|
Pierre Auger Observatory
The Pierre Auger Observatory is an international cosmic ray observatory in Argentina designed to detect ultra-high-energy cosmic rays: sub-atomic particles traveling nearly at the speed of light and each with energies beyond . In Earth's atmosphere such particles interact with air nuclei and produce various other particles. These effect particles (called an "air shower (physics), air shower") can be detected and measured. But since these high energy particles have an estimated arrival rate of just 1 per km2 per century, the Auger Observatory has created a detection area of —the size of Rhode Island, or Luxembourg—in order to record a large number of these events. It is located in the western Mendoza Province, Argentina, near the Andes. Construction began in 2000, the observatory has been taking production-grade data since 2005 and was officially completed in 2008. The northern site was to be located in southeastern Colorado, United States and hosted by Lamar Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malargüe
Malargüe () is a city in the southwest part of the province of Mendoza, Argentina, about 370 km south of the provincial capital Mendoza. It is the head town of the Malargüe Department, and it has about 27,000 inhabitants as per the . Etymology The name ''Malargüe'' is a rendering of the Mapundungun name ''Malal Hue'', meaning "stone corral" or "place of corrals". Overview The city is located in a semi-arid area. Agriculture is focused on the production of seed potato, along with minor crops such as alfalfa, onion and garlic. In the past, the local industries included oil exploration and production (now almost completely deactivated) and uranium mining. As a touristic area, Malargüe provides hotels and cabins for visitors interested in eco-tourism in the summer and skiing in the winter at the nearby resorts of Las Leñas and Los Molles. The city is known for its traditional dish, the (baby goat). It hosts the annual National Festival of the Goat and the Provincial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford at the Department_of_Physics_and_Astronomy,_University_of_Manchester , University of Manchester based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden experiments, Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. An atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force. The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of () for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about for uranium. These dimensions are much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FD Building
FD or similar may refer to: Science and technology *Canon FD lens mount, a standard for connecting a lens to a camera *Familial dysautonomia, a disorder of the autonomic nervous system *Fermi–Dirac statistics (F–D statistics), in quantum statistics *Ferredoxin, iron–sulfur proteins *File descriptor, in Unix and related computer operating systems *Freedesktop.org (fd.o), an interoperability project *Functional dependency, a constraint in a relation from a database *Nissan FD engine, for trucks and buses Transportation *Thai AirAsia, IATA airline code FD *Mazda RX-7 (FD), a car *FD Phantom, original name for the FH Phantom jet fighter *Russian locomotive class FD *Flight director (aeronautics), a flight instrument *Flying Dutchman (dinghy) Other uses *Formula Drift, an American motorsport series *Fidei defensor (Latin, 'Defender of the Faith'), part of the full style of many English/British monarchs *Fixed deposit, a financial instrument *Finance Director, or chief fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observatorio Pierre Auger Tanque Rayos Cósmicos
Observatorio may refer to: * Observatorio metro station (Mexico City), Mexico * Observatorio metro station (Santiago), Chile * Observatorio railway station ''El Insurgente'' () is a commuter rail line between the State of Mexico and Mexico City that is partially operational. Also known as Interurban Train Mexico City–Toluca, the passenger railway line will connect the cities of Toluca, Mexic ..., an El Insurgente commuter station in Mexico City * Observatorio Island, an alternative name for Gamma Island, in Antarctica See also {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haverah Park Experiment
The Haverah Park experiment was a cosmic ray air shower detection array consisting of water Cherenkov detectors distributed over an area of 12 km2 on Haverah Park on the Pennine moorland near Harrogate, North Yorkshire. The experiment was operated by University of Leeds for 20 years, and was switched off in 1987. Air showers of secondary particles generated from a primary cosmic ray hitting the Earth's atmosphere are spread over many kilometres when they hit the ground. An array allows for detection of secondary particles caused by a single cosmic ray at several detectors. The geographic spread of the detectors allows for calculation of the following: *The total number of particles detected can be used to estimate the number of particles in the air shower and from the model of the energy required to generate those particles, the energy of the primary cosmic ray. *The difference in the time of arrival of recorded particles at multiple detectors can be used to estimate the arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherenkov Detector
A Cherenkov detector (pronunciation: /tʃɛrɛnˈkɔv/; Russian: Черенко́в) is a type particle detector designed to detect and identify particles by the Cherenkov Radiation produced when a charged particle travels through the medium of the detector. Fundamental A particle passing through a material at a velocity greater than that at which light can travel through the material emits light. This is similar to the production of a sonic boom when an airplane is traveling through the air faster than sound waves can move through the air. The direction this light is emitted is on a cone with angle θc about the direction in which the particle is moving, with cos(θc) = (c = the vacuum speed of light, n = the refractive index of the medium, and v is the speed of the particle). The angle of the cone θc thus is a direct measure of the particle's speed. The Frank–Tamm formula gives the number of photons produced. Aspects Most Cherenkov detectors aim at recording the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Leeds
The University of Leeds is a public research university in Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. It was established in 1874 as the Yorkshire College of Science. In 1884, it merged with the Leeds School of Medicine (established 1831) and was renamed Yorkshire College. It became part of the federal Victoria University (UK), Victoria University in 1887, joining Owens College (which became the University of Manchester) and University College Liverpool (which became the University of Liverpool).Charlton, H. B. (1951) ''Portrait of a University''. Manchester: U. P.; chap. IV In 1904, a royal charter was granted to the University of Leeds by Edward VII, King Edward VII. Leeds is the list of universities in the United Kingdom by enrolment, tenth-largest university in the United Kingdom by total enrolment and receives over 68,000 undergraduate applications per year, making it the fourth-most popular university (behind University of Manchester, Manchester, University College London and King's C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAO SDTank
Pao or PAO may refer to: Fiction * Pao-chan, a character from the Japanese magical girl anime television series, ''Ojamajo Doremi'' * Pao, setting of ''The Languages of Pao'', a science fiction novel by Jack Vance * Pao, a Rebel commando in the film '' Rogue One: A Star Wars Story'' People * Pao Ching-yen (also spelled Bao Jingyan), a Chinese anarchist philosopher who presumably lived in the early fourth century C.E. * Yih-Ho Michael Pao, an American entrepreneur and hydro-engineer * Pa'O people, an ethnic group in Burma * Pao language (other) * Ellen Pao, American lawyer and former Reddit executive * Yue-Kong Pao, Hong Kong businessman Places * Barangay Pao, an administrative division of Manaoag, Pangasinan * PAO, the IATA airport code for Palo Alto Airport, Santa Clara County * Pao River, a tributary of the Chi River in northeast Thailand * Pao, Trakan Phuet Phon, Ubon Ratchathani Province, Thailand * Pão de Açúcar, Alagoas, a municipality located in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Hess
Victor Franz Hess (; 24 June 1883 – 17 December 1964) was an Austrian-American particle physicist who shared the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics with Carl David Anderson "for his discovery of cosmic radiation". Biography He was born to Vinzenz Hess and Serafine Edle von Grossbauer-Waldstätt, in Waldstein Castle, near Peggau in Styria, Austria, on 24 June 1883. His father was a royal forester in Prince Louis of Oettingen-Wallerstein's service. He attended secondary school at Graz Gymnasium from 1893 to 1901. From 1901 to 1905, Hess was an undergraduate student at the University of Graz. In 1910, Hess received his PhD from the University of Vienna. He worked as Assistant under Stefan Meyer at the Institute for Radium Research, Austrian Academy of Sciences, from 1910 to 1920. In 1920, he married Marie Bertha Warner Breisky. Hess took a leave of absence in 1921 and traveled to the United States, working at the United States Radium Corporation, in New Jersey, and as consulting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce air shower (physics), showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the Earth's surface, surface, although the bulk are Deflection (physics), deflected off into space by the Earth's magnetic field, magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Francis Hess, Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
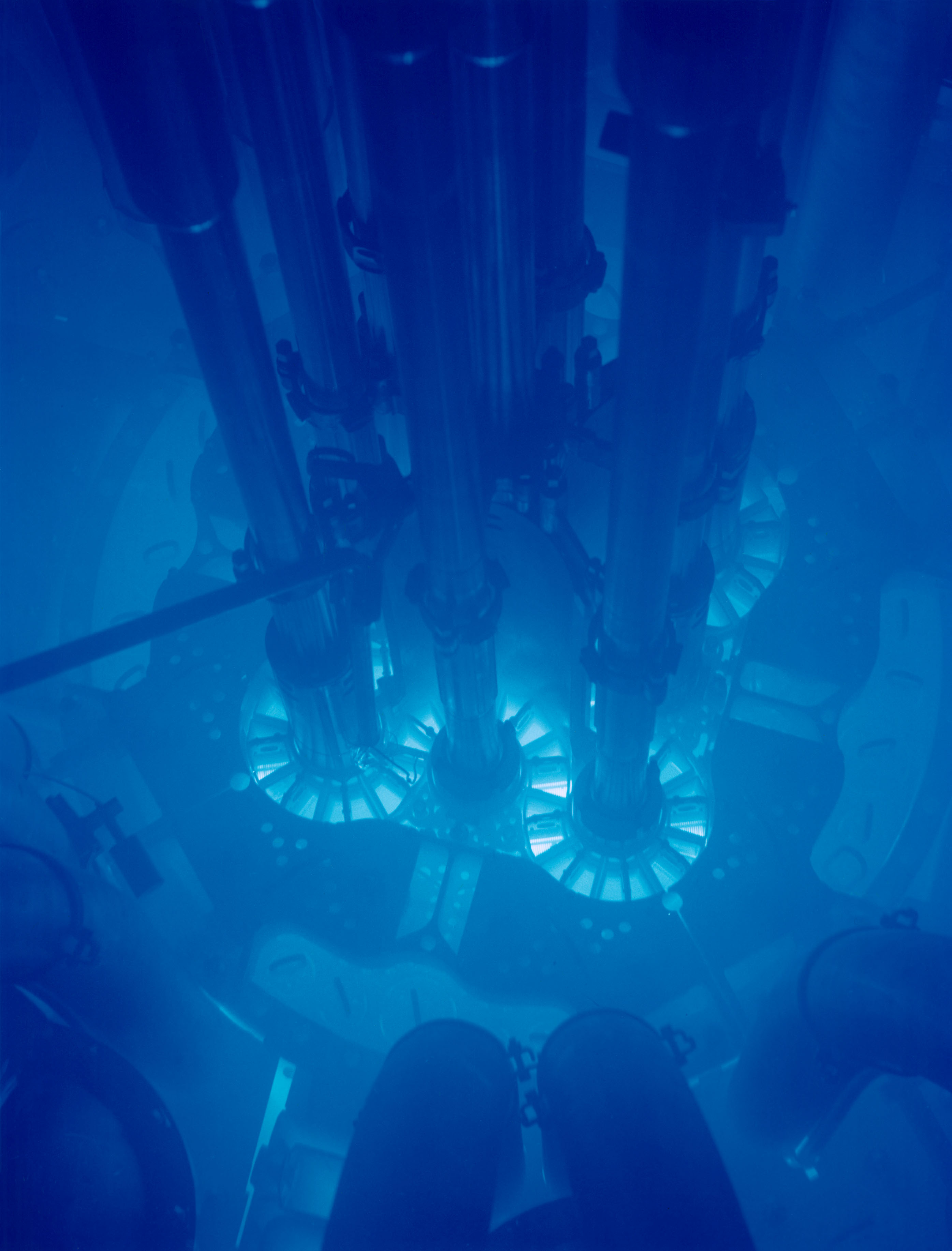
Cherenkov Radiation
Cherenkov radiation () is electromagnetic radiation emitted when a charged particle (such as an electron) passes through a dielectric medium (such as distilled water) at a speed greater than the phase velocity (speed of propagation of a wavefront in a medium) of light in that medium. A classic example of Cherenkov radiation is the characteristic blue glow of an underwater nuclear reactor. Its cause is similar to the cause of a sonic boom, the sharp sound heard when faster-than-sound movement occurs. The phenomenon is named after Soviet physicist Pavel Cherenkov. History The radiation is named after the Soviet scientist Pavel Cherenkov, the 1958 Nobel Prize winner, who was the first to detect it experimentally under the supervision of Sergey Vavilov at the Lebedev Institute in 1934. Therefore, it is also known as Vavilov–Cherenkov radiation. Cherenkov saw a faint bluish light around a radioactive preparation in water during experiments. His doctorate thesis was on lumin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |