|
Prison Of Anemas
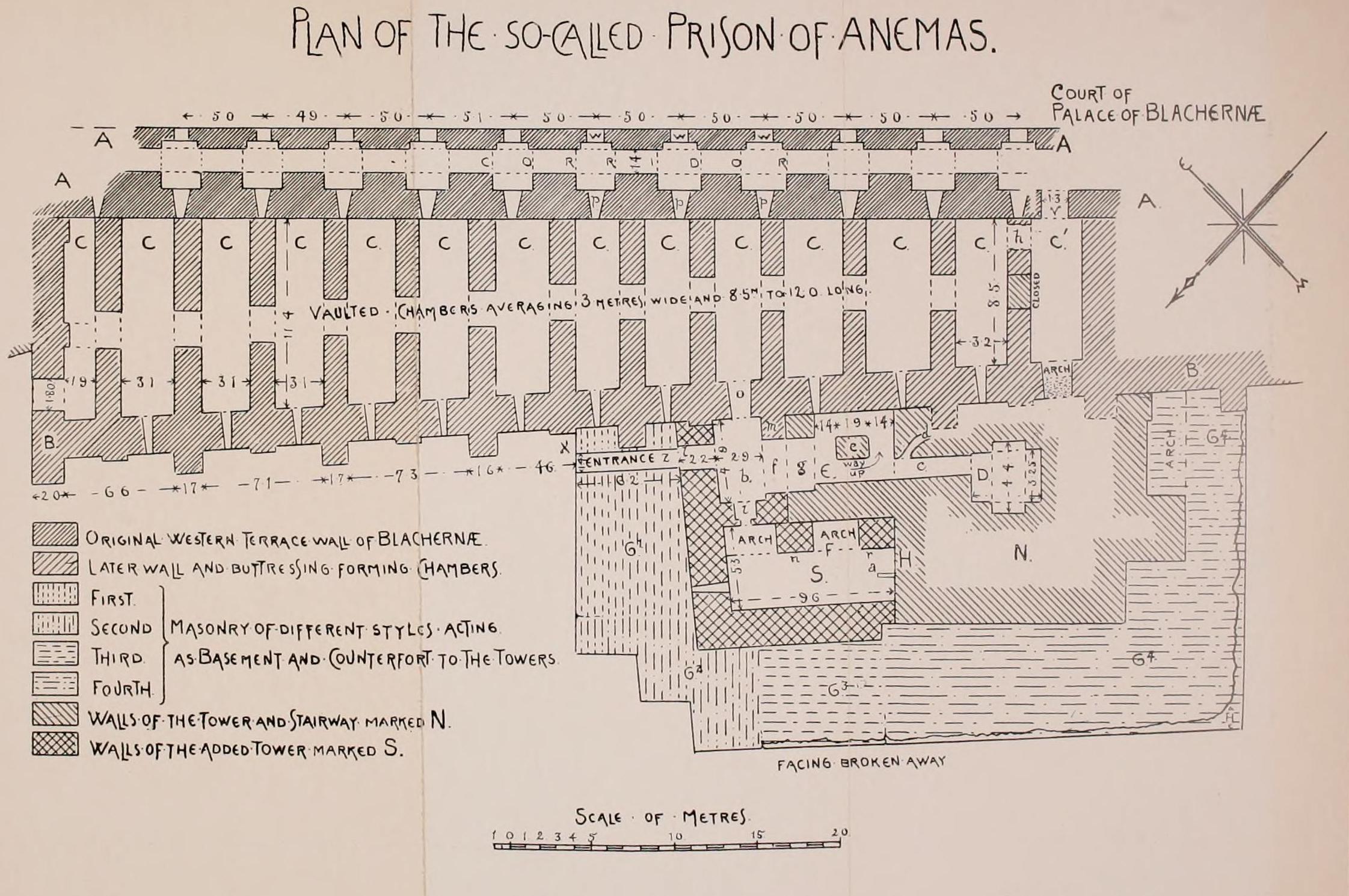
The Prison of Anemas () is a large Byzantine building attached to the walls of the city of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul, Turkey). It is traditionally identified with the prisons named after Michael Anemas, a Byzantine general who rose in unsuccessful revolt against Emperor Alexios I Komnenos (r. 1081–1118) and was the first person to be imprisoned there. The prison features prominently in the last centuries of the Byzantine Empire, when four Byzantine emperors were imprisoned there. Description The building is located in the suburb of Blachernae, between the mid-12th century stretch of walls constructed by the Emperor Manuel I Komnenos (r. 1143–1180) and the earlier walls of Byzantine emperors Heraclius (r. 610–641) and Leo V the Armenian (r. 813–820). A small stretch of wall connects the structure to the east with the wall of Manuel Komnenos. The structure's outer wall itself is extraordinarily high, rising as high as 23 m above the ground in front of it, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millingen - Plan Of Anemas Prison
{{surname, name=Millingen ...
Millingen or van Millingen is a surname, and may refer to: *Alexander van Millingen (1840–1915), scholar * Evelina van Millingen (1831—1900), hostess, a cultivator of gardens, and novelist *James Millingen (1774–1845), Dutch-English archaeologist * John G. Millingen (1782–1862), British army surgeon and author *Julius Michael Millingen (1800–1878), English physician and writer See also *Millingen aan de Rijn Millingen aan de Rijn ( ) is a former municipality and a town in the eastern Netherlands, on the border with Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buttress
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall. Buttresses are fairly common on more ancient (typically Gothic) buildings, as a means of providing support to act against the lateral (sideways) forces arising out of inadequately braced roof structures. The term ''counterfort'' can be synonymous with buttress and is often used when referring to dams, retaining walls and other structures holding back earth. Early examples of buttresses are found on the Eanna Temple (ancient Uruk), dating to as early as the 4th millennium BC. Terminology In addition to flying and ordinary buttresses, brick and masonry buttresses that support wall corners can be classified according to their ground plan. A clasping or clamped buttress has an L-shaped ground plan surrounding the corner, an angled buttress has two buttresses meeting at the corner, a setback buttress is similar to an angled buttress but the buttresses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaldia
Chaldia (, ''Khaldia'') was a historical region located in the mountainous interior of the eastern Black Sea, northeast Anatolia (modern Turkey). Its name was derived from a people called the ''Chaldoi'' (or '' Chalybes'') that inhabited the region in antiquity. Chaldia was used throughout the Byzantine period and was established as a formal theme, known as the Theme of Chaldia (Greek: θέμα Χαλδίας), by 840. During the Late Middle Ages, it formed the core of the Empire of Trebizond until its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1461. Anthony Bryer traces the origin of its name not to Chaldea, as Constantine VII had done, but to the Urartian language, for whose speakers Ḫaldi was the Sun God. Bryer notes at the time of his writing that a number of villages in the Of district were still known as "Halt". Other scholars, however, reject the Urartian connection. Χάλυψ, the tribe's name in Greek, means "tempered iron, steel", a term that passed into Latin as ''chalybs'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory Taronites (governor Of Chaldia)
Gregory Taronites (; ) was a Byzantine governor of the theme of Chaldia (modern north-eastern Black Sea coast of Turkey) who rebelled against Emperor Alexios I Komnenos in 1103/4 and governed his province as a virtually independent ruler until his defeat in battle in 1106/7. He was then imprisoned for some time in the Prison of Anemas, before obtaining an imperial pardon. Some scholars have proposed an identification with Gregory Gabras, but this is disputed. Origin and early life Gregory belonged to the aristocratic family of the Taronitai, a clan of princely Armenian origin from Taron. His parents are unknown, but he was the nephew of the ''panhypersebastos'' Michael Taronites, who married Maria Komnene, the sister of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos (r. 1081–1118). Some scholars, beginning with Karl Hopf and including Alexander Vasiliev and Claude Cahen, argued that Gregory Taronites was the same as Gregory Gabras, attested for the last time c. 1091. This was the son of Theodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mese (Constantinople)
The ''Mese'' ( ''i Mése dós', lit. "Middle treet) was the main thoroughfare of ancient Constantinople and the scene of many Byzantine imperial processions. Its ancient course is largely followed by the modern ''Divan Yolu'' ("Road to the Divan"). Route of the Mese The ''Mese'' started at the Milion monument, close to the Hagia Sophia, and led straight westwards. It passed the Hippodrome and the palaces of Lausos and Antiochus, and after ca. 600 meters reached the oval-shaped Forum of Constantine where one of the city's two Senate houses stood. This stretch of the street was also known as the ''Regia'' (, "Imperial Road"), as it formed the original ceremonial route from the Great Palace and the Augustaion square to the forum of the city's founder. From there, the street continued to the square Forum of Theodosius or Forum of the Bull (''Forum Tauri''), as it was also known. In about the middle of this stretch, the great mall known as ''Makros Embolos'' joined the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Mutilation In Byzantine Culture
Mutilation was a common method of punishment for criminals in the Byzantine Empire, but it also had a role in the empire's political life. By blinding a rival, one would not only restrict his mobility but also make it almost impossible for him to lead an army into battle, then an important part of taking control of the empire. Castration was also used to eliminate potential opponents. In the Byzantine Empire, for a man to be castrated meant that he was no longer a man—half-dead, "life that was half death". Castration also eliminated any chance of heirs being born to threaten either the emperor's or the emperor's children's place at the throne. Other mutilations were the severing of the nose ( rhinotomy), or the amputating of limbs. Rationale The mutilation of political rivals by the emperor was deemed an effective way of side-lining from the line of succession a person who was seen as a threat. Castrated men were not seen as a threat, as no matter how much power they gained t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Alexiad
The ''Alexiad'' () is a medieval historical and biographical text written around the year 1148, by the Byzantine princess Anna Komnene, daughter of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos. It was written in a form of artificial Attic Greek. Anna described the political and military history of the Byzantine Empire during the reign of her father, thus providing a significant account on the Byzantium of the High Middle Ages. Among other topics, the ''Alexiad'' documents the Byzantine Empire's interaction with the Crusades and highlights the conflicting perceptions of the East and West in the early 12th century. It does not mention the schism of 1054 – a topic which is very common in contemporary writing. It documents firsthand the decline of Byzantine cultural influence in eastern and western Europe, particularly in the West's increasing involvement in its geographic sphere. The ''Alexiad'' was paraphrased in vernacular medieval Greek in mid-14th century to increase its readability, which tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Komnene
Anna Komnene (; 1 December 1083 – 1153), commonly Latinized as Anna Comnena, was a Byzantine Greek historian. She is the author of the '' Alexiad'', an account of the reign of her father, Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos. Her work constitutes the most important primary source of Byzantine history of the late 11th and early 12th centuries, as well as of the early Crusades. Although she is best known as the author of the ''Alexiad'', Anna played an important part in the politics of the time and attempted to depose her brother John II Komnenos as emperor in favour of her husband, Nikephoros Bryennios the Younger.Hanawalt 1982, p. 303. At birth, Anna was betrothed to Constantine Doukas,Hanawalt 1982, p. 303. and she grew up in his mother's household.Neville 2016, p. 2. She was well-educated in "Greek literature and history, philosophy, theology, mathematics, and medicine." Anna and Constantine were next in the line to throne until Anna's younger brother, John II Komnenos, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revetment
A revetment in stream restoration, river engineering or coastal engineering is a facing of impact-resistant material (such as stone, concrete, sandbags, or wooden piles) applied to a bank or wall in order to absorb the energy of incoming water and protect it from erosion. River or coastal revetments are usually built to preserve the existing uses of the shoreline and to protect the slope. In architecture generally, it means a retaining wall. In military engineering it is a structure formed to secure an area from artillery, bombing, or stored explosives. Freshwater revetments Many revetments are used to line the banks of freshwater rivers, lakes, and man-made reservoirs, especially to prevent damage during periods of floods or heavy seasonal rains (see riprap). Many materials may be used: wooden piles, loose-piled boulders or concrete shapes, or more solid banks. Concrete revetments are the most common type of infrastructure used to control the Mississippi River. More than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brick
A brick is a type of construction material used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a unit primarily composed of clay. But is now also used informally to denote building units made of other materials or other chemically cured construction blocks. Bricks can be joined using Mortar (masonry), mortar, adhesives or by interlocking. Bricks are usually produced at brickworks in numerous classes, types, materials, and sizes which vary with region, and are produced in bulk quantities. Concrete masonry unit, ''Block'' is a similar term referring to a rectangular building unit composed of clay or concrete, but is usually larger than a brick. Lightweight bricks (also called lightweight blocks) are made from expanded clay aggregate. Fired bricks are one of the longest-lasting and strongest building materials, sometimes referred to as artificial stone, and have been used since . Air-dried bricks, also known as mudbricks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Blachernae
The Palace of Blachernae (). was an imperial Roman residence in the suburb of Blachernae, located in the northwestern section of Constantinople (today located in the quarter of Ayvansaray in Fatih, Istanbul, Turkey). The area of the palace is now mostly overbuilt, and only literary sources are available as to its description. History The Palace of Blachernae was constructed on the northern slopes of the Sixth Hill of the city in circa 500. The hill itself was partially remodelled, particularly in later times, and a number of terraces created to support the various buildings comprising the palace complex. Although the main imperial residence during the 4th–11th centuries was the Great Palace at the eastern end of the city, the Blachernae palace was used at times, and is attested in the ceremonial protocols contained in the 10th-century ''De Ceremoniis'', or Explanation of the Order of the Palace, Chapters I.27, I.34, II.9, II.12) of Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitos (r. 91 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |