|
Pontarddulais Railway Station
Pontarddulais railway station serves the town of Pontarddulais and village of Hendy in Swansea, Wales. The station is located at street level not far from the town centre and the Loughor estuary. All trains serving the station are operated by Transport for Wales. History Before the arrival of the railway, due to the local rivers, Pontarddulais was already a noted local industrialised town, with two mills and two factories in existence, alongside home-based woollen looms. The station was built in 1840 on the original Llanelly Railway (LR) main line, from to . There a direct connection was made with the Central Wales Railway, which along with other lines was controlled by the London and North Western Railway (LNWR), enabling the LNWR to connect the South Wales coast with industrialised Northwest England, via , Shrewsbury and Crewe. In 1868, the LR made the mistake of not renewing its right to the lease of the Vale of Towy. The LNWR subsequently negotiated a track-access agree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontarddulais
Pontarddulais (), also spelled Pontardulais (), is a town and community in Swansea, Wales. It is northwest of the city centre. It is in the Pontarddulais ward of the City and County of Swansea Council. Pontarddulais adjoins the village of Hendy in Carmarthenshire. The built-up population was 9,073. History An English translation of the name Pontarddulais is "Bridge over the Dulais", with Dulais meaning "black stream", probably due to its course through coal measures. The earlier name of Pontaberdulais referred to a dismantled 14th-century road bridge which carried the main highway between Swansea and Carmarthen over the River Loughor (Afon Llwchwr). The bridge was so named because of its position upstream of the mouth (''aber'') of the Dulais stream. This bridge was also known as ''Y Bont Fawr'' ("the big bridge"). The village that developed around this bridge took the shortened name of Pontardulais, also written incorrectly as Pontarddulais because of the assumption that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
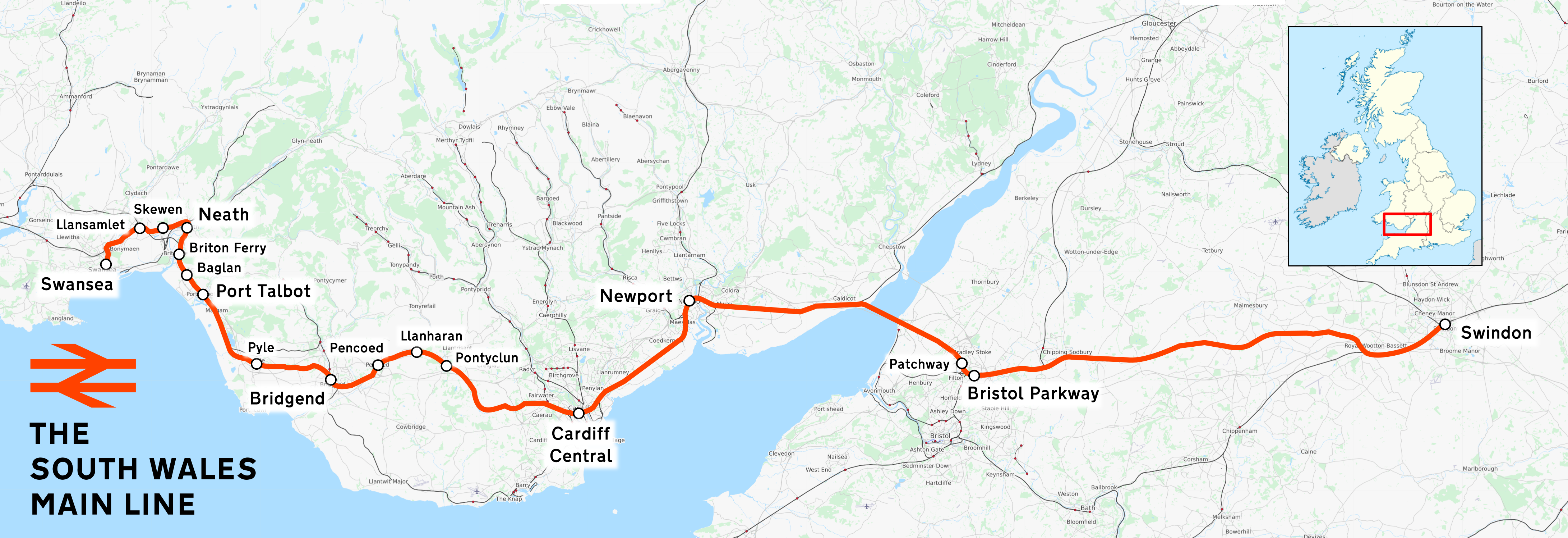
South Wales Main Line
The South Wales Main Line (), originally known as the London, Bristol and South Wales Direct Railway or simply as the Bristol and South Wales Direct Railway, is a branch of the Great Western Main Line in Great Britain. It diverges from the core London-Bristol line at Royal Wootton Bassett beyond Swindon, first calling at Bristol Parkway, after which the line continues through the Severn Tunnel into South Wales. Much of the South Wales Main Line was built between the 1830s and 1886; originally trains to and from destinations in England ran via Chepstow, Gloucester and Stroud, joining the Great Western Main Line at Swindon. A more direct route was challenging yet desirable, leading to the construction of the line's most prominent civil engineering feature, the Severn Tunnel. Completed in 1886, it permitted a significant reduction in journey times between various destinations, especially after the construction of the Badminton Line in 1903. During the British Rail era, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M4 Motorway
The M4, originally the London-South Wales Motorway, is the third longest motorway in the United Kingdom, running from west London to southwest Wales. The English section to the Severn Bridge was constructed between 1961 and 1971; the Welsh element was largely complete by 1980, though a non-motorway section around Briton Ferry bridge remained until 1993. On the opening of the Second Severn Crossing in 1996, the M4 was rerouted over it. The line of the motorway from London to Bristol runs closely in parallel with the A4 road (England), A4. After crossing the River Severn, toll-free since 17 December 2018, the motorway follows the A48 road (Great Britain), A48, to terminate at the Pont Abraham services in Carmarthenshire. The M4 is the only motorway in Wales apart from its two Spur route, spurs: the A48(M) motorway, A48(M) and the M48 motorway, M48. The major towns and cities along the routea distance of approximately include Slough, Reading, Berkshire, Reading, Swindon, Bristol, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beeching Axe
The Beeching cuts, also colloquially referred to as the Beeching Axe, were a major series of route closures and service changes made as part of the restructuring of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain in the 1960s. They are named for Dr. Richard Beeching, then-chair of the British Railways Board and the author of two reports''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the Major Railway Trunk Routes'' (1965) that set out proposals for restructuring the railway network, with the stated aim of improving economic efficiency. The first report identified 2,363 stations and of railway line for closure, amounting to 55% of stations, 30% of route miles, and the loss of 67,700 British Rail jobs, with an objective of stemming the large losses being incurred during a period of increasing competition from road transport and reducing the rail subsidies necessary to keep the network running. The second report identified a small number of major routes f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felindre, Swansea
Felindre is a rural village in the City and County of Swansea, south Wales. Felindre is located in the far north of the city of Swansea, in the electoral ward of Mawr. The nearby Lower Lliw Reservoirs are a popular venue for walking and fishing. The water mill in the village was working until the late 1960s, there was also an abattoir and a post office in the village. It has three shops. There is also a public house in the village, the Shepherds Inn. The primary school in the village was Welsh speaking and closed in 2019. Felindre works site In 1956, the Steel Company of Wales opened a tinplate works at Felindre to complement new facilities at Port Talbot and Trostre. In 1967, the Steel Company of Wales was nationalised, becoming part of British Steel Corporation, which inherited the additional tinplate works at Ebbw Vale Steelworks. By 1970, Felindre works employed 2,500 people and was producing 490,000 tonnes of tinplate per annum. Having already closed the tinplate works a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trostre Steelworks
Trostre Steelworks is a tinplate manufacturing facility located in Pemberton, Carmarthenshire. Planned by the Steel Company of Wales in 1947, today it is part of Tata Steel Europe's infrastructure. Background The name of the area derives from the Pemberton family, landowners and industrialists from the North of England, who played a role in the development of Llanelli (especially the local coal industry) in the early 19th century. History On formation in 1947, the nationalised Steel Company of Wales was under UK Government pressure to both increase production and profits, and rationalise its production base. As part of its strategic plan, the company envisaged creating two new tinplate works, one at Trostre and one at Felindre, Swansea. With in excess of 12,000 men unemployed in post-World War II Llanelli, the decision was made to focus on construction of the Trostre plant to make best use of the area’s developed skills in tinplate manufacture. Chosen due to its close locati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
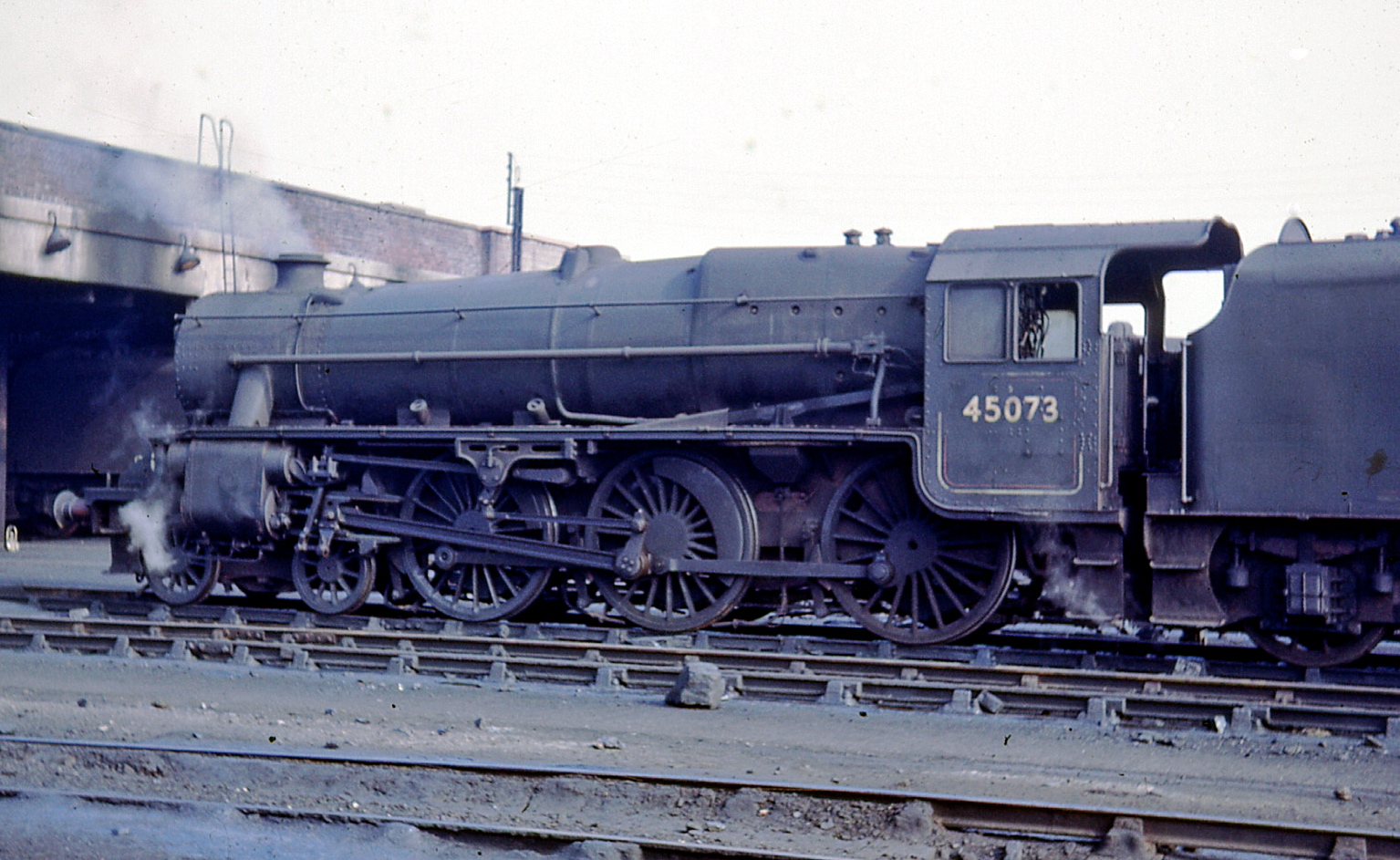
LMS Black 5
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) Stanier Class 5 4-6-0, commonly known as the Black Five, is a class of steam locomotives. It was introduced by William Stanier and built between 1934 and 1951. A total of 842 were built, initially numbered 4658-5499 then renumbered 44658-45499 by BR. Several members of the class survived to the last day of steam on British Railways in 1968, and eighteen are preserved. Origins The Black Five was a mixed-traffic locomotive, a "do-anything go-anywhere" type, designed by Stanier, who had previously been with the GWR. In his early LMS days, he designed his Stanier Mogul , experimenting with the GWR school of thought on locomotive design. A number of details in this design he would never use again, realising the superiority of details not used on the GWR. Stanier realised that there was a need for larger locomotives. These were to be the LMS version of the GWR Halls, but they were not copies, as the Hall was too wide to run in most p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Region Of British Railways
The Western Region was a region of British Railways from 1948. The region ceased to be an operating unit in its own right on completion of the "Organising for Quality" initiative on 6 April 1992. The Region consisted principally of ex-Great Western Railway lines, minus certain lines west of Birmingham, which were transferred to the London Midland Region in 1963 and with the addition of all former Southern Railway routes west of Exeter, which were subsequently rationalised. History When British Railways was created at the start of 1948, it was immediately subdivided into six Regions, largely based upon pre-nationalisation ownership. The Western Region initially consisted of the former Great Western Railway system, totalling 3,782 route miles and with its headquarters at Paddington. To this was added some minor railways and joint lines in which the GWR had an interest: * Brynmawr and Western Valleys Railway * Clifton Extension Railway * Easton and Church Hope Railway *Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land border, as well as List of islands of Italy, nearly 800 islands, notably Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares land borders with France to the west; Switzerland and Austria to the north; Slovenia to the east; and the two enclaves of Vatican City and San Marino. It is the List of European countries by area, tenth-largest country in Europe by area, covering , and the third-most populous member state of the European Union, with nearly 59 million inhabitants. Italy's capital and List of cities in Italy, largest city is Rome; other major cities include Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo, Bologna, Florence, Genoa, and Venice. The history of Italy goes back to numerous List of ancient peoples of Italy, Italic peoples—notably including the ancient Romans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinplate
Tinplate consists of sheet metal, sheets of steel coated with a thin layer of tin to impede rust, rusting. Before the advent of cheap mild steel, the backing metal (known as "") was wrought iron. While once more widely used, the primary use of tinplate now is the manufacture of steel and tin cans, tin cans. In the tinning process, tinplate is made by rolling the steel (or formerly iron) in a rolling mill, removing any mill scale by pickling it in acid and then coating it with a thin layer of tin. Plates were once produced individually (or in small groups) in what became known as a ''pack mill''. In the late 1920s pack mills began to be replaced by ''strip mills'' which produced larger quantities more economically. Formerly, tinplate was used for tin ceiling, and holloware (cheap pots and pans), also known as tinware. The people who made tinware (metal spinning) were tinplate workers. For many purposes, tinplate has been replaced by galvanised metal, the base being treated with a z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gower Peninsula
The Gower Peninsula (), or simply Gower (), is a peninsula in the South West Wales, south-west of Wales. It is the most westerly part of the historic county of Glamorgan, and is now within the City and County of Swansea. It projects towards the Bristol Channel. In 1956, the majority of Gower became the first area in the United Kingdom to be designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. Until 1974, Gower was administered as a rural district. It was then merged with the county borough of Swansea. From 1974 to 1996, it formed the Swansea (district), Swansea district. Since 1996, Gower has been administered as part of the unitary authority of the City and County of Swansea council, City and County of Swansea. Since its establishment in 1999, the Gower (Senedd constituency), Gower Senedd constituency has only elected Labour members. The Gower (UK Parliament constituency), Gower constituency in Westminster had previously also elected only Labour Member of Parliament (United King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |