|
Prowler (satellite)
Prowler was an American reconnaissance satellite launched aboard in 1990 to study Soviet Union, Soviet satellites in geosynchronous orbit. The government of the United States has never acknowledged its existence, however it has been identified by satellite watching, amateur observers and through leaked information. Spacecraft Prowler was based on the HS-376 satellite bus, developed by Hughes Aircraft, Hughes. It had a mass of around and carried modifications to reduce its visibility to ground-based observers and to radar. Following the satellite's retirement these modifications ceased to be effective, allowing it to be found by amateur observers. Prowler was designed to maneuver to within a few meters of satellites in geosynchronous orbit. Its purpose was either to monitor them and return data about them, or to perform a signals intelligence mission such as intercepting communications between those satellites and the ground. Launch It seems that Prowler was deployed from Space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Reconnaissance Office
The National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) is a member of the United States Intelligence Community and an agency of the United States Department of Defense which designs, builds, launches, and operates the reconnaissance satellites of the U.S. federal government. It provides satellite intelligence to several government agencies, particularly signals intelligence (SIGINT) to the National Security Agency (NSA), imagery intelligence (IMINT) to the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA), and measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) to the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA). The NRO announced in 2023 that it plans within the following decade to quadruple the number of satellites it operates and increase the number of signals and images it delivers by a factor of ten. NRO is considered, along with the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), NSA, DIA, and NGA, to be one of the "big five" U.S. intelligence agencies. The NRO is headquartered in Chantilly, Virginia, south of Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
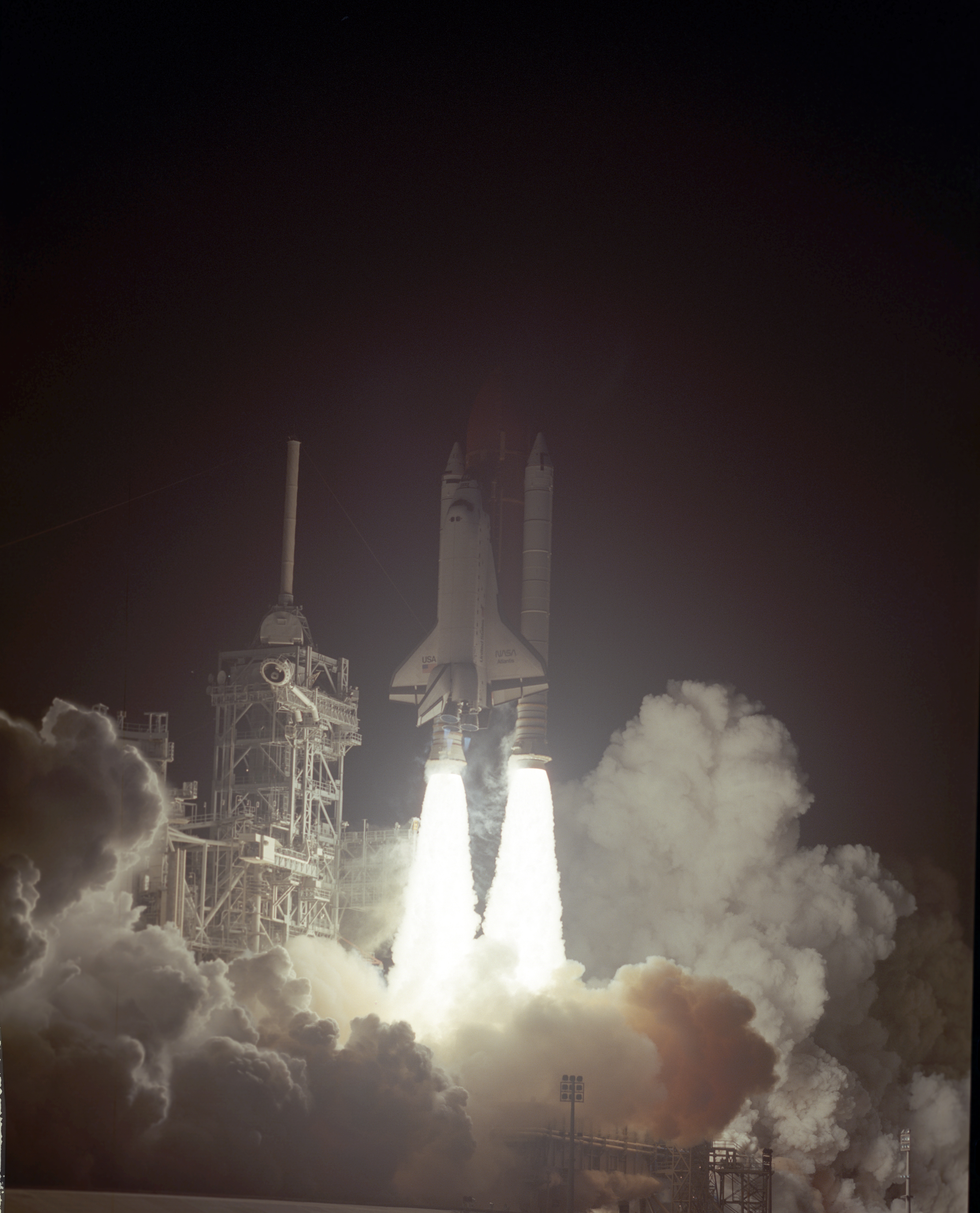
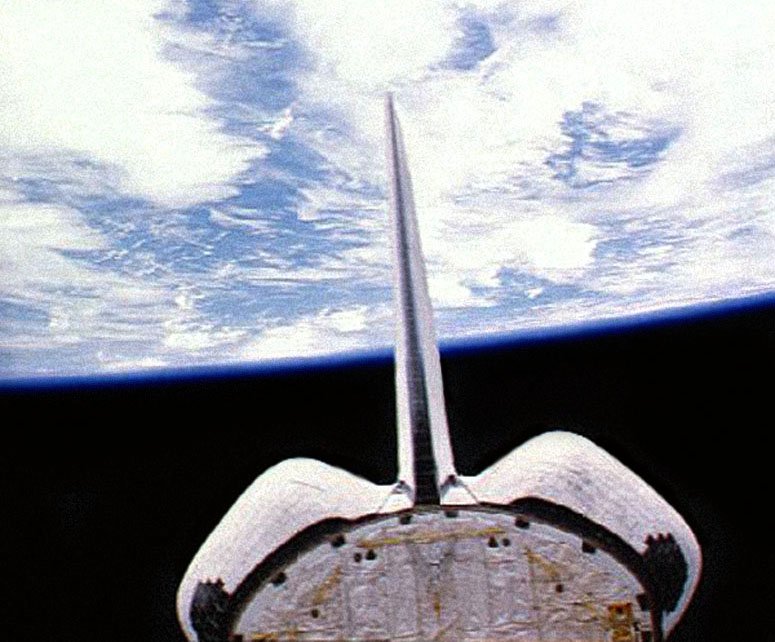
STS038-84-23 Atlantis
STS, or sts, may refer to: Medicine * Secondary traumatic stress, a condition which leads to a diminished ability to empathize * Sequence-tagged site, a gene-reference in genomics * Soft-tissue sarcoma * Staurosporine, an antibiotic * STS (gene), which codes for steroid sulfatase * Superior temporal sulcus * Sinus tarsi syndrome, a foot condition Places * Semipalatinsk Test Site for Soviet nuclear weapons * Staffordshire, county in England, Chapman code Transport * Cadillac STS, a luxury car * NASA Space Transportation System, the system in which the NASA shuttle is part of and only surviving component of; starting as a 1969 NASA proposal system for reusable space vehicles ** NASA Space Shuttle program, the shuttle program itself, whose mission were referred to with STS-numbering * Sail training ship, a ship prefix * Satellite Transit System, now called the SEA Underground, airport transit in Seattle-Tacoma International Airport * Ship-to-ship transfer, between seagoing ships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 1990
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather satellite, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, Planetary science, planetary exploration, and Space transport, transportation of Human spaceflight, humans and cargo spacecraft, cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Geocentric orbit, Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other Astronomical object, celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Satellites
A military satellite is an artificial satellite used for a military purpose. The most common missions are intelligence gathering, navigation and military communications. The first military satellites were photographic reconnaissance missions. Some attempts were made to develop satellite based weapons but this work was halted in 1967 following the ratification of international treaties banning the deployment of weapons of mass destruction in orbit. As of 2013, there are 950 satellites of all types in Earth orbit. It is not possible to identify the exact number of these that are military satellites partly due to secrecy and partly due to dual purpose missions such as GPS satellites that serve both civilian and military purposes. As of December 2018 there are 320 known military or dual-use satellites in the sky, half of which are owned by the US, followed by Russia, China and India. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zirconic
Zirconic was a National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) codename for a program initiated under the Presidency of Ronald Reagan to develop reconnaissance satellites equipped with stealth technology. Concealed within the Byeman Control System (BYEMAN), Zirconic operated as a special compartment and encompassed the Misty and Prowler spacecraft, each designed to minimize radar, visible, infrared, and laser signatures. Access to any Zirconic-related data required a dedicated “Zirconic clearance,” and the underlying development effort was internally codenamed Nebula. Misty deployments began in 1990, when Misty‑1 launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis and was deployed “over the side” rather than through a conventional payload bay ejection; amateur observers nevertheless visually tracked Misty within months. Misty 2 followed in 1999 atop a Titan IV-B rocket, during which observers noted the ejection of a high‑altitude decoy intended to obscure the true payload’s orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Based Space Surveillance
The Space Based Space Surveillance (SBSS) system is a planned United States Space Force constellation of satellites and supporting ground infrastructure that will improve the ability of the United States Department of Defense (DoD) to detect and track space objects in orbit around the Earth. The SBSS development work is being conducted in coordination with the Space Situational Awareness Group in the Space Superiority Systems Wing of the Space and Missile Systems Center. Pathfinder satellite The first "pathfinder" satellite of the SBSS system (SBSS 1, aka USA 216, COSPAR 2010-048A, SATCAT 37168) was successfully placed into orbit on board a Minotaur IV rocket on 26 September 2010 (UTC). Originally, the launch was scheduled for December 2008 but was rescheduled for Spring of 2009, and again delayed until 22 October 2009. The launch delays were caused by problems with the booster, and not the satellite itself. A launch expected for 8 July 2010 was also postponed. The program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MiTEx
The Micro-satellite Technology Experiment (MiTEx) is a Miniaturized satellite, microsatellite-based mission launched into geosynchronous orbit 21 June 2006 aboard a Delta II rocket. The United States Air Force, USAF described the mission as a joint "technology demonstration" mission for the DARPA, Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the United States Air Force (USAF) and the United States Navy (US Navy). MiTEx consists of three spacecraft; two inspection satellites, designated List of USA satellites, USA-187 and USA-188, and an experimental upper stage, designated List of USA satellites, USA-189. The two inspection satellites were initially used to inspect each other; however, they were later used to inspect Defense Support Program, DSP-23, a failed missile detection satellite, to find out why it stopped operating. The MiTEx goal was to demonstrate technologies such as lightweight power and propulsion systems, avionics, structures, commercial off-the-shelf c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Misty (satellite)
Misty is reportedly the name of a classified project by the United States National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) to operate stealthy reconnaissance satellites. The satellites are conjectured to be photo reconnaissance satellites and the program has been the subject of atypically public debates about its worthiness in the defense budget since December 2004. The estimated project costs in 2004 were, at the time of statement, US$9.5 billion (inflation adjusted US$ billion in ). Launches The first satellite (USA-53 or 1990-019B, 19,600 kg) launched for the program was deployed on 1 March 1990 by the Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' as part of Mission STS-36. Objects associated with the satellite decayed on 31 March 1990, but the satellite was seen and tracked later that year and in the mid-1990s by amateur observers. The second satellite (USA-144 or 1999-028A ) was launched on 22 May 1999, and by 2004 the launch of a third satellite was planned for 2009. Circumstantial evidence sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 in the context of European integration. Its 2025 annual budget was €7.7 billion. The ESA Human and Robotic Exploration programme includes human spaceflight (mainly through participation in the International Space Station programme); as well as the launch and operation of missions to Mars and Moon. Further activities include science missions to Jupiter, Mercury, the Sun, Earth observation, Asteroid impact avoidance and Telecommunications missions, designing launch vehicles; and maintaining Europe's Spaceport, the Guiana Space Centre at Kourou (French Guiana). Further programmes include space safety, satellite navigation, applications and commercialisation. The main European launch vehicle Ariane 6 is operated through Arianespace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ted Molczan
Satellite watching or satellite spotting is a hobby which consists of the observation and tracking of artificial satellites that are geocentric orbit, orbiting Earth. People with this hobby are variously called satellite watchers, trackers, spotters, observers, etc. Since satellites outside Earth's shadow reflect sunlight, those especially in low Earth orbit may visibly glint (or "satellite flare, flare") as they pass (spaceflight), traverse the observer's sky, usually during twilight. History Amateur satellite spotting traces back to the days of early artificial satellites when the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory launched the Operation Moonwatch program in 1956 to enlist amateur astronomers in an early citizen science effort to track Soviet Union, Soviet ''sputniks''. The program was an analog to the World War II Ground Observer Corps citizen observation program to spot enemy bombers. Moonwatch was crucial until professional stations were deployed in 1958. The program w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Catalog Number
The Satellite Catalog Number (SATCAT), also known as NORAD Catalog Number, NORAD ID, USSPACECOM object number, is a sequential nine-digit number assigned by the United States Space Command (USSPACECOM), and previously the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD), in the order of launch or discovery to all artificial objects in the orbits of Earth and those that left Earth's orbit. For example, catalog number 1 is the Sputnik 1 launch vehicle, with the Sputnik 1 satellite having been assigned catalog number 2. Objects that fail to orbit or orbit for a short time are not catalogued. The minimum object size in the catalog is in diameter. , the catalog listed 58,010 objects, including 16,645 satellites that had been launched into orbit since 1957 of which 8,936 were still active. 25,717 of the objects were well tracked while 2,055 were lost. In addition USSPACECOM was also tracking 16,600 analyst objects. Analyst objects are variably tracked and in constant flux, so their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |