|
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) or simply plug-in hybrid is a type of hybrid electric vehicle equipped with a rechargeable battery pack that can be directly replenished via a charging cable plugged into an external electric power source, in addition to charging internally by its on-board internal combustion engine-powered generator. While PHEVs are predominantly passenger cars, there are also plug-in hybrid variants of sports cars, commercial vehicles, vans, utility trucks, buses, trains, motorcycles, mopeds, military vehicles and boats. Similar to battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrids can use centralized generators of renewable energy (e.g. solar, wind or hydroelectric) to be largely emission-free, or a fossil plant in which case they displace greenhouse gas emissions from the car tailpipe exhaust to the power station. As opposed to conventional hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), PHEVs generally have a larger battery pack that can be recharged (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BYD Song
The BYD Song (, after the Song dynasty) is a series of compact crossover SUVs produced by BYD Auto since 2015. The Song nameplate consists of several different models. It includes the original first-generation Song, later renamed to Song Classic and was sold until 2019. Another versions are the slightly larger BYD Song Pro, Song Pro was introduced in 2019, followed by the more upmarket BYD Song Plus, Song Plus in 2020, a larger electric vehicle called the BYD Song L EV, Song L EV since 2023, and a plug-in hybrid called the BYD Song L DM-i, Song L DM-i. The Song nameplate is also adopted by the BYD Song Max, Song Max compact MPV. Since 2024, the Song Plus is exported overseas as the BYD Seal U and BYD Sealion 6. Similar to other BYD models, the Song has been available in petrol, plug-in hybrid DM (Dual Mode) system, and pure Battery electric vehicle, EV powertrains. The petrol versions were discontinued in March 2022 as BYD ended Internal combustion engine, ICE vehicle production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery Electric Vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that uses electrical energy exclusively from an electric vehicle battery, on-board battery pack to power one or more electric motor, electric traction motors, on which the vehicle solely relies for propulsion. This definition excludes hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs; including mild hybrid, mild, full hybrid, full and plug-in hybrids), which use internal combustion engines (ICEs) in adjunct to electric motors for propulsion; and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) and range extender, range-extended electric vehicles (REEVs), which consume fuel through a fuel cell or an ICE-driven electric generator, generator to produce electricity needed for the electric motors. BEVs have no fuel tanks and replenish their energy storage by plug-in electric vehicle, plugging into a charging station, electrical grid or getting a new bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . Just as a linear force is a push or a pull applied to a body, a torque can be thought of as a twist applied to an object with respect to a chosen point; for example, driving a screw uses torque to force it into an object, which is applied by the screwdriver rotating around its axis to the drives on the head. Historical terminology The term ''torque'' (from Latin , 'to twist') is said to have been suggested by James Thomson and appeared in print in April, 1884. Usage is attested the same year by Silvanus P. Thompson in the first edition of ''Dynamo-Electric Machinery''. Thompson describes his usage of the term as follows: Today, torque is referred to using d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to generate Laplace force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in reverse, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, Inverter (electrical), inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may also be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be brushed motor, brushed or brushless motor, brushless, single-phase electric power, single-phase, two-phase electric power, two-phase, or three-phase electric p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-depleting
Charge-depleting or EV mode refers to an operation mode of an electric vehicle's powertrain that is chiefly dependent on the energy storage from the on-board battery pack. Battery electric vehicles operate solely in charge-depleting mode, and most plug-in hybrids operate in this mode at startup and switch to charge-sustaining A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of hybrid vehicle that couples a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) with one or more electric engines into a hybrid vehicle drivetrain, combined propulsion system. The presence of the electri ... mode after the battery has reached its minimum state of charge (SOC) threshold, exhausting the vehicle's all-electric range (AER). Although there is no technically mandated minimum all-electric range, future state and/or federal legislation may address this for policy purposes. Another charge-depleting strategy is called blended mode, in which the engine supplements the battery during medium to heavy loads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Efficiency (physics)
Energy conversion efficiency (''η'') is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The input, as well as the useful output may be chemical, electric power, mechanical work, light (radiation), or heat. The resulting value, ''η'' (eta), ranges between 0 and 1. Overview Energy conversion efficiency depends on the usefulness of the output. All or part of the heat produced from burning a fuel may become rejected waste heat if, for example, work is the desired output from a thermodynamic cycle. Energy converter is an example of an energy transformation. For example, a light bulb falls into the categories energy converter. \eta = \frac Even though the definition includes the notion of usefulness, efficiency is considered a technical or physical term. Goal or mission oriented terms include effectiveness and efficacy. Generally, energy conversion efficiency is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1.0, or 0% to 100%. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Grid
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power transmission to carry power over long distances, and finally electric power distribution to customers. In that last step, voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage. Power stations are typically built close to energy sources and far from densely populated areas. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. From small to large there are microgrids, wide area synchronous grids, and super grids. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the ''power grid''. Grids are nearly always synchronous, meaning all distribution areas operate with three phase alternating current (AC) frequencies synchronized (so that voltage swings occur at almost the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Station
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the electricity generation, generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid. Many power stations contain one or more Electric generator, generators, rotating machine that converts mechanical power into three-phase electric power. The relative motion between a magnetic field and a Electrical conductor, conductor creates an electric current. The energy source harnessed to turn the generator varies widely. Most power stations in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity. Low-carbon power sources include nuclear power, and use of renewable energy, renewables such as solar power, solar, wind power, wind, geothermal power, geothermal, and hydroelectricity, hydroelectric. History In early 1871 Belgian inventor Zénobe Gramme invented a generator powerfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhaust Gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an exhaust pipe, flue gas stack, or propelling nozzle. It often disperses downwind in a pattern called an ''exhaust plume''. It is a major component of motor vehicle emissions (and from stationary internal combustion engines), which can also include crankcase blow-by and evaporation of unused gasoline. Air pollution from burning fossil fuels is estimated to kill over 5 million people each year. Motor vehicle emissions are a common source of air pollution and are a major ingredient in the creation of smog in some large cities. Composition The largest part of most combustion gas is nitrogen (N2), water vapor (H2O) (except with pure-carbon fuels), and carbon dioxide (CO2) (except for fuels without carbon); these are not toxic or noxiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailpipe
An exhaust system is used to guide reaction exhaust gases away from a controlled combustion inside an engine or stove. The entire system conveys burnt gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes. Depending on the overall system design, the exhaust gas may flow through one or more of the following: *Cylinder head and exhaust manifold *A turbocharger to increase engine power. *A catalytic converter to reduce air pollution. *A muffler (North America) / silencer (UK/India), to reduce noise. Design criteria An exhaust pipe must be carefully designed to carry toxic and noxious gases away from the users of the machine. Indoor generators and furnaces can quickly fill an enclosed space with poisonous exhaust gases such as hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, if they are not properly vented to the outdoors. Also, the gases from most machines are scorching; the pipe must be heat-resistant and not pass through or near anything that can burn or be dama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
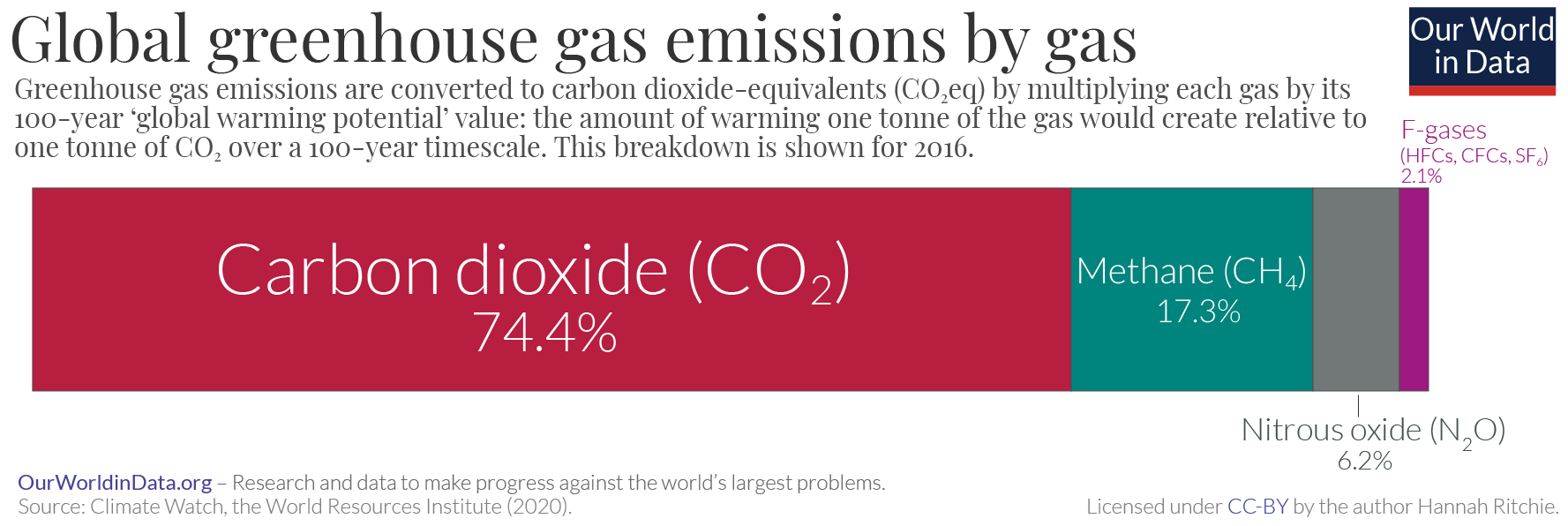
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |