states' rights" has often been considered a loaded term or dog whistle because of its use in opposition to federally-mandated racial desegregation and, more recently, same-sex marriage and reproductive rights. Background The balance of federal powers and those powers held by the states as defined in the Supremacy Clause of the U.S. Constitution was first addressed in the case of '' McCulloch v. Maryland'' (1819). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Power Plant
A thermal power station, also known as a thermal power plant, is a type of power station in which the heat energy generated from various fuel sources (e.g., coal, natural gas, nuclear fuel, etc.) is converted to electrical energy. The heat from the source is converted into mechanical energy using a thermodynamic power cycle (such as a Diesel cycle, Rankine cycle, Brayton cycle, etc.). The most common cycle involves a working fluid (often water) heated and boiled under high pressure in a pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam. This high pressure-steam is then directed to a turbine, where it rotates the turbine's blades. The rotating turbine is mechanically connected to an electric generator which converts rotary motion into electricity. Fuels such as natural gas or oil can also be burnt directly in gas turbines ( internal combustion), skipping the steam generation step. These plants can be of the open cycle or the more efficient combined cycle type. The majorit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Fuel
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geological formations. Reservoirs of such compound mixtures, such as coal, petroleum and natural gas, can be extracted and burnt as fuel for human consumption to provide energy for direct use (such as for cooking, heating or lighting), to power heat engines (such as steam or internal combustion engines) that can propel vehicles, or to generate electricity via steam turbine generators. Some fossil fuels are further refined into derivatives such as kerosene, gasoline and diesel, or converted into petrochemicals such as polyolefins ( plastics), aromatics and synthetic resins. The origin of fossil fuels is the anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The conversion from these organic materials to high-carbon fossil fuels is ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Utility
An electric utility, or a power company, is a company in the electric power industry (often a public utility) that engages in electricity generation and distribution of electricity for sale generally in a regulated market. Electric utilities are major providers of energy in most countries. Electric utilities include investor owned, publicly owned, cooperatives, and nationalized entities. They may be engaged in all or only some aspects of the industry. Electricity markets are also considered electric utilities—these entities buy and sell electricity, acting as brokers, but usually do not own or operate generation, transmission, or distribution facilities. Utilities are regulated by local and national authorities. Electric utilities are facing increasing demandsBy Candace Lombardi, CNET. �Utilities: Green tech good for planet, bad for business” February 23, 2010. including aging infrastructure, reliability, and regulation. In 2009, the French company EDF was the world's l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NERC Tag
{{Unsourced, date=November 2021 A NERC Tag, also commonly referred to as an E-Tag, represents a transaction on the North American bulk electricity market scheduled to flow within, between or across electric utility company territories. The NERC Tag is named for the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), which is the entity that was responsible for the implementation of the first energy tagging processes. NERC Tags were first introduced in 1997, in response to the need to track the increasingly complicated energy transactions which were produced as a result of the beginning of electric deregulation in North America. Electric deregulation in North America The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC)'s Energy Policy Act of 1992 was the first major step towards electric deregulation in North America, and was followed by a much more definitive action when FERC issued Orders 888 and 889 in 1996, which laid the groundwork for formalized deregulation of the industry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Monopoly
A natural monopoly is a monopoly in an industry in which high infrastructural costs and other barriers to entry relative to the size of the market give the largest supplier in an industry, often the first supplier in a market, an overwhelming advantage over potential competitors. Specifically, an industry is a natural monopoly if the total cost of one firm, producing the total output, is lower than the total cost of two or more firms producing the entire production. In that case, it is very probable that a company (monopoly) or minimal number of companies (oligopoly) will form, providing all or most relevant products and/or services. This frequently occurs in industries where capital costs predominate, creating large economies of scale about the size of the market; examples include public utilities such as water services, electricity, telecommunications, mail, etc. Natural monopolies were recognized as potential sources of market failure as early as the 19th century; John Stua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cogeneration
Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. Cogeneration is a more efficient use of fuel or heat, because otherwise- wasted heat from electricity generation is put to some productive use. Combined heat and power (CHP) plants recover otherwise wasted thermal energy for heating. This is also called combined heat and power district heating. Small CHP plants are an example of decentralized energy. By-product heat at moderate temperatures ( can also be used in absorption refrigerators for cooling. The supply of high-temperature heat first drives a gas or steam turbine-powered generator. The resulting low-temperature waste heat is then used for water or space heating. At smaller scales (typically below 1 MW), a gas engine or diesel engine may be used. Cogeneration is also common with geothermal power plants as they often produce relatively low grade heat. Binary cycle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |