|
Phyre2
Phyre and Phyre2 (Protein Homology/AnalogY Recognition Engine; pronounced as ''fire'') are free web-based services for protein structure prediction. Phyre is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction having been cited over 1,500 times. Like other remote Homology (biology), homology recognition techniques (see protein threading), it is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when other widely used methods such as BLAST (biotechnology), PSI-BLAST cannot. Phyre2 has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods. Its development is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. Description The Phyre and Phyre2 servers predict the three-dimensional structure of a protein sequence using the principles and techniques of homology modeling. Because the structure of a protein is more conserved in evolution than its amino acid sequence, a protein sequence of interest (the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Sternberg
Michael Joseph Ezra Sternberg (born 24 June 1951) is a professor at Imperial College London, where he is director of the Centre for Integrative Systems Biology and Bioinformatics and Head of the Structural bioinformatics Group. Education Sternberg was educated at Hendon School, Hendon County Grammar School and Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge, where he was awarded a Bachelor of Arts degree in Natural Sciences (Cambridge), natural sciences (theoretical physics) in 1972. He went on to do a Master of Science degree in Computing at Imperial College London followed by a Doctor of Philosophy, DPhil degree from the University of Oxford (Wolfson College, Oxford) in 1978 for research supervised by David Chilton Phillips. Career After postdoctoral research at the University of Oxford, Sternberg became a Lecturer in the Department of Crystallography at Birkbeck, University of London, Birkbeck College, London. He went on to work at the Cancer Research UK, Imperial Cancer Research Fund a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
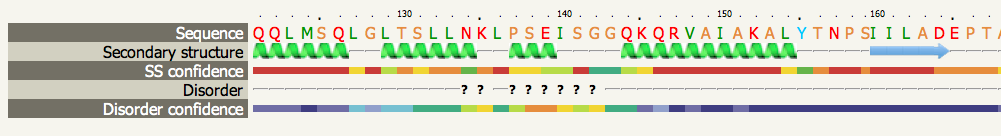
Phyre2 Secondary Structure And Disorder
Phyre and Phyre2 (Protein Homology/AnalogY Recognition Engine; pronounced as ''fire'') are free web-based services for protein structure prediction. Phyre is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction having been cited over 1,500 times. Like other remote homology recognition techniques (see protein threading), it is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when other widely used methods such as PSI-BLAST cannot. Phyre2 has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods. Its development is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. Description The Phyre and Phyre2 servers predict the three-dimensional structure of a protein sequence using the principles and techniques of homology modeling. Because the structure of a protein is more conserved in evolution than its amino acid sequence, a protein sequence of interest (the target) can be modeled with reasonable ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, a Guanine, G nucleotide present at a specific location in a reference genome may be replaced by an Adenine, A in a minority of individuals. The two possible nucleotide variations of this SNP – G or A – are called alleles. SNPs can help explain differences in susceptibility to a wide range of diseases across a population. For example, a common SNP in the Factor H, CFH gene is associated with increased risk of age-related macular degeneration. Differences in the severity of an illness or response to treatments may also be manifestations of genetic variations caused by SNPs. For example, two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Replacement
Molecular replacement (MR) is a method of solving the phase problem in X-ray crystallography. MR relies upon the existence of a previously solved protein structure which is similar to our unknown structure from which the diffraction data is derived. This could come from a homologous protein, or from the lower-resolution protein NMR structure of the same protein. The first goal of the crystallographer is to obtain an electron density map, density being related with diffracted wave as follows: : \rho(x,y,z)=\frac \sum_h\sum_k\sum_\ell, F_, \exp(2\pi i(hx+ky+\ell z)+i\Phi(hk\ell)). With usual detectors the intensity I=F\cdot F^* is being measured, and all the information about phase (\Phi) is lost. Then, in the absence of phases (Φ), we are unable to complete the shown Fourier transform relating the experimental data from X-ray crystallography (in reciprocal space) to real-space electron density, into which the atomic model is built. MR tries to find the model which fits best exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site-directed Mutagenesis
Site-directed mutagenesis is a molecular biology method that is used to make specific and intentional mutating changes to the DNA sequence of a gene and any gene products. Also called site-specific mutagenesis or oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis, it is used for investigating the structure and biological activity of DNA, RNA, and protein molecules, and for protein engineering. Site-directed mutagenesis is one of the most important laboratory techniques for creating DNA libraries by introducing mutations into DNA sequences. There are numerous methods for achieving site-directed mutagenesis, but with decreasing costs of oligonucleotide synthesis, artificial gene synthesis is now occasionally used as an alternative to site-directed mutagenesis. Since 2013, the development of the CRISPR/Cas9 technology, based on a prokaryotic viral defense system, has also allowed for the editing of the genome, and mutagenesis may be performed ''in vivo'' with relative ease. History Early atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MODELLER
Modeller, often stylized as MODELLER, is a computer program used for homology modeling to produce models of protein tertiary structures and quaternary structures (rarer). It implements a method inspired by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (protein NMR), termed '' satisfaction of spatial restraints'', by which a set of geometrical criteria are used to create a probability density function for the location of each atom in the protein. The method relies on an input sequence alignment between the target amino acid sequence to be modeled and a template protein which structure has been solved. The program also incorporates limited functions for ab initio structure prediction of loop regions of proteins, which are often highly variable even among homologous proteins and thus difficult to predict by homology modeling. Modeller was originally written and is currently maintained by Andrej Sali at the University of California, San Francisco. It runs on the operating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CASP
Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP), sometimes called Critical Assessment of Protein Structure Prediction, is a community-wide, worldwide experiment for protein structure prediction taking place every two years since 1994. CASP provides research groups with an opportunity to objectively test their structure prediction methods and delivers an independent assessment of the state of the art in protein structure modeling to the research community and software users. Even though the primary goal of CASP is to help advance the methods of identifying protein three-dimensional structure from its amino acid sequence many view the experiment more as a "world championship" in this field of science. More than 100 research groups from all over the world participate in CASP on a regular basis and it is not uncommon for entire groups to suspend their other research for months while they focus on getting their servers ready for the experiment and on performing the detailed predictio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FASTA Format
In bioinformatics and biochemistry, the FASTA format is a text-based format for representing either nucleotide sequences or amino acid (protein) sequences, in which nucleotides or amino acids are represented using single-letter codes. The format allows for sequence names and comments to precede the sequences. It originated from the FASTA software package and has since become a near-universal standard in bioinformatics. The simplicity of FASTA format makes it easy to manipulate and parse sequences using text-processing tools and scripting languages. Overview A sequence begins with a greater-than character (">") followed by a description of the sequence (all in a single line). The lines immediately following the description line are the sequence representation, with one letter per amino acid or nucleic acid, and are typically no more than 80 characters in length. For example: >MCHU - Calmodulin - Human, rabbit, bovine, rat, and chicken MADQLTEEQIAEFKEAFSLFDKDGDGTITTKELGTV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jmol
Jmol is computer software for molecular modelling of chemical structures in 3 dimensions. It is an open-source Java viewer for chemical structures in 3D. The name originated from ''Jva (the programming language) + olcules, and also the mol file format. JSmol is an implementation in JavaScript of the functionality of Jmol. It can hence be embedded in web pages to display interactive 3D models of molecules and other structures without the need for any software apart from the web browser (''it does not use Java''). Both Jmol and JSmol render an interactive 3D representation of a molecule or other structure that may be used as a teaching tool, or for research, in several fields, e.g. chemistry, biochemistry, materials science, crystallography, symmetry or nanotechnology. Software Jmol is written in the programming language Java, so it can run on different operating systems: Windows, macOS, Linux, and Unix, as long as they have Java installed. It is free and open-source so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
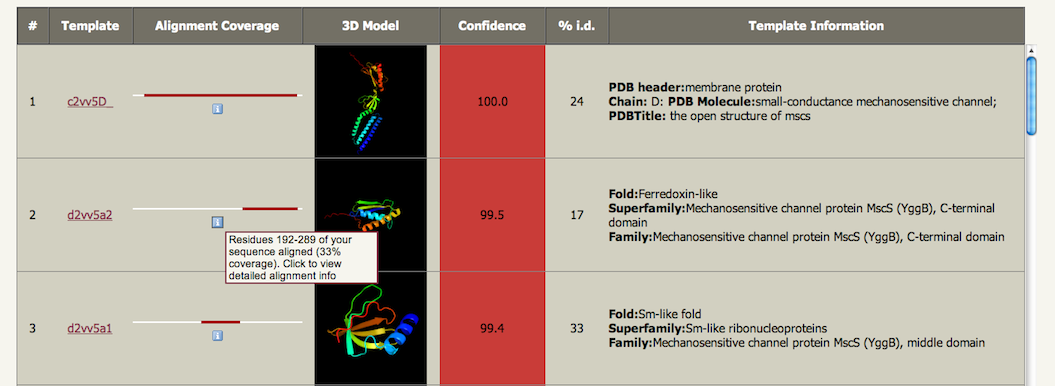
Phyre2 Alignment View
Phyre and Phyre2 (Protein Homology/AnalogY Recognition Engine; pronounced as ''fire'') are free web-based services for protein structure prediction. Phyre is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction having been cited over 1,500 times. Like other remote homology recognition techniques (see protein threading), it is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when other widely used methods such as PSI-BLAST cannot. Phyre2 has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods. Its development is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. Description The Phyre and Phyre2 servers predict the three-dimensional structure of a protein sequence using the principles and techniques of homology modeling. Because the structure of a protein is more conserved in evolution than its amino acid sequence, a protein sequence of interest (the target) can be modeled with reasonable ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids, which is overseen by the Worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB). This structural data is obtained and deposited by biologists and biochemists worldwide through the use of experimental methodologies such as X-ray crystallography, Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins, NMR spectroscopy, and, increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy. All submitted data are reviewed by expert Biocuration, biocurators and, once approved, are made freely available on the Internet under the CC0 Public Domain Dedication. Global access to the data is provided by the websites of the wwPDB member organizations (PDBe, PDBj, RCSB PDB, and BMRB). The PDB is a key in areas of structural biology, such as structural genomics. Most major scientific journals and some funding agencies now require scientists to submit their structure data to the PDB. Many other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Classification Of Proteins Database
The Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database is a largely manual classification of protein structural domains based on similarities of their structures and amino acid sequences. A motivation for this classification is to determine the evolutionary relationship between proteins. Proteins with the same shapes but having little sequence or functional similarity are placed in different superfamilies, and are assumed to have only a very distant common ancestor. Proteins having the same shape and some similarity of sequence and/or function are placed in "families", and are assumed to have a closer common ancestor. Similar to CATH and Pfam databases, SCOP provides a classification of individual structural domains of proteins, rather than a classification of the entire proteins which may include a significant number of different domains. The SCOP database is freely accessible on the internet. SCOP was created in 1994 in the Centre for Protein Engineering and the Lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |