|
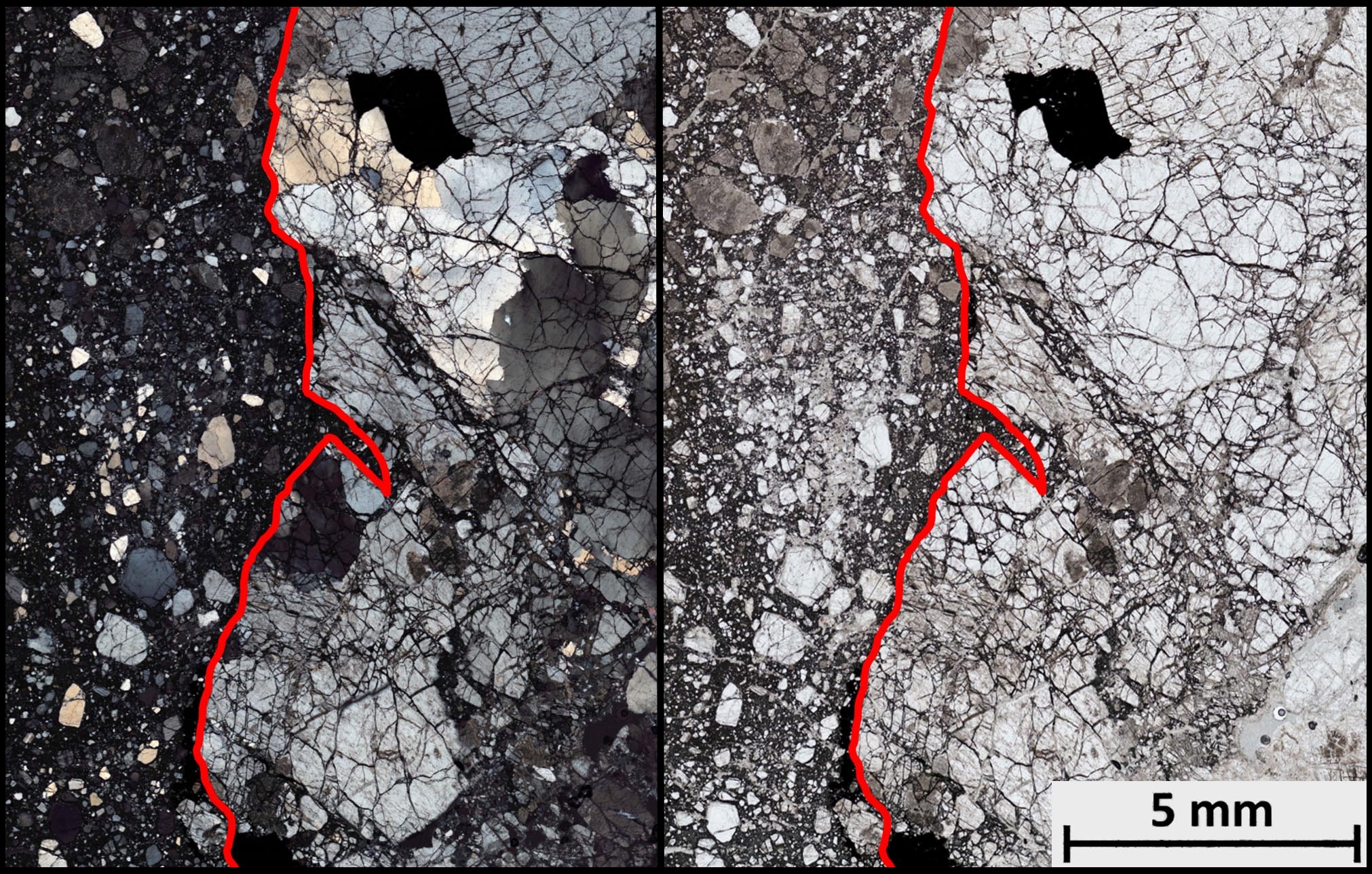
Pseudotachylite
Pseudotachylyte (sometimes written as pseudotachylite) is an extremely fine-grained to glassy, dark, cohesive rock occurring as veinsTrouw, R.A.J., C.W. Passchier, and D.J. Wiersma (2010) ''Atlas of Mylonites- and related microstructures.'' Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany. 322 pp. that form through frictional melting and subsequent quenching during earthquakes, large-scale landslides, and impacts events. Chemical composition of pseudotachylyte generally reflects the local bulk chemistry, though may skew to slightly more mafic compositions due to the preferential incorporation of hydrous and ferro-magnesian minerals (mica and amphibole, respectively) into the melt phase. Pseudotachylyte was first documented by Shand in the Vredefort Impact Structure and was named due to its close resemblance to tachylyte, a basaltic glass. Though pseudotachylyte is reported to have a glassy appearance, they are extremely susceptible to alteration and are thus rarely found to be entirely compose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mylonite
Mylonite is a fine-grained, compact metamorphic rock produced by dynamic recrystallization of the constituent minerals resulting in a reduction of the grain size of the rock. Mylonites can have many different mineralogical compositions; it is a classification based on the textural appearance of the rock. Formation Mylonites are ductilely deformed rocks formed by the accumulation of large shear strain, in ductile fault zones. There are many different views on the formation of mylonites, but it is generally agreed that crystal-plastic deformation must have occurred, and that fracturing and cataclastic flow are secondary processes in the formation of mylonites. Mechanical abrasion of grains by milling does not occur, although this was originally thought to be the process that formed mylonites, which were named from the Greek μύλος ''mylos'', meaning mill. Mylonites form at depths of no less than 4 km. There are many different mechanisms that accommodate crystal-plastic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vredefort Impact Structure
The Vredefort impact structure is one of the largest impact structures on Earth. The crater, which has since been eroded away, has been estimated at across when it was formed, the latter estimate suggesting the initial crater was larger than Chicxulub crater, the largest mostly intact impact crater on Earth. The remaining structure, comprising the deformed underlying bedrock, is located in present-day Free State province of South Africa. It is named after the town of Vredefort, which is near its centre. The structure's central uplift is known as the Vredefort Dome, which is around in diameter. The impact structure was formed during the Paleoproterozoic Era, 2.023 billion (± 4 million) years ago. It is among the oldest known impact structures on Earth, after Yarrabubba (2.23 billion years old) and Antarctic Creek (3.47 billion years old). In 2005, the Vredefort Dome was added to the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites for its geologic interest. Formation and struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiating Microcrystallites On Survivor Grain In Pseudotachylyte
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes: * ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma radiation (γ) * ''particle radiation'' consisting of particles of non-zero rest energy, such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), proton radiation and neutron radiation * '' acoustic radiation'', such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves, all dependent on a physical transmission medium * ''gravitational radiation'', in the form of gravitational waves, ripples in spacetime Radiation is often categorized as either ''ionizing'' or '' non-ionizing'' depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 electron volts (eV), which is enough to ionize atoms and molecules and break chemical bonds. This is an important distinction due to the larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Landslide
A volcanic landslide or volcanogenic landslide is a type of mass wasting that takes place at volcanoes. Occurrences All volcanic edifices are susceptible to landslides, particularly stratovolcanoes and shield volcanoes where landslides are important processes. Volcanic landslides range in size from less than to more than . The largest volcanic landslides on Earth occur from submarine volcanoes and are several times larger than those that occur on land. Submarine landslides with volumes of have occurred in the Canary Islands within the last 43 million years, but the largest submarine landslides could have been up to in volume. Massive submarine landslides have also taken place in the Hawaiian Islands over the last several million years, the largest of which constitute significant portions of the islands from which they originated. Smaller landslides have also been identified at volcanoes on Mars and Venus. Martian landslides reach lengths of and more whereas the largest Venus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arequipa
Arequipa (; Aymara language, Aymara and ), also known by its nicknames of ''Ciudad Blanca'' (Spanish for "White City") and ''León del Sur'' (Spanish for "South's Lion"), is a city in Peru and the capital of the eponymous Arequipa (province), province and department of Arequipa, department. It is the seat of the Constitutional Court of Peru and often dubbed the "legal capital of Peru". It is the second most populated city in Peru, after the capital Lima, with an urban population of 1,296,278 inhabitants according to the 2017 national census. known for its colonial architecture and volcanic stone buildings, it is a major cultural and economic center. Its metropolitan area integrates twenty-one districts, including the foundational central area, which it is the seat of the city government. The city had a nominal GDP of US$9,445 million, equivalent to US$10,277 per capita (US$18,610 per capita PPP) in 2015, making Arequipa the city with the second-highest economic activity in Peru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detachment Fault
A detachment fault is a gently dipping normal fault associated with large-scale extensional tectonics. Detachment faults often have very large displacements (tens of km) and juxtapose unmetamorphosed hanging walls against medium to high-grade metamorphic footwalls that are called metamorphic core complexes. They are thought to have formed as either initially low-angle structures or by the rotation of initially high-angle normal faults modified also by the isostatic effects of tectonic denudation. They may also be called denudation faults. Examples of detachment faulting include: *The Snake Range detachment system of the Basin and Range Province of western North America which was active during the Miocene *The Nordfjord-Sogn detachment of western Norway active during the Devonian Period *The Whipple detachment in southeastern California Detachment faults have been found on the sea floor close to divergent plate boundaries characterised by a limited supply of upwelling magma, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cataclasite
Cataclasite is a cohesive granular Fault (geology)#Fault rock, fault rock. Comminution, also known as cataclasis, is an important process in forming cataclasites. They fall into the category of cataclastic rocks which are formed through faulting or fracturing in the upper Crust (geology), crust. Cataclasites are distinguished from fault gouge, which is incohesive, and fault breccia, which contains coarser fragments. Types Cataclasites are composed of fragments of the pre-existing wall rock as well as a Matrix (geology), matrix consisting of crushed microfragments, which cohesively holds the rock together. There are different types of classification schemes for cataclasites in the fault rock literature. The original classification scheme by Sibson classifies them by their proportion of fine-grained matrix to angular fragments. The term fault breccia is used for describing a cataclasite with coarser grains. A fault breccia is a cataclastic rock with clasts that are larger t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismicity
Seismicity is a measure encompassing earthquake occurrences, mechanisms, and magnitude at a given geographical location. As such, it summarizes a region's seismic activity. The term was coined by Beno Gutenberg and Charles Francis Richter in 1941. Seismicity is studied by geophysicists. Calculation of seismicity Seismicity is quantitatively computed. Generally, the region under study is divided in equally sized areas defined by latitude and longitude, and the Earth's interior is divided into various depth intervals on account of Earth's layering: Up to depth, , and > . The usual formula to calculate seismicity is: S = \frac where : _i: is the energy of a single seismic event (i.e., earthquake); : _0: interval of latitude; : _0: interval of longitude : _0: interval of the hypocenter; : _0: interval of the time of the seismic event. : The result is seismicity as energy per cubic unit. See also * Moment magnitude scale * Plate tectonics * Seismology * Wadati–Benioff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Record
The geologic record in stratigraphy, paleontology and other natural sciences refers to the entirety of the layers of rock strata. That is, deposits laid down by volcanism or by deposition of sediment derived from weathering detritus (clays, sands etc.). This includes all its fossil content and the information it yields about the history of the Earth: its past climate, geography, geology and the evolution of life on its surface. According to the law of superposition, sedimentary and volcanic rock layers are deposited on top of each other. They harden over time to become a solidified ( competent) rock column, that may be intruded by igneous rocks and disrupted by tectonic events. Correlating the rock record At a certain locality on the Earth's surface, the rock column provides a cross section of the natural history in the area during the time covered by the age of the rocks. This is sometimes called the ''rock history'' and gives a window into the natural history of the locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coefficient Of Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of the processes involved is called tribology, and has a history of more than 2000 years. Friction can have dramatic consequences, as illustrated by the use of friction created by rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire. Another important consequence of many types of friction can be wear, which may lead to performance degradation or damage to components. It is known that frictional energy losses account for about 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world. As briefly discussed later, there are many different contributors to the retarding force in friction, ranging from asperity deformation to the generation of charges and changes in local structure. When two bodies in contact move relative to each other, due to these various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |