|
Prince Qian
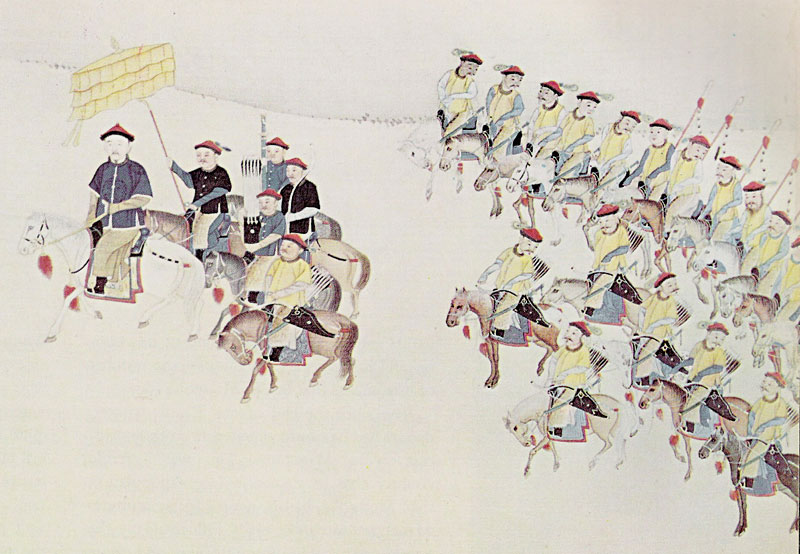
Prince Qian of the Second Rank, or simply Prince Qian, was the title of a princely peerage used in China during the Manchu-led Qing dynasty (1644â1912). As the Prince Qian peerage was not awarded "iron-cap" status, this meant that each successive bearer of the title would normally start off with a title downgraded by one rank ''vis-à -vis'' that held by his predecessor. However, the title would generally not be downgraded to any lower than a ''feng'en fuguo gong'' except under special circumstances. The first bearer of the title was Wakeda (ç¦å é; 1606â1652), DaiÅ¡an's fourth son and a grandson of Nurhaci (the founder of the Qing dynasty). In 1651, Wakeda was granted the title "Prince Qian of the Second Rank" by the Shunzhi Emperor. The peerage was discontinued in 1698 after the Kangxi Emperor stripped Lioyung (çé; Wakeda's son) of his title for committing an offence. However, the Qianlong Emperor restored the peerage in 1778 and granted it to Dongfu (æ´ç¦; Lioyung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal And Noble Ranks Of The Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty (1644â1912) of China developed a complicated peerage system for royal and noble ranks. Rule of inheritance In principle, titles were downgraded one grade for each generation of inheritance. * Direct imperial princes with the ''Eight Privileges'' were downgraded for four generations, after which the title can be inherited without further downgrades. * Direct imperial princes without the ''Eight Privileges'' were downgraded until the rank of ''feng'en jiangjun'', which then became perpetual. * Cadet line imperial princes and lords were downgraded until they reached ''feng'en jiangjun'', which could be further inherited three times before the title expired completely. * For non-imperial peers, the title could be downgraded to ''en jiwei'' before becoming perpetually heritable. Occasionally, a peer could be granted the privilege of ''shixi wangti'' ( zh, t=ä¸è¥²ç½æ¿, p=shìxà wÇngtì, labels=no; "perpetual heritability"), which allowed the title to be p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchu People
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616â1636), Later Jin (1616â1636) and Qing dynasty, Qing (1636â1912) dynasties of China were established and ruled by the Manchus, who are descended from the Jurchen people who earlier established the Jin dynasty (1115â1234), Jin dynasty (1115â1234) in northern China. Manchus form the largest branch of the Tungusic peoples and are distributed throughout China, forming the fourth largest ethnic group in the country. They are found in 31 Chinese provincial regions. Among them, Liaoning has the largest population and Hebei, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Inner Mongolia and Beijing have over 100,000 Manchu residents. About half of the population live in Liaoning and one-fifth in Hebei. There are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912â1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616â1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aisin Gioro
The House of Aisin-Gioro is a Manchu clan that ruled the Later Jin dynasty (1616â1636), the Qing dynasty (1636â1912), and Manchukuo (1932â1945) in the history of China. Under the Ming dynasty, members of the Aisin Gioro clan served as chiefs of the Jianzhou Jurchens, one of the three major Jurchen tribes at this time. Qing bannermen passed through the gates of the Great Wall in 1644, and eventually conquered the short-lived Shun dynasty, Xi dynasty and Southern Ming dynasty. After gaining total control of China proper, the Qing dynasty later expanded into other adjacent regions, including Xinjiang, Tibet, Outer Mongolia, and Taiwan. The dynasty reached its zenith during the High Qing era and under the Qianlong Emperor, who reigned from 1735 to 1796. This reign was followed by a century of gradual decline. The house lost power in 1912 following the Xinhai Revolution. Puyi, the last Aisin-Gioro emperor, nominally maintained his imperial title in the Forbidden City un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daišan
DaiÅ¡an (Manchu: ; 19 August 1583 – 25 November 1648) was an influential Manchu prince and statesman of the Qing dynasty. Family background DaiÅ¡an was born in the Manchu Aisin Gioro clan as the second son of Nurhaci, the founder of the Qing dynasty. His mother was Nurhaci's first consort, Lady Tunggiya (ä½ä½³æ°). He was an older half-brother of Nurhaci's successor, Hong Taiji. Career Nurhaci's reign During Nurhaci's campaign against the Ula clan and its ''beile'' Bujantai in 1607, DaiÅ¡an distinguished himself on the battlefield by assisting Å urhaci and Cuyen. For his efforts, he was granted the title of "Guyen Baturu" () (literally: "exploring hero"). In 1613, DaiÅ¡an again distinguished himself on the battlefield in Nurhaci's campaign against the Ula clan. In 1616, when Nurhaci declared himself khan and established the Later Jin dynasty, DaiÅ¡an was the first selected as '' beile'' of a special rank by Nurhaci to assist in administration. These four ''beile'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 â 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing, was the founding khan of the Jurchen people, Jurchen-led Later Jin (1616â1636), Later Jin dynasty. As the leader of the House of Aisin-Gioro, Nurhaci reorganized and united various Jurchen tribes (the later "Manchu people, Manchu"), consolidated the Eight Banners military system, and eventually launched attacks on both the Ming dynasty, Ming and Joseon dynasties. His conquest of Ming dynasty's northeastern Liaodong region laid the groundwork for the Qing conquest of the Ming by his descendants, who proclaimed the Qing dynasty in 1636. He is also generally credited with ordering the creation of a new written script for the Manchu language based on the Mongolian script, Mongolian vertical script. Name and titles Nurhaci is written as in Manchu language. Some suggest that the meaning of the name in the Manchu language is "the skin of a wild boar". Another explanation is "brav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 â 5 February 1661), also known by his temple name Emperor Shizu of Qing, personal name Fulin, was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper. Upon the death of his father Hong Taiji, a Deliberative Council of Princes and Ministers, committee of Manchu princes chose the 5-year-old Fulin as successor. The princes also appointed two co-regents: Dorgon, the 14th son of Nurhaci, and Jirgalang, one of Nurhaci's nephews, both of whom were members of the Qing imperial clan. In November 1644, the Shunzhi Emperor was enthroned as emperor of China in Beijing. From 1643 to 1650, political power lay mostly in the hands of the prince regent Dorgon. Under his leadership, the Qing conquered most of the territory of the fallen Ming dynasty, chased Southern Ming, Ming loyalist regimes deep into the southwestern provinces, and established the basis of Qing rule over China proper despite highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 165420 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, personal name Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign of 61 years makes him the longest-reigning emperor in Chinese history and one of the longest-reigning rulers in history. He is considered one of China's greatest emperors. The third son of the Shunzhi Emperor, Kangxi was enthroned at the age of seven while actual power was held for six more years by the four regents nominated by his father. After assuming personal rule, Kangxi's attempt to revoke the fiefdoms of feudal princes sparked the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, which he suppressed. He also forced the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan and Mongols in the north and northwest to submit to Qing rule, and launched an expedition that incorporated Tibet into the empire. Domestically, he initially welcomed the Jesuits and the propagation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Li (禮)
Prince Li of the First Rank (Manchu language, Manchu: ; ''hoÅ¡oi doronggo cin wang''), or simply Prince Li, was the title of a Royal and noble ranks of the Qing dynasty#Rule of inheritance, princely peerage of the Manchu people, Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. It was also one of the Aisin Gioro#Iron-cap princes and their descendants, 12 "iron-cap" princely peerages in the Qing dynasty, which meant that the title could be passed down without being downgraded. The first bearer of the title was DaiÅ¡an (1583â1648), the second son of Nurhaci, the founder of the Later Jin (1616â1636), Later Jin dynasty. He was awarded the title in 1636 by his half-brother, Hong Taiji, who succeeded their father to the Later Jin throne and who later founded the Qing dynasty. The peerage was renamed to Prince Xun of the First Rank (Prince Xun) in 1651 during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor, and to Prince Kang of the First Rank (Prince Kang) in 1659, before it was renamed back to Prince Li of the Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft History Of Qing
The ''Draft History of Qing'' () is a draft of the official history of the Qing dynasty compiled and written by a team of over 100 historians led by Zhao Erxun who were hired by the Beiyang government of the Republic of China. The draft was published in 1928, but the Chinese Civil War caused a lack of funding for the project and it was put to an end in 1930. The two sides of the Chinese civil war, the People's Republic of China and Republic of China have attempted to complete it. History The Qing imperial court had previously established a Bureau of State Historiography that pre-compiled its own dynastic history. The massive book was started in 1914, and the rough copy was finished in about 1927. 1,100 copies of the book were published. The Beiyang government moved 400 of the original draft into the northern provinces, where it re-edited the content twice, thus creating three different versions of the book. It was banned by the Nationalist Government in 1930. The ban was lift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |