|
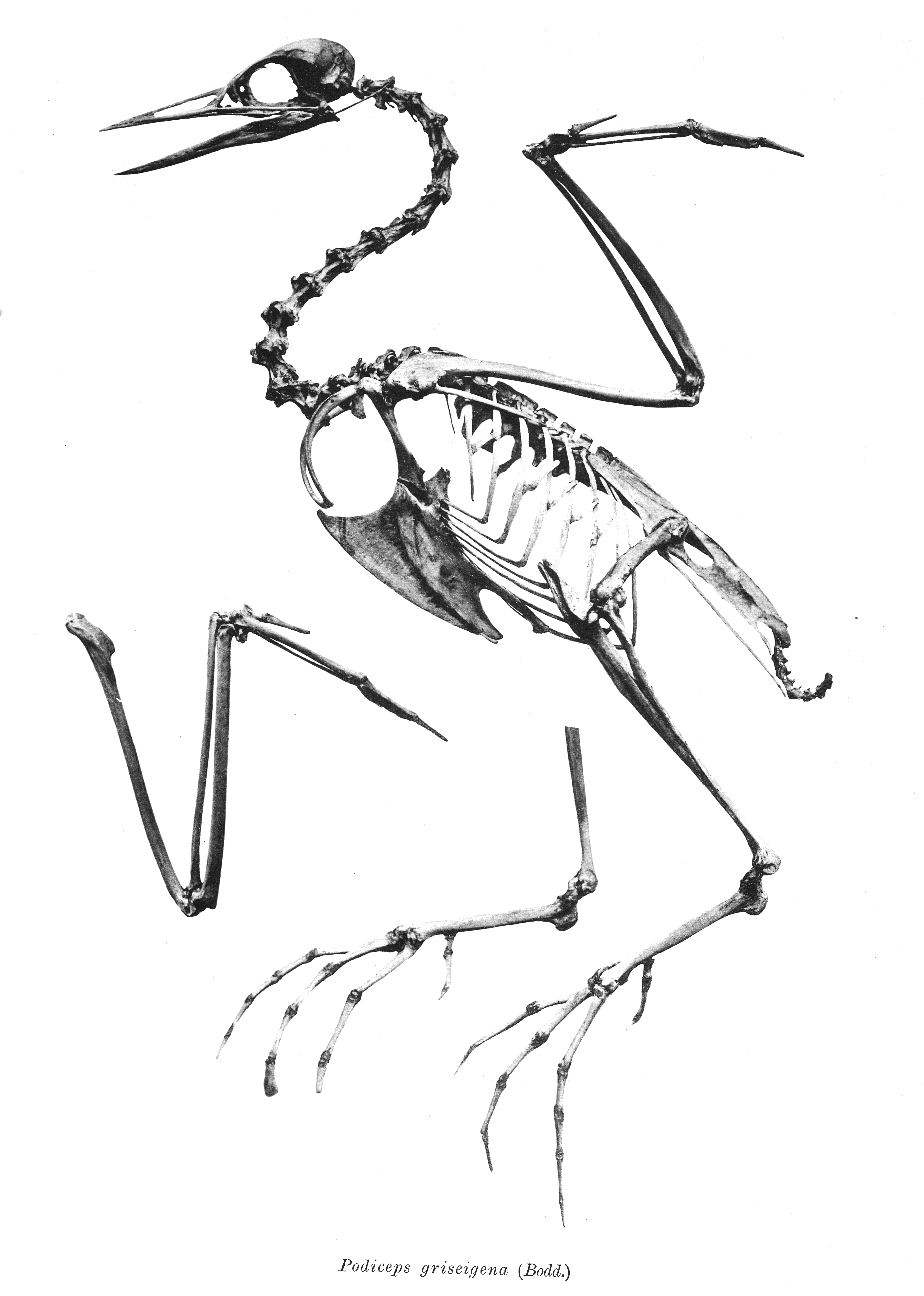
Podiceps Discors
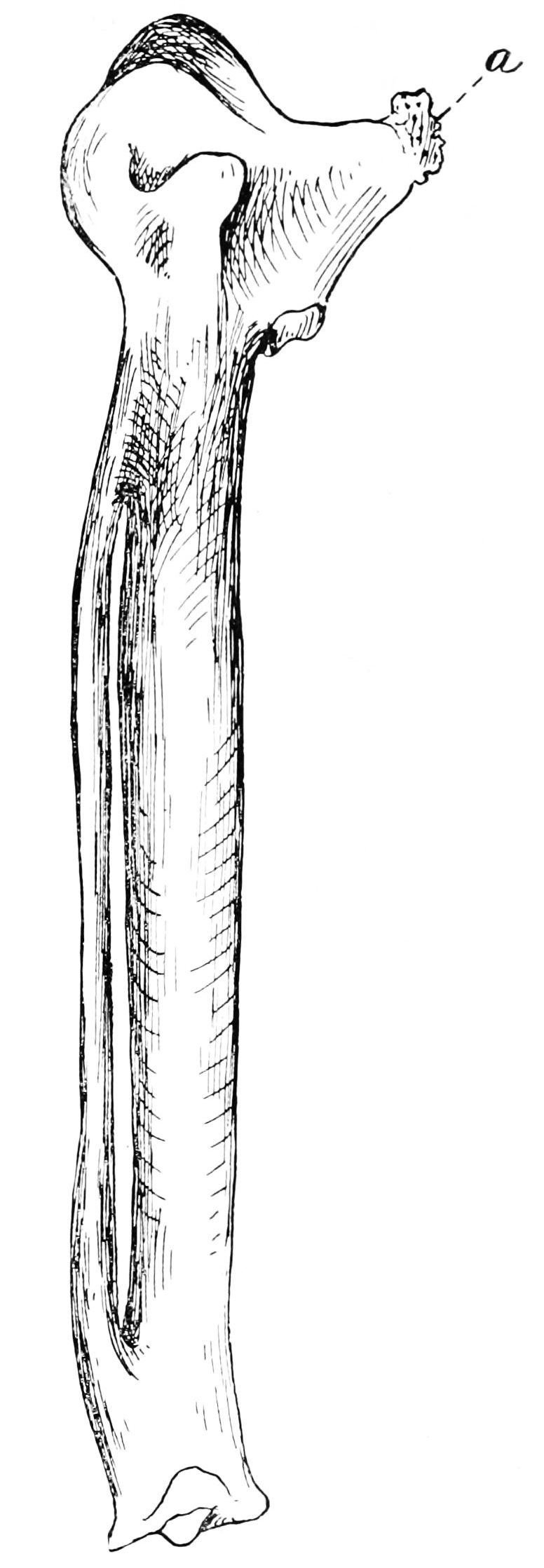
''Podiceps discors'' is an extinct species of grebe from the Upper Pliocene of western North America. It was similar to the black-necked grebe. History The specimens were collected in the summer of 1951 from Kansas, United States by Claude W. Hibbard and the species was named in 1967 by Bertram G. Murray. The species name "discors" refers to how different it is from other members of ''Podiceps''. Description The holotype ( UMMP 29079) is a complete left tarsometatarsus, which is comparable in size to tarsometatarsi of the black-necked grebe and of the females of the horned grebe (''P. auritus''). It differs from them by its internal condyle is not internally flared, and the head is small relative to the length of the bone. Further when viewed at the medial perspective, the tarsometatarsus of ''P. discors'' is not as long or it is directed so far anteriorly as seen in other species of the genus. Additional material has been found in Idaho which represent a complete femur (UMMP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grebe
Grebes () are aquatic diving birds in the order (biology), order Podicipediformes (). Grebes are widely distributed freshwater birds, with some species also found in sea, marine habitats during Bird migration, migration and winter. Most grebes fly, although some flightless species exist, most notably in stable lakes. The order contains a single family (biology), family, the Podicipedidae, which includes 22 species in six extant genus, genera. Although, superficially, they resemble other diving birds such as loons and coots, they are most closely related to flamingos, as supported by morphology (biology), morphological, molecular and paleontology, paleontological data. Many species are monogamy in animals, monogamous and are known for their courtship displays, with the pair performing synchronized dances across the water's surface. The birds build floating vegetative nests where they lay several eggs. About a third of the world's grebes are listed at various levels of conservatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid
A coracoid is a paired bone which is part of the shoulder assembly in all vertebrates except therian mammals (marsupials and placentals). In therian mammals (including humans), a coracoid process is present as part of the scapula, but this is not homologous with the coracoid bone of most other vertebrates. In other tetrapods, it joins the scapula to the front end of the sternum and has a notch on the dorsal surface which, along with a similar notch on the ventral surface of the scapula, forms the socket in which the proximal end of the humerus (upper arm bone) is located. The acrocoracoid process is an expansion adjacent to this contact surface, to which the shoulderward end of the biceps brachii muscle attaches in these animals. In birds (and generally theropods and related animals), the entire unit is rigid and called scapulocoracoid. This plays a major role in bird flight. In other dinosaurs, the main bones of the pectoral girdle were the scapula (shoulder blade) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1967
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piacenzian
The Piacenzian is in the international geologic time scale the upper stage (stratigraphy), stage or latest age (geology), age of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 3.6 ± 0.005 year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma and 2.58 Ma (million years ago). The Piacenzian is after the Zanclean and is followed by the Gelasian (part of the Pleistocene). The Piacenzian is roughly coeval with the European land mammal age MN 16, overlaps the late Chapadmalalan and early Uquian South American land mammal age and falls inside the more extensive Blancan North American land mammal age. It also correlates with the Astian, Redonian, Reuverian and Romanian regional stages of Europe, and the Waipipian and Mangapanian stages of New Zealand geologic time scale, New Zealand. Some authorities describe the British Red Crag Formation and Waltonian Stage as late Piacenzian, while others regard them as early Pleistocene. Carbon dioxide levels during the Piacenzian were similar to those of today, making this age, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Diego Formation
The San Diego Formation is a geological formation in southwestern San Diego County, California, United States, and northwestern Baja California, Mexico. Geology It is a coastal transitional marine and non-marine pebble and cobble conglomerate deposit and marine sandstone rock with marine fossils, from a former bay, deposited during the Middle Pliocene to Late Pliocene ages (2–3 million years ago), of the Pliocene period during the Cenozoic Era. This formation is found from the south side of Mount Soledad in San Diego County to Rosarito Beach in northern Baja California, including Tijuana, Mexico, and the southwestern corner of San Diego County from San Ysidro to Pacific Beach. San Diego Formation deposits were formed in a large, open, crescent-shaped bay similar in size to Monterey Bay that existed on the coast in Pliocene times. Aquifer The formation contains the San Diego Formation Basin, a large aquifer under Imperial Beach, Chula Vista, National City, and souther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenns Ferry Formation
The Glenns Ferry Formation is a Pliocene stratigraphic unit in the western United States. Outcrops of the formation in Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument preserve the remains of seven fish species, five of which are extinct. These include the teleosteans '' Mylopharodon hagermanensis'', '' Sigmopharyngodon idahoensis'', and '' Ptychocheilus oregonensis'', '' Ameirurus vespertinus'', and the sunfish '' Archoplites taylori''. A nearly complete skull of the catfish '' Ameirurus vespertinus'' was recovered in 2001 from the wall of the Smithsonian Horse Quarry. The formation was deposited by Lake Idaho. References References *Hunt, ReBecca K., Vincent L. Santucci and Jason Kenworthy. 2006. "A preliminary inventory of fossil fish from National Park Service units." in S.G. Lucas, J.A. Spielmann, P.M. Hester, J.P. Kenworthy, and V.L. Santucci (ed.s), Fossils from Federal Lands. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science The New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rexroad Formation
The Rexroad Formation is a geologic formation in Kansas. It preserves fossils dating back to the Neogene period. These fossils include two types of skunk (''Spilogale rexroadi'' and ''Brachyprotoma breviramus''), a tree bat (''Lasiurus fossilis''), a ringtail (''Bassariscus casei''), several snakes, such as ''Elaphe obsoleta'', and a turkey ('' Agriocharis progenes''). See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Kansas * Paleontology in Kansas Paleontology in Kansas refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the United States, U.S. state of Kansas. Kansas has been the source of some of the most spectacular fossil discoveries in US history. The fossil ... References * Neogene geology of Kansas Neogene geology of Oklahoma {{Neogene-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibiotarsus
The tibiotarsus is the large bone between the femur and the tarsometatarsus in the leg of a bird. It is the fusion of the proximal part of the tarsus with the tibia. A similar structure also occurred in the Mesozoic Heterodontosauridae. These small ornithischian dinosaurs were unrelated to birds and the similarity of their foot bones is best explained by convergent evolution. See also * Bird anatomy References * Proctor, Nobel S. ''Manual of Ornithology: Avian Structure and Function''. Yale University Press Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day and Clarence Day, grandsons of Benjamin Day, and became a department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and ope .... (1993) Bird anatomy Dinosaur anatomy {{ornithology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: intrinsic, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpometacarpus
The carpometacarpus is a bone found in the hands of birds. It results from the fusion of the carpal and metacarpal bone, and is essentially a single fused bone between the wrist and the knuckles. It is a smallish bone in most birds, generally flattened and with a large hole in the middle. In flightless birds, however, its shape may be slightly different, or it might be absent entirely. It forms the tip of the wing skeleton in birds. To it, most of the primary remiges attach. The alula, by contrast, is formed by the thumb, which does not completely fuse with the other hand-bones. Likewise, the tipmost primaries attach to the phalanx bone The phalanges (: phalanx ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structu ...s. To non- biologists the carpometacarpus may be best known from buffalo wings. Buffalo wings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic, Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time scale, which placed the four most recent major glaciations entirely within the Pleistocene, the Pliocene also included the Gelasian Stage, which lasted from 2.59 to 1.81 Ma, and is now included in the Pleistocene. As with other older geologic periods, the Stratum, geological strata that define the start and end are well-identified but the exact dates of the start a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg. The Femoral head, top of the femur fits into a socket in the pelvis called the hip joint, and the bottom of the femur connects to the shinbone (tibia) and kneecap (patella) to form the knee. In humans the femur is the largest and thickest bone in the body. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper Human leg, leg. The two femurs converge Anatomical terms of location, medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the Anatomical terms of location, proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle at which the femora converge is an important factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. In females, thicker pelvic bones cause the femora to converge more than in males. In the condition genu valgum, ''genu valgum'' (knock knee), the femurs conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |