|
Piula Theological College
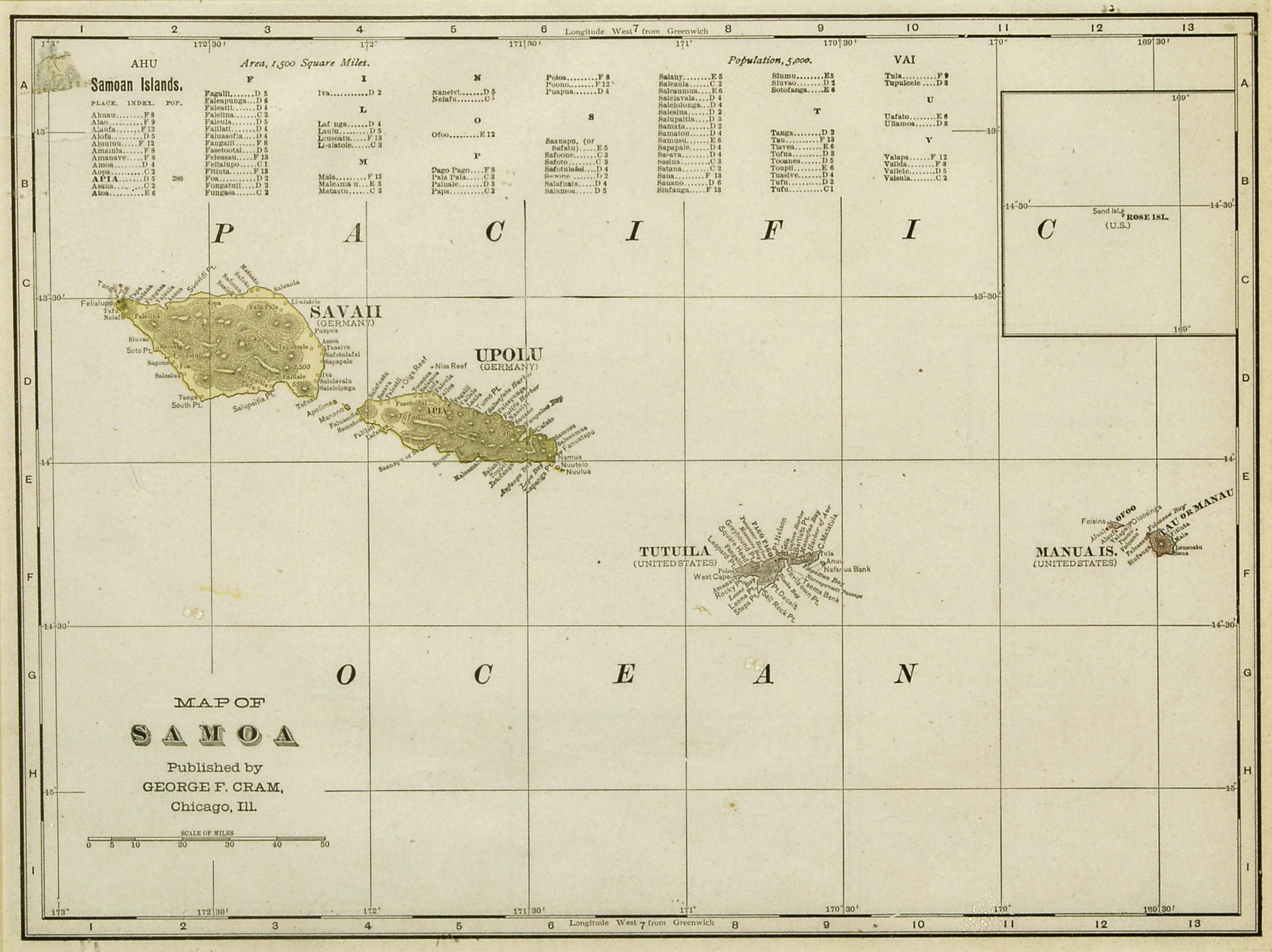
Piula Theological College is a Methodist training institution in Samoa. It was established in 1868 in Lufilufi on the north coast of Upolu island after its initial beginnings in 1859 at Satupa'itea on the south coast of Savai'i island. The Methodist Mission in Samoa purchased the land at the Methodist leaning district and later named their training center Piula Theological College. The name ''Piula'' is a transliteration of the biblical name ''Beulah'' which means ''married'' (to the Lord). The college includes the recently renovated historic Piula chapel, large open grounds, and Samoan fale. At the front of the chapel are steps leading down to the sea where ''Fatumea'', the oval Piula Cave Pool is, a popular swimming hole for locals and visitors. History In Samoa, the Methodist religion is referred to as 'lotu tonga' through the early initial contact with converts and the church's mission in Tonga during the early 19th century. The decision to set up the training institutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manono Island
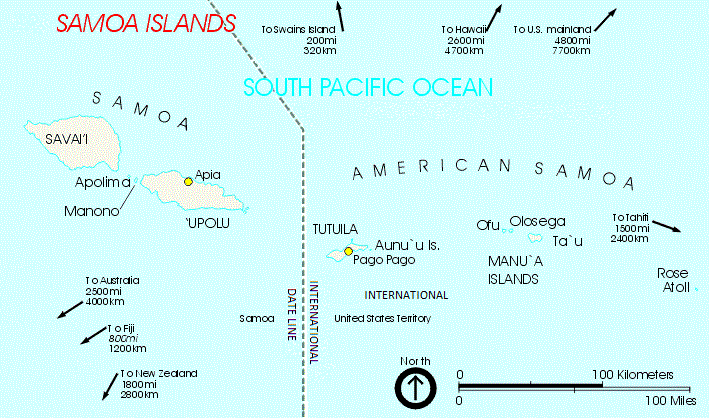
Manono is an island of Samoa, situated in the Apolima Strait between the main islands of Savai'i and Upolu, 3.4 km west-northwest off Lefatu Cape, the westernmost point of Upolu. By population, as well as by area, it is Samoa’s third largest island. There are four villages on the island with a total population of 889 (2006 Census). Electricity was only introduced in 1995 and there are several shops with beach fale accommodation for visitors. The boat trip from Upolu island takes about 20 minutes. The neighbouring islands are Apolima, which has a small village settlement and the islet Nu'ulopa. Manono Island is part of the political district Aiga-i-le-Tai. The majority of people in the Aiga-i-le-Tai district live on the 'mainland' at the west end of Upolu island. Dogs of any kind are prohibited on Manono island. Villages The four villages and their populations on Manono Island are #Apai, west (111) #Faleu, south (354) #Lepuia'i, southwest (223) #Salua, north (201) Out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1868 Establishments In Samoa
Events January * January 2 – British Expedition to Abyssinia: Robert Napier leads an expedition to free captive British officials and missionaries. * January 3 – The 15-year-old Mutsuhito, Emperor Meiji of Japan, declares the ''Meiji Restoration'', his own restoration to full power, under the influence of supporters from the Chōshū and Satsuma Domains, and against the supporters of the Tokugawa shogunate, triggering the Boshin War. * January 5 – Paraguayan War: Brazilian Army commander Luís Alves de Lima e Silva, Duke of Caxias, enters Asunción, Paraguay's capital. Some days later he declares the war is over. Nevertheless, Francisco Solano López, Paraguay's president, prepares guerrillas to fight in the countryside. * January 7 – The Arkansas constitutional convention meets in Little Rock. * January 9 – Penal transportation from Britain to Australia ends, with arrival of the convict ship ''Hougoumont'' in Western Australia, after an 89- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universities And Colleges In Samoa
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the Middl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodist Seminaries And Theological Colleges
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother Charles Wesley were also significant early leaders in the movement. They were named ''Methodists'' for "the methodical way in which they carried out their Christian faith". Methodism originated as a Christian revival, revival movement within Anglicanism with roots in the Church of England in the 18th century and became a separate denomination after Wesley's death. The movement spread throughout the British Empire, the United States and beyond because of vigorous Christian mission, missionary work, and today has about 80 million adherents worldwide. Most List of Methodist denominations, Methodist denominations are members of the World Methodist Council. Wesleyan theology, which is upheld by the Methodist denominations, focuses on Sanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Samoa
German Samoa officially Malo Kaisalika / Kingdom of Samoa (; Samoan: ''Malo Kaisalika'') was a German protectorate from 1900 to 1920, consisting of the islands of Upolu, Savai'i, Apolima and Manono, now wholly within the Independent State of Samoa, formerly ''Western Samoa''. Samoa was the last German colonial acquisition in the Pacific basin, received following the Tripartite Convention signed at Washington on 2 December 1899 with ratifications exchanged on 16 February 1900.Ryden, George Herbert. ''The Foreign Policy of the United States in Relation to Samoa''. New York: Octagon Books, 1975. (Reprint by special arrangement with Yale University Press. Originally published at New Haven: Yale University Press, 1928), p. 574; the Tripartite Convention (United States, Germany, Great Britain) was signed at Washington on 2 December 1899 with ratifications exchanged on 16 February 1900 It was the only German colony in the Pacific, aside from the Jiaozhou Bay Leased Territory i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Samoa
The Samoan Islands were first settled some 3,500 years ago as part of the Austronesian expansion. Both Samoa's early history and its more recent history are strongly connected to the histories of Tonga and Fiji, nearby islands with which Samoa has long had genealogical links as well as shared cultural traditions. European explorers first reached the Samoan islands in the early 18th century. In 1768, Louis-Antoine de Bougainville named them the ''Navigator Islands''. The United States Exploring Expedition (1838–42), led by Charles Wilkes, reached Samoa in 1839. In 1855, J.C. Godeffroy & Sohn expanded its trading business into the Samoan archipelago. The first Samoan Civil War (1886-1894) led to the so-called Samoan crisis, a struggle between Western powers for control of the area. This in turn led to the Second Samoan Civil War (1898-1899), which was resolved by the Tripartite Convention, in which the United States, Great Britain and Germany agreed to partition the islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Samoa
Christianity is the State religion, official and largest religion in Samoa, with its various denominations accounting for around 98% of the total population. The article 1 of the Constitution of Samoa states that "Samoa is a Christian nation founded of God the Father, the Son and the Holy Spirit". The following is a distribution of Christian groups as of 2021 (the most recent census available): Congregational church, Congregational Christian (27 percent), Roman Catholic (18 percent), The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in Samoa, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (17.6 percent), Methodist (11.8 percent), Assemblies of God (10.1 percent) and Seventh-day Adventist (4.9 percent). Groups together constituting less than 5 percent of the population include Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí, Jehovah's Witnesses, Congregational church, Congregational Church of Jesus, Church of the Nazarene, Nazarene, nondenominational Protestant, Baptist, Worship Centre, Peace Chapel, Sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apia
Apia () is the Capital (political), capital and largest city of Samoa. It is located on the central north coast of Upolu, Samoa's second-largest island. Apia falls within the political district (''itūmālō'') of Tuamasaga. The Apia Urban Area (generally known as the City of Apia) has a population of 35,974 (2021 census). Its geographic boundaries extend from the east approximately from Letogo village in Vaimauga to the west in the newer, industrialized region of Apia which extends to Vaitele village in Faleata. History Apia was originally a small village (the 1800 population was 304), from which the country's capital took its name. Apia Village still exists within the larger modern capital of Apia, which has grown into a sprawling urban area that encompasses many villages. Like every other settlement in the country, Apia Village has its own ''matai'' (leaders) and ''fa'alupega'' (genealogy and customary greetings) according to fa'a Samoa. The modern city of Apia was foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samoan Language
Samoan ( or , ) is a Polynesian languages, Polynesian language spoken by Samoans of the Samoan Islands. Administratively, the islands are split between the sovereign country of Samoa and the Unincorporated territories of the United States, United States territory of American Samoa. It is an official language, alongside English language, English, in both jurisdictions. It is widely spoken across the Pacific region, heavily so in New Zealand and in Australia and the United States. Among the Polynesian languages, Samoan is the most widely spoken by number of native speakers. Samoan is spoken by approximately 260,000 people in the archipelago and with many Samoans living in diaspora in a number of countries, the total number of speakers worldwide was estimated at 510,000 in 2015. It is the third-most widely spoken language in New Zealand, where 2.2% of the population, 101,900 people, were able to speak it as of 2018. The language is notable for the phonology, phonological differenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Brown (missionary)
George Brown (7 December 1835 – 7 April 1917) was an English Methodist missionary and ethnographer. Early life and education George Brown was born in Barnard Castle, County Durham, England, the son of George Brown, barrister, and his wife Elizabeth, ''née'' Dixon. Elizabeth's sister was married to Rev. Thomas Buddle, a missionary in New Zealand. Brown was educated at a private school and on leaving, became an assistant in a doctors surgery, for a chemist, and then in a draper's shop. Brown reacted badly to his stepmother's discipline and attempted to run away to sea. Seagoing life Brown, when 16 years old, sailed in a large East Indiaman chartered by the government as a troop-ship. After going to the Mediterranean, the ship went to Quebec. There Brown had an accident and broke his leg, fortunately in his case, as the vessel was lost with all hands on her next voyage. After a short stay in Canada, Brown returned to England but could not settle down. In March 1855 Brown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |