|
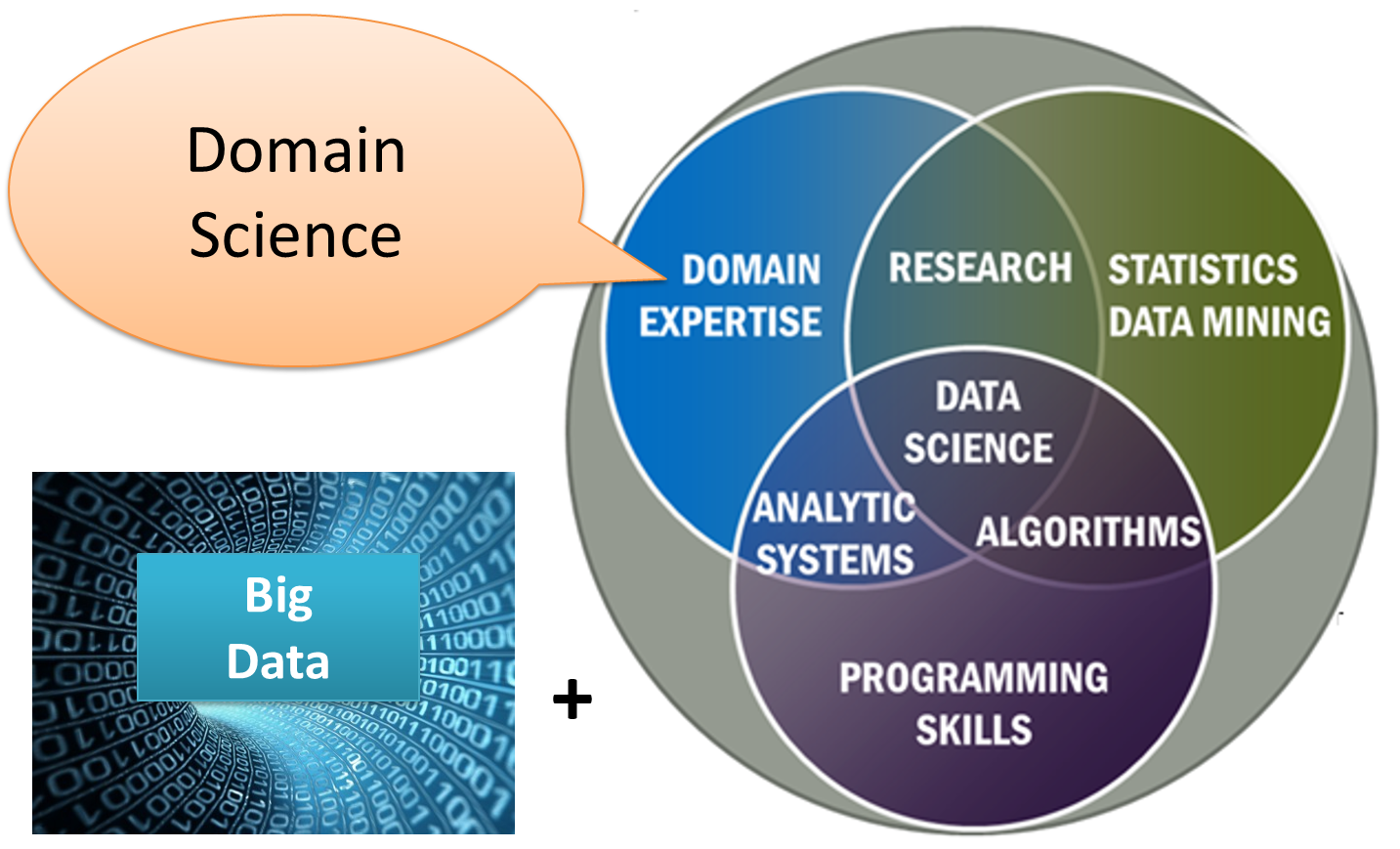
Population Informatics
The field of population informatics is the systematic study of populations via secondary analysis of massive data collections (termed " big data") about people. Scientists in the field refer to this massive data collection as the social genome, denoting the collective digital footprint of our society. Population informatics applies data science to social genome data to answer fundamental questions about human society and population health much like bioinformatics applies data science to human genome data to answer questions about individual health. It is an emerging research area at the intersection of SBEH (Social, Behavioral, Economic, & Health) sciences, computer science, and statistics in which quantitative methods and computational tools are used to answer fundamental questions about our society. Introduction History The term was first used in August 2012 when the Population Informatics Lab was founded at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill by Dr. Hye-Cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Data
Though used sometimes loosely partly because of a lack of formal definition, the interpretation that seems to best describe Big data is the one associated with large body of information that we could not comprehend when used only in smaller amounts. In it primary definition though, Big data refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data-processing application software. Data with many fields (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data analysis challenges include capturing data, data storage, data analysis, search, sharing, transfer, visualization, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: ''volume'', ''variety'', and ''velocity''. The analysis of big data presents challenges in sampling, and thus previously allowing for only observations and sampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Economics
Computational Economics is an interdisciplinary research discipline that involves computer science, economics, and management science.''Computational Economics''."About This Journal"an"Aims and Scope" This subject encompasses computational modeling of economic systems. Some of these areas are unique, while others established areas of economics by allowing robust data analytics and solutions of problems that would be arduous to research without computers and associated numerical methods.• Hans M. Amman, David A. Kendrick, and John Rust, ed., 1996. ''Handbook of Computational Economics'', v. 1, ElsevierDescription & chapter-previelinks. • Kenneth L. Judd, 1998. ''Numerical Methods in Economics'', MIT Press. Links tdescription anchapter previews Computational methods have been applied in various fields of economics research, including but not limiting to: Econometrics: Non-parametric approaches, Semi-parametric approaches, and Machine Learning. Dynamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Data
Economic data are data describing an actual economy, past or present. These are typically found in time-series form, that is, covering more than one time period (say the monthly unemployment rate for the last five years) or in cross-sectional data in one time period (say for consumption and income levels for sample households). Data may also be collected from surveys of for example individuals and firms or aggregated to sectors and industries of a single economy or for the international economy. A collection of such data in table form comprises a data set. Methodological economic and statistical elements of the subject include measurement, collection, analysis, and publication of data. 'Economic statistics' may also refer to a subtopic of official statistics produced by official organizations (e.g. statistical institutes, intergovernmental organizations such as United Nations, European Union or OECD, central banks, ministries, etc.). Economic data provide an empirical basis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioural Sciences
Behavioral sciences explore the cognitive processes within organisms and the behavioral interactions between organisms in the natural world. It involves the systematic analysis and investigation of human and animal behavior through naturalistic observation, controlled scientific experimentation and mathematical modeling. It attempts to accomplish legitimate, objective conclusions through rigorous formulations and observation.Klemke, E. D., Hollinger, R., and Kline, A. D., (1980), Introduction to the book in 'Introductory Readings in the Philosophy of Science': Buffalo, New York, Prometheus Books p 11-12 Examples of behavioral sciences include psychology, psychobiology, anthropology, economics, and cognitive science. Generally, behavioral science primarily has shown how human action often seeks to generalize about human behavior as it relates to society and its impact on society as a whole. Categories Behavioral sciences include two broad categories: neural ''Information science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computing And Society
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology and software engineering. The term "computing" is also synonymous with counting and calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by mechanical computing machines, and before that, to human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. Computing is intimately tied to the representation of numbers, though mathematical concepts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Science
Computational science, also known as scientific computing or scientific computation (SC), is a field in mathematics that uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex problems. It is an area of science that spans many disciplines, but at its core, it involves the development of models and simulations to understand natural systems. * Algorithms ( numerical and non-numerical): mathematical models, computational models, and computer simulations developed to solve science (e.g., biological, physical, and social), engineering, and humanities problems * Computer hardware that develops and optimizes the advanced system hardware, firmware, networking, and data management components needed to solve computationally demanding problems * The computing infrastructure that supports both the science and engineering problem solving and the developmental computer and information science In practical use, it is typically the application of computer simulation and other f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Genome
The social genome is the collection of data about members of a society that is captured in ever-larger and ever-more complex databases (e.g., government administrative data, operational data, social media data etc.). Some have used the term digital footprint to refer to individual traces. History There have been two distinct uses of the term. First, the word Social Genome was used in a letter to the editor submission to Science in response to a seminal article about using big data for social science by King. The letter was published, but the word social genome was edited out of the letter. The original submission states, “A well-integrated federated data system of administrative databases updated on an ongoing basis could hold a collective representation of our society, our social genome.” Kum and others continue to use the word since 2011, with it being defined in a peer reviewed article in 2013. It states “Today there is a constant flow of data into, out of, and betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulation
A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time. Often, computers are used to execute the simulation. Simulation is used in many contexts, such as simulation of technology for performance tuning or optimizing, safety engineering, testing, training, education, and video games. Simulation is also used with scientific modelling of natural systems or human systems to gain insight into their functioning, as in economics. Simulation can be used to show the eventual real effects of alternative conditions and courses of action. Simulation is also used when the real system cannot be engaged, because it may not be accessible, or it may be dangerous or unacceptable to engage, or it is being designed but not yet built, or it may simply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Sociology
Computational sociology is a branch of sociology that uses computationally intensive methods to analyze and model social phenomena. Using computer simulations, artificial intelligence, complex statistical methods, and analytic approaches like social network analysis, computational sociology develops and tests theories of complex social processes through bottom-up modeling of social interactions. It involves the understanding of social agents, the interaction among these agents, and the effect of these interactions on the social aggregate. Although the subject matter and methodologies in social science differ from those in natural science or computer science, several of the approaches used in contemporary social simulation originated from fields such as physics and artificial intelligence. Some of the approaches that originated in this field have been imported into the natural sciences, such as measures of network centrality from the fields of social network analysis and netw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Economics
Computational Economics is an interdisciplinary research discipline that involves computer science, economics, and management science.''Computational Economics''."About This Journal"an"Aims and Scope" This subject encompasses computational modeling of economic systems. Some of these areas are unique, while others established areas of economics by allowing robust data analytics and solutions of problems that would be arduous to research without computers and associated numerical methods.• Hans M. Amman, David A. Kendrick, and John Rust, ed., 1996. ''Handbook of Computational Economics'', v. 1, ElsevierDescription & chapter-previelinks. • Kenneth L. Judd, 1998. ''Numerical Methods in Economics'', MIT Press. Links tdescription anchapter previews Computational methods have been applied in various fields of economics research, including but not limiting to: Econometrics: Non-parametric approaches, Semi-parametric approaches, and Machine Learning. Dynamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics encompasses a variety of statistical techniques from data mining, predictive modeling, and machine learning that analyze current and historical facts to make predictions about future or otherwise unknown events. In business, predictive models exploit patterns found in historical and transactional data to identify risks and opportunities. Models capture relationships among many factors to allow assessment of risk or potential associated with a particular set of conditions, guiding decision-making for candidate transactions. The defining functional effect of these technical approaches is that predictive analytics provides a predictive score (probability) for each individual (customer, employee, healthcare patient, product SKU, vehicle, component, machine, or other organizational unit) in order to determine, inform, or influence organizational processes that pertain across large numbers of individuals, such as in marketing, credit risk assessment, fraud det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Record Linkage
Record linkage (also known as data matching, data linkage, entity resolution, and many other terms) is the task of finding records in a data set that refer to the same entity across different data sources (e.g., data files, books, websites, and databases). Record linkage is necessary when joining different data sets based on entities that may or may not share a common identifier (e.g., database key, URI, National identification number), which may be due to differences in record shape, storage location, or curator style or preference. A data set that has undergone RL-oriented reconciliation may be referred to as being ''cross-linked''. Naming conventions "Record linkage" is the term used by statisticians, epidemiologists, and historians, among others, to describe the process of joining records from one data source with another that describe the same entity. However, many other terms are used for this process. Unfortunately, this profusion of terminology has led to few cross-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |