|
Polysilane
Polysilanes are organosilicon compounds with the formula (R2Si)n. They are relatives of traditional organic polymers but their backbones are composed of silicon atoms. They exhibit distinctive optical and electrical properties. They are mainly used industrially as precursors to silicon carbide. The simplest polysilane would be (SiH2)n, which is mainly of theoretical, not practical interest. Synthesis left, Dodecamethylcyclohexasilane is a crystalline polysilane. The first polysilane, poly(dimethylsilylene), CH3)2Sisub>''x'', was reported in 1949 by Charles A. Burkhard (1916 - 1991) of General Electric. It was prepared by heating sodium metal with dimethyldichlorosilane: :(CH3)2SiCl2 + 2 Na → CH3)2Sisub>n + 2 NaCl The modified Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes remains a viable and general route to high molecular weight, linear polysilane derivatives. This reaction is conducted at elevated temperature in an inert solvent using a dispersion of the alkali metal. The polymerizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
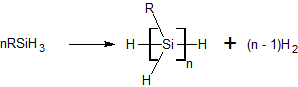
Dehydrogenative Coupling Of Silanes
The dehydrogenative coupling of silanes is a reaction type for the formation of Si-Si bonds. Although never commercialized, the reaction has been demonstrated for the synthesis of certain disilanes as well as polysilanes. These reactions generally require catalysts. Metallocene-based catalysts Titanocene and related their complexes are typical catalysts. A typical reaction involves phenylsilane: :n PhSiH3 → hSiHsub>n + n H2 Para- and meta-substituted phenylsilanes polymerize readily but ortho-substituted polymers were failed to form. Polymers white/colorless, tacky and soluble in organic solvents. Crosslinking was not observed. Using Cp2Ti(OPh)2 as a catalyst, the dehydrogenative coupling of phenylsilane in the presence of vinyltriethoxysilane produces a polysilane terminated with a triethoxysilylvinyl group. Other catalysts The nickel(I) complex dippe)Ni(µ-H)sub>2 promotes the dehydrogenative coupling of some silanes. While catalysts for dehydrogenative couplin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyldichlorosilane
Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral, organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)2Cl2. At room temperature it is a colorless liquid that readily reacts with water to form both linear and cyclic Si-O chains. Dimethyldichlorosilane is made on an industrial scale as the principal precursor to dimethylsilicone and polysilane compounds. History The first organosilicon compounds were reported in 1863 by Charles Friedel and James Crafts who synthesized tetraethylsilane from diethylzinc and silicon tetrachloride.Silicon: Organosilicon Chemistry. Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry Online, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New Jersey, 2005. However, major progress in organosilicon chemistry did not occur until Frederick Kipping and his students began experimenting with diorganodichlorosilanes (R2SiCl2) that were prepared by reacting silicon tetrachloride with Grignard reagents. Unfortunately, this method suffered from many experimental problems. In the 1930s, the demand for silicones increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen. The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions. An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloalkane by removal of a hydrogen atom from a ring and has the general formula . Typically an alkyl is a part of a larger molecule. In structural formulae, the symbol R is used to designate a generic (unspecified) alkyl group. The smallest alkyl group is methyl, with the formula . Related concepts Alkylation is an important operation in refineries, for example in the production of high-octane gasoline. Alkylating antineoplastic agents are a class of compounds that are used to treat cancer. In such case, the term alkyl is used loosely. For example, nitrogen mustards are well-known alkylating agents, but they are not simple hydrocarbons. In chemistry, alkyl is a group, a substituent, that is attached to other molecular fragments. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysilyne
Polysilynes are organosilicon compounds with the formula Sisub>n. Although their name suggests a relationship to alkynes, polysilynes are a class of silicon-based random network polymers primarily composed of tetrahedral silicon centers, each connected to one carbon and three Si centers. These compounds are prepared by Wurtz coupling of alkyltrichlorosilanes (RSiCl3): :3 Na + RSiCl3 → Sisub>n + 3 NaCl The methyl and hexyl derivatives have been described. Poly(methylsilyne) (PMSy) is a dark yellow powder. With some solvents (tetrahydrofuran, ether, toluene etc.) it forms a colloidal suspension that is clear and non-viscous, which may then be deposited as a film or coating on various substrates. Upon thermolysis, poly(methylsilyne) decomposes to silicon carbide Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
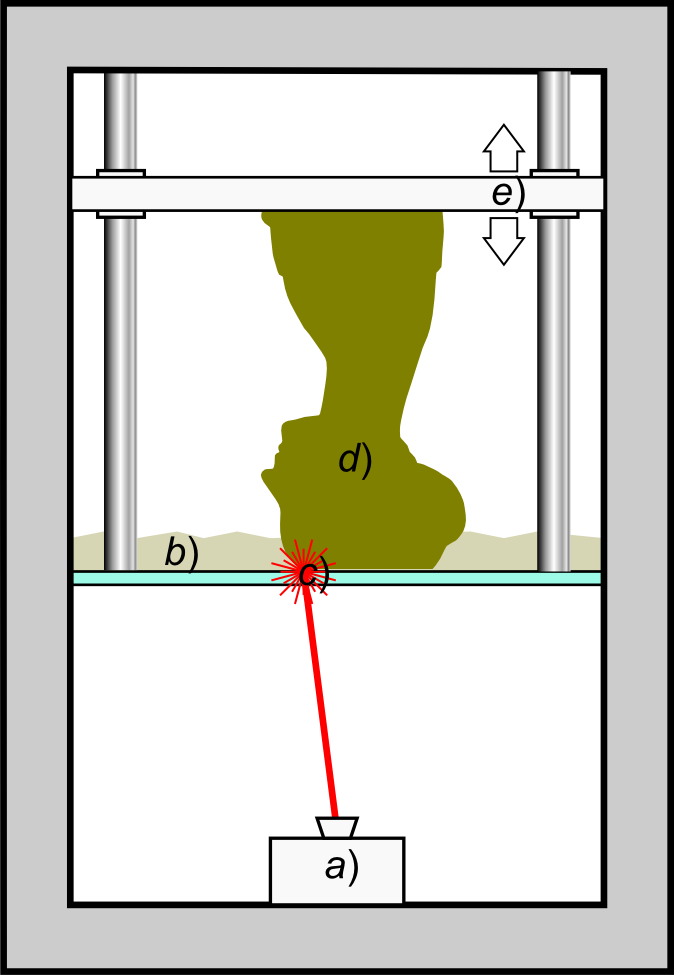
Additive Manufacturing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology, whereby the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very complex shapes or geometries that would be otherwise impossible to construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrolysis
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''pyro'' "fire", "heat", "fever" and ''lysis'' "separating". Pyrolysis is most commonly used in the treatment of organic materials. It is one of the processes involved in charring wood.''Burning of wood'' , InnoFireWood's website. Accessed on 2010-02-06. In general, pyrolysis of organic substances produces volatile products and leaves char, a carbon-rich solid residue. Extreme pyrolysis, which leaves mostly |
Stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA or SL; also known as vat photopolymerisation, optical fabrication, photo-solidification, or resin printing) is a form of 3D printing technology used for creating models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts in a layer by layer fashion using photochemical processes by which light causes chemical monomers and oligomers to cross-link together to form polymers. U.S. Patentbr>4,575,330(“Apparatus for Production of Three-Dimensional Objects by Stereolithography”) Those polymers then make up the body of a three-dimensional solid. Research in the area had been conducted during the 1970s, but the term was coined by Chuck Hull in 1984 when he applied for a patent on the process, which was granted in 1986. Stereolithography can be used to create prototypes for products in development, medical models, and computer hardware, as well as in many other applications. While stereolithography is fast and can produce almost any design, it can be expensive. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Oxycarbide
Oxycarbide glass, also referred to as silicon oxycarbide, is a type of glass that contains oxygen and carbon in addition to silicon dioxide. It is created by substituting some oxygen atoms with carbon atoms. This glass may contain particles of amorphous carbon, and silicon carbide. SiOC materials of varying stoichiometery are attractive owing to their generally high density, hardness and high service temperatures. Through diverse forming techniques high performance parts in complex shapes can be achieved. Unlike pure SiC, the versatile stoichiometry of SiOC offers further avenues to tune physical properties through appropriate selection of processing parameters. Amorphous silicon oxycarbide can form as the pyrolysis product of preceramic polymers including polycarbosilane. Such materials are of increasing interest towards the additive manufacturing 3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preceramic Polymer
The term preceramic polymer refers to one of various polymeric compounds, which through pyrolysis under appropriate conditions (generally in the absence of oxygen) are converted to ceramic compounds, having high thermal and chemical stability. Ceramics resulting from the pyrolysis of preceramic polymers are known as polymer derived ceramics, or PDCs. Polymer derived ceramics are most often silicon based and include silicon carbide, silicon oxycarbide, silicon nitride and silicon oxynitride. Such PDCs are most commonly amorphous, lacking long-range crystalline order. Kizhakke Veettil et alA versatile stereolithographic approach assisted by thiol-ene click chemistry, ''Additive Manufacturing 2019, volume 27 pages 80-90'' The field of preceramic polymers and polymer derived ceramics in general emerged from the requirements in aerospace industries for heat shield materials such as fiber reinforced ceramic / ceramic composite materials. The use of preceramic polymers allows for divers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrolysis
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''pyro'' "fire", "heat", "fever" and ''lysis'' "separating". Pyrolysis is most commonly used in the treatment of organic materials. It is one of the processes involved in charring wood.''Burning of wood'' , InnoFireWood's website. Accessed on 2010-02-06. In general, pyrolysis of organic substances produces volatile products and leaves char, a carbon-rich solid residue. Extreme pyrolysis, which leaves mostly |
_【_Pictures_taken_in_Japan_】_(cropped).jpg)