|
Proplatynotia
''Proplatynotia'' is an extinct genus of varanoid lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. Fossils have been found in the Barun Goyot Formation, which is mid-Campanian in age. The type and only species, ''P. longirostratia'', was named in 1984. Description ''Proplatynotia'' was named in 1984 from a single holotype skull cataloged as ZPAL MgR-I/68. The skull is mostly complete except for damage in the posterior area. Rounded plates of osteoderms cover the top surface and would have been covered in scales in life. Compared to other Cretaceous varanoids, ''Proplatynotia'' was medium-sized with a skull about long. Its skull is long and slender, giving the type species ''P. longirostratia'' its name, which means "long snout." Bones in the back of the skull called parietals are enlarged, indicating that it may have had larger jaw muscles and a stronger bite than most monitor lizards. ''Proplatynotia'' has many primitive varanoid features, including nostrils that are placed near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platynota
Platynota is a polyphyletic group of anguimorph lizards and thus belongs to the order Squamata of the class Reptilia. Since it was named in 1839, it has included several groups, including monitor lizards, snakes, mosasaurs, and helodermatids. Its taxonomic use still varies, as it is sometimes considered equivalent to the group Varanoidea and other times viewed as a distinct group. It is phylogenetically defined as a clade containing Varanidae (the monitor lizards). It also includes many extinct species. Description Many skeletal features support the grouping of monitor lizards, helodermatids, and several extinct species in Platynota. All platynotans have a hinged upper jaw with widely spaced teeth, each having a large base, that erupt from behind existing teeth. The teeth are plicidentine, meaning that they have highly folded layers of dentine in their centers. Many have fused frontal and nasal bones on the top of their skulls (in other lizards, these bones are separated into p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barun Goyot Formation
The Barun Goyot Formation (also known as Baruungoyot Formation or West Goyot Formation) is a geological formation dating to the Late Cretaceous Period. It is located within and is widely represented in the Gobi Desert Basin, in the Ömnögovi Province of Mongolia. Description It was previously known as the Lower Nemegt Beds occurring beneath the Nemegt Formation and above the Djadokhta Formation. It has been suggested that the Djadokhta and Barun Goyot Formations are lower and upper parts, respectively, of the same lithological unit and the boundary between the two does not exist. The stratotype of the Barun Goyot Formation is the Khulsan locality, east of Nemegt. At Nemegt, only the uppermost barungoyotian beds are visible. The ''Red Beds of Khermeen Tsav'' are also considered part of the Barun Goyot Formation. It is approximately in thickness,Gradzinski, R.; & Jerzykiewicz, T. (1974). Sedimentation of the Barun Goyot formation. Palaeontologica Polonica, 30, 111-146. and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helodermatidae
The Helodermatidae or beaded lizards are a small family of lizards endemic to North America today, but formerly more widespread in the ancient past. Traditionally, the Gila monster and the Mexican beaded lizard were the only species recognized, although the latter has recently been split into several species. While the fossil record of this family may date back to as far as the Cretaceous with genera such as ''Primaderma'' and ''Paraderma'' of North America, the oldest definitive members of the Helodermatidae date to the Early Oligocene, with ''Lowesaurus matthewi'' from North America (Nebraska) and ''Euheloderma gallicum'' from Europe (France). References {{Reflist Lizard families Taxa named by John Edward Gray Helodermatidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given case predicable, so ancestral characters should not be imputed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is homoplasy. The recurrent evolution of flight is a classic example, as flying insects, birds, pterosaurs, and bats have independently evolved the useful capacity of flight. Functionally similar features that have arisen through convergent evolution are ''analogous'', whereas ''homologous'' structures or traits have a common origin but can have dissimilar functions. Bird, bat, and pterosaur wings are analogous structures, but their forelimbs are homologous, sharing an ancestral state despite serving different functions. The opposite of convergence is divergent evolution, where related species evolve different traits. Convergent evolution is similar to paralle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
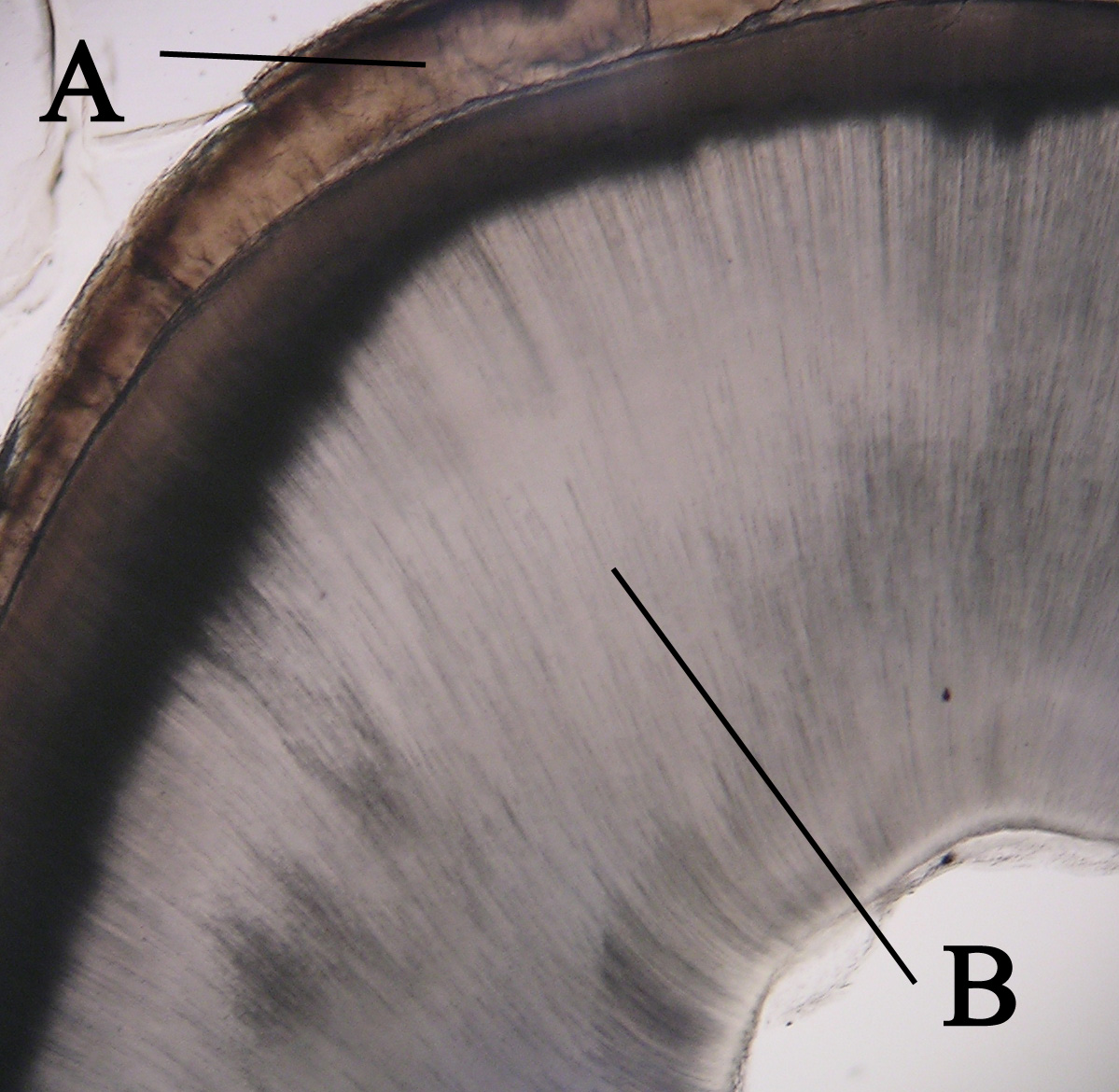
Pulp (tooth)
The pulp is the connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and odontoblasts that comprise the innermost layer of a tooth. The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour. Anatomy The pulp is the neurovascular bundle central to each tooth, permanent or primary. It is composed of a central pulp chamber, pulp horns, and radicular canals. The large mass of the pulp is contained within the pulp chamber, which is contained in and mimics the overall shape of the crown of the tooth.Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 164. Because of the continuous deposition of the dentine, the pulp chamber becomes smaller with the age. This is not uniform throughout the coronal pulp but progresses faster on the floor than on the roof or sidewalls. Radicular pulp canals extend down from the cervical region of the crown to the root apex. They are not always straight but vary in shape, size, and number. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentine
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |