|
Principality Of Leiningen
The Principality of Leiningen (german: Fürstentum Leiningen) was a short-lived principality ruled by the Prince of Leiningen. History The principality emerged in 1803 in the course of secularization and was created when the princely branch of the House of Leiningen, which had been raised to the rank of a Prince of the Holy Roman Empire in 1779, was deprived of its lands on the left bank of the Rhine by France, namely at Dagsburg, Hardenburg and Dürkheim, and subsequently received the secularized Amorbach Abbey as an ample compensation in 1803. A few years later, the Principality of Leiningen was mediatized in 1806. Its territory is now included mainly in Baden-Württemberg, but partly in Bavaria and in Hesse Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Da .... Amorbach Abbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Of The Holy Roman Empire
Prince of the Holy Roman Empire ( la, princeps imperii, german: Reichsfürst, cf. '' Fürst'') was a title attributed to a hereditary ruler, nobleman or prelate recognised as such by the Holy Roman Emperor. Definition Originally, possessors of the princely title bore it as immediate vassals of the Emperor who held a fief (secular or ecclesiastical) that had no suzerain except the Emperor. However, by the time the Holy Roman Empire was abolished in 1806, there were a number of holders of Imperial princely titles who did not meet these criteria. Thus, there were two main types of princes: those who exercised ''Landeshoheit'' (sovereignty within one's territory while respecting the laws and traditions of the empire) as well as an individual or shared vote in the College of Princes, and those whose title was honorary (the possessor lacking an immediate Imperial fief and/or a vote in the Imperial Diet). The first came to be reckoned as "royalty" in the sense of being treated as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
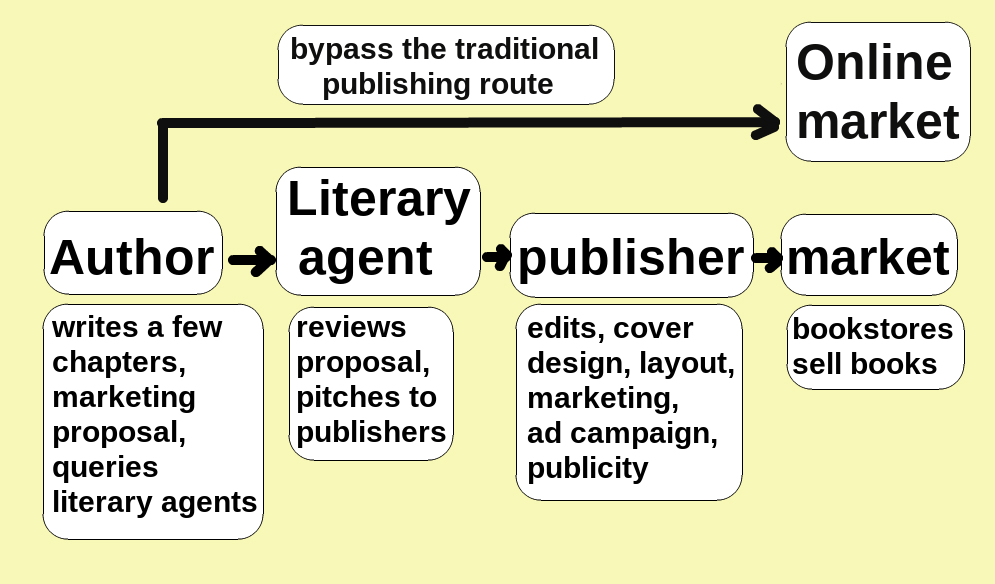
Books On Demand
Self-publishing is the publication of media by its author at their own cost, without the involvement of a publisher. The term usually refers to written media, such as books and magazines, either as an ebook or as a physical copy using POD (print on demand) technology. It may also apply to albums, pamphlets, brochures, games, video content, artwork, and zines. Web fiction is also a major medium for self-publishing. Definitions Although self-publishing is not a new phenomenon, dating back to the 18th century, it has transformed during the internet age with new technologies and services providing increasing alternatives to traditional publishing, becoming a $1 billion market.Jennifer Alsever, Fortune magazine, 30 December 2016The Kindle Effect Retrieved 9 November 2017, "...has become a $1 billion industry..." However, with the increased ease of publishing and the range of services available, confusion has arisen as to what constitutes self-publishing. In 2022, the Society o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Darmstadt and Kassel. With an area of 21,114.73 square kilometers and a population of just over six million, it ranks seventh and fifth, respectively, among the sixteen German states. Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Germany's second-largest metropolitan area (after Rhine-Ruhr), is mainly located in Hesse. As a cultural region, Hesse also includes the area known as Rhenish Hesse (Rheinhessen) in the neighbouring state of Rhineland-Palatinate. Name The German name '' Hessen'', like the names of other German regions (''Schwaben'' "Swabia", ''Franken'' "Franconia", ''Bayern'' "Bavaria", ''Sachsen'' "Saxony"), derives from the dative plural form of the name of the inhabitants or eponymous tribe, the Hessians (''Hessen'', singular ''Hesse''). The g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a total area of nearly , it is the third-largest German state by both area (behind Bavaria and Lower Saxony) and population (behind North Rhine-Westphalia and Bavaria). As a federated state, Baden-Württemberg is a partly-sovereign parliamentary republic. The largest city in Baden-Württemberg is the state capital of Stuttgart, followed by Mannheim and Karlsruhe. Other major cities are Freiburg im Breisgau, Heidelberg, Heilbronn, Pforzheim, Reutlingen, Tübingen, and Ulm. What is now Baden-Württemberg was formerly the historical territories of Baden, Prussian Hohenzollern, and Württemberg. Baden-Württemberg became a state of West Germany in April 1952 by the merger of Württemberg-Baden, South Baden, and Württemberg-Hohe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorbach Abbey
Amorbach Abbey (german: Kloster Amorbach) was a Benedictine imperial abbey of the Holy Roman Empire located at Amorbach. It was later the residence of the rulers of the short-lived Principality of Leiningen, before that became part of the Kingdom of Bavaria, and its historic buildings still belong to the princely family. The abbey is now in the district of Miltenberg in Lower Franconia, Bavaria, Germany. History The abbey was one of four Carolingian foundations intended to establish Christianity in the region of the Odenwald, the others being the monasteries of Lorsch, Fulda, and Mosbach). According to legend, a ''Gaugraf'' named Ruthard called the Frankish bishop Saint Pirmin to the area to set up a monastic settlement with chapel west of today's town, at the entrance to the Otterbachtal. A disciple of Pirmin, an Aquitanian called "Amor" is reported to have moved the monastery to its current location in 734. The patrons were the Virgin Mary, with Saints Simplicius, Faus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Dürkheim
Bad Dürkheim () is a spa town in the Rhine-Neckar urban agglomeration, and is the seat of the Bad Dürkheim district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Geography Location Bad Dürkheim lies at the edge of Palatinate Forest on the German Wine Route some 30 km east of Kaiserslautern and just under 20 km west of Ludwigshafen and Mannheim. Roughly 15 km to the south lies Neustadt an der Weinstraße. In Bad Dürkheim, ''Bundesstraßen'' 37 and 271 cross each other. From west to east through the town flows the river Isenach. Constituent communities Bad Dürkheim's ''Ortsteile'' are Grethen, Hardenburg, Hausen, Leistadt, Seebach and Ungstein including Pfeffingen. Climate Yearly precipitation in Bad Dürkheim is 574 mm, which is low, falling into the lowest quarter of the precipitation chart for all Germany. Lower figures recorded at only 16% of the German Weather Service's weather stations. The driest month is February. The most rainfall comes in May. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardenburg (Bad Dürkheim)
The Hardenburg on the eastern edge of the Palatinate Forest near the Rhineland-Palatinate town of Bad Dürkheim is even as a ruin one of the mightiest castles of Palatinate Palatinate or county palatine may refer to: *the territory or jurisdiction of a count palatine United Kingdom and Ireland *County palatine in England and Ireland * Palatinate (award), student sporting award of Durham University *Palatinate (col .... Literature * * * References External links Kreisstadt Bad Dürkheim: ''Burg Hardenburg''Burgen in Rheinland-Pfalz: ''Burg Hardenburg'' Wolfgang Braun: ''Rekonstruktionszeichnung'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Hardenburg (Bad Durkheim) Castles in Rhineland-Palatinate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagsburg
Dabo (german: Dagsburg) is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. History Previous names:Dictionnaire géographique de la Meurthe - Henri Lepage ''Dasburch'' (1188), ''Dasburg'' (1189) ''Dagesburg'' (1227), ''Tagesburg'' (1239), ''Dagespurg'' (1313), ''Dachspurg'' (1576). An informal Franco-German summit between President Mitterrand and Chancellor Kohl took place in Dabo July 19, 1983. Population References See also *Communes of the Moselle department The following is a list of the 725 communes of the Moselle department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Moselle (department) {{SarrebourgChâteauSalins-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Alsatian and Low Alemannic German; ksh, label=Ripuarian language, Ripuarian and Low Franconian languages, Low Franconian, Rhing; la, Rhenus ; hu, Rajna . is one of the major List of rivers of Europe, European rivers. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein, Swiss-Austrian border, Swiss-Austrian, Swiss-German border, Swiss-German borders. After that the Rhine defines much of the Franco-German border, after which it flows in a mostly northerly direction through the German Rhineland. Finally in Germany the Rhine turns into a predominantly westerly direction and flows into the Netherlands where it eventually empties into the North Sea. It drains an area of 9,9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Leiningen
The House of Leiningen is the name of an old German noble family whose lands lay principally in Alsace, Lorraine, Saarland, Rhineland, and the Palatinate. Various branches of this family developed over the centuries and ruled counties with Imperial immediacy. Origins The first count of Leiningen about whom anything definite is known was a certain Emich II (d. before 1138). He (and perhaps his father Emich I) built Leiningen Castle, which is now known as "Old Leiningen Castle" (German: ''Burg Altleiningen''), around 1100 to 1110. Nearby Höningen Abbey was built around 1120 as the family's burial place. This family became extinct in the male line when Count Frederick I died about 1220. Frederick I's sister, Liutgarde, married Simon II, Count of Saarbrücken. One of Liutgarde's sons, also named Frederick, inherited the lands of the counts of Leiningen, and he took their arms and their name as Frederick II (d. 1237). He became known as a '' Minnesinger'', and one of his son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |