|
Photoentrainment (chronobiology)
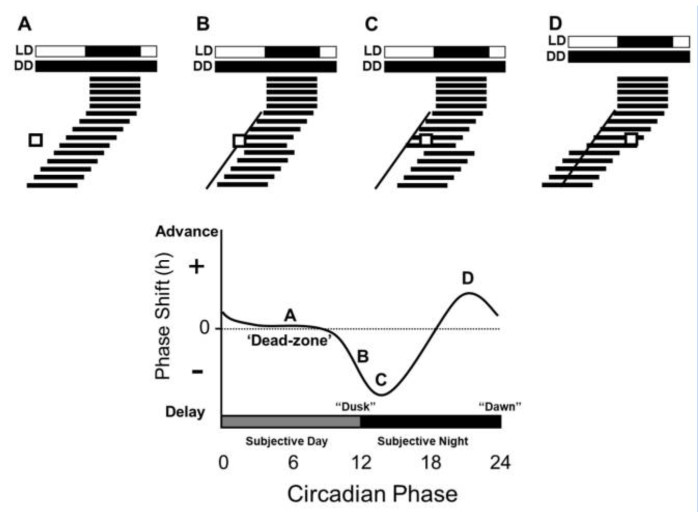
In chronobiology, photoentrainment refers to the process by which an organism's biological clock, or circadian rhythm, synchronizes to daily cycles of light and dark in the environment. The mechanisms of photoentrainment differ from organism to organism. Photoentrainment plays a major role in maintaining proper timing of physiological processes and coordinating behavior within the natural environment. Studying organisms’ different photoentrainment mechanisms sheds light on how organisms may adapt to anthropogenic changes to the environment. Background 24-hour physiological rhythms, known now as circadian rhythms, were first documented in 1729 by Jean Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan, a French astronomer who observed that mimosa plants (''Mimosa pudica'') would orient themselves to be toward the position of the sun despite being in a dark room. That observation spawned the field of chronobiology, which seeks to understand the mechanisms that underlie endogenously expressed daily rhythm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronobiology
Chronobiology is a field of biology that examines timing processes, including periodic (cyclic) phenomena in living organisms, such as their adaptation to solar- and lunar-related rhythms. These cycles are known as biological rhythms. Chronobiology comes from the ancient Greek χρόνος (''chrónos'', meaning "time"), and biology, which pertains to the study, or science, of life. The related terms ''chronomics'' and ''chronome'' have been used in some cases to describe either the molecular mechanisms involved in chronobiological phenomena or the more quantitative aspects of chronobiology, particularly where comparison of cycles between organisms is required. Chronobiological studies include but are not limited to comparative anatomy, physiology, genetics, molecular biology and behavior of organisms related to their biological rhythms. Other aspects include epigenetics, development, reproduction, ecology and evolution. The subject Chronobiology studies variations of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMAL1
Basic helix-loop-helix ARNT-like protein 1 or aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1 (ARNTL), or brain and muscle ARNT-like 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BMAL1'' gene on chromosome 11, region p15.3. It's also known as ''MOP3'', and, less commonly, ''bHLHe5'', ''BMAL'', ''BMAL1C'', ''JAP3'', ''PASD3'', and ''TIC''. ''BMAL1'' encodes a transcription factor with a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) and two PAS domains. The human ''BMAL1'' gene has a predicted 24 exons, located on the p15 band of the 11th chromosome. The BMAL1 protein is 626 amino acids long and plays a key role as one of the positive elements in the mammalian auto-regulatory transcription-translation negative feedback loop (TTFL), which is responsible for generating molecular circadian rhythms. Research has revealed that ''BMAL1'' is the only clock gene without which the circadian clock fails to function in humans. ''BMAL1'' has also been identified as a candidate gene for susc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biophysical Journal
''Biophysical Journal'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Cell Press on behalf of the Biophysical Society. The journal was established in 1960 and covers all aspects of biophysics. The journal occasionally publishes special issues devoted to specific topics. In addition, a supplemental "abstracts issue" is published, containing abstracts of presentations at the Biophysical Society Annual Meeting. The editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accoun ... is Vasanthi Jayaraman. History The following persons are or have been editor-in-chief: References External links * Cell Press academic journals Academic journals established in 1960 Biophysics journals Biweekly journals English-language journals Academic journals associated with l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoautotrophism
Photoautotrophs are organisms that can utilize light energy from sunlight, and chemical element, elements (such as carbon) from inorganic compounds, to produce organic materials needed to sustain their own metabolism (i.e. autotrophy). Such biological activities are known as photosynthesis, and examples of such organisms include plants, algae and cyanobacteria. Eukaryotic photoautotrophs absorb photonic energy through the photopigment chlorophyll (a porphyrin derivative) in their endosymbiont chloroplasts, while prokaryotic photoautotrophs use chlorophylls and bacteriochlorophylls present in free-floating cytoplasmic thylakoids. Plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform oxygenic photosynthesis that produces oxygen as a byproduct, while some bacteria perform anoxygenic photosynthesis. Origin and the Great Oxidation Event Chemical and geological evidence indicate that photosynthetic cyanobacteria existed about 2.6 billion years ago and anoxygenic photosynthesis had been taking pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cone Cell
Cone cells or cones are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the vertebrate eye. Cones are active in daylight conditions and enable photopic vision, as opposed to rod cells, which are active in dim light and enable scotopic vision. Most vertebrates (including humans) have several classes of cones, each sensitive to a different part of the visible spectrum of light. The comparison of the responses of different cone cell classes enables color vision. There are about six to seven million cones in a human eye (vs ~92 million rods), with the highest concentration occurring towards the macula and most densely packed in the fovea centralis, a diameter rod-free area with very thin, densely packed cones. Conversely, like rods, they are absent from the optic disc, contributing to the blind spot. Cones are less sensitive to light than the rod cells in the retina (which support vision at low light levels), but allow the perception of color. They are also able to perceive finer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rod Cell
Rod cells are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in lower light better than the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Rods are usually found concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in peripheral vision. On average, there are approximately 92 million rod cells (vs ~4.6 million cones) in the human retina. Rod cells are more sensitive than cone cells and are almost entirely responsible for night vision. However, rods have little role in color vision, which is the main reason why colors are much less apparent in dim light. Structure Rods are a little longer and leaner than cones but have the same basic structure. Opsin-containing disks lie at the end of the cell adjacent to the retinal pigment epithelium, which in turn is attached to the inside of the eye. The stacked-disc structure of the detector portion of the cell allows for very high efficiency. Rods are much more common than cones, with about 120 million rod cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cell
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), also called photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGC), or melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells (mRGCs), are a type of neuron in the retina of the mammalian eye. The presence of an additional photoreceptor was first suspected in 1927 when mice lacking rod and cone cells still responded to changing light levels through pupil constriction; this suggested that rods and cones are not the only light-sensitive tissue. However, it was unclear whether this light sensitivity arose from an additional retinal photoreceptor or elsewhere in the body. Recent research has shown that these retinal ganglion cells, unlike other retinal ganglion cells, are intrinsically photosensitive due to the presence of melanopsin, a light-sensitive protein. Therefore, they constitute a third class of photoreceptors, in addition to rod and cone cells. Overview Compared to the rods and cones, the ipRGCs respond more sluggishly and signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanopsin
Melanopsin is a type of photopigment belonging to a larger family of light-sensitive retinylidene protein, retinal proteins called opsins and encoded by the gene ''Opn4''. In the mammalian retina, there are two additional categories of opsins, both involved in the formation of visual images: rhodopsin and photopsin (types I, II, and III) in the Rod cell, rod and Cone cell, cone photoreceptor cells, respectively. In humans, melanopsin is found in intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs). It is also found in the iris of mice and primates. Melanopsin is also found in rats, amphioxus, and other chordates. ipRGCs are photoreceptor cells which are particularly sensitive to the absorption of short-wavelength (blue) visible light and communicate information directly to the area of the brain called the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), also known as the central "body clock", in mammals. Melanopsin plays an important non-image-forming role in the Entrainment (chronobiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacterial Clock Proteins
In molecular biology, the cyanobacterial clock proteins are the main circadian regulator in cyanobacteria. The cyanobacterial clock proteins comprise three proteins: KaiA, KaiB and KaiC. The kaiABC complex may act as a promoter-nonspecific transcription regulator that represses transcription, possibly by acting on the state of chromosome compaction. This complex is expressed from a ''KaiABC'' operon. In the complex, KaiA enhances the phosphorylation status of kaiC. In contrast, the presence of kaiB in the complex decreases the phosphorylation status of kaiC, suggesting that kaiB acts by antagonising the interaction between kaiA and kaiC. The activity of KaiA activates kaiBC expression, while KaiC represses it. Also in the KaiC family is RadA/Sms, a highly conserved eubacterial protein that shares sequence similarity with both RecA strand transferase and lon protease. The RadA/Sms family are probable ATP-dependent proteases involved in both DNA repair and degradation of protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
The suprachiasmatic nucleus or nuclei (SCN) is a small region of the brain in the hypothalamus, situated directly above the optic chiasm. It is responsible for regulating sleep cycles in animals. Reception of light inputs from photosensitive retinal ganglion cells allow it to coordinate the subordinate cellular clocks of the body and entrain to the environment. The neuronal and hormonal activities it generates regulate many different body functions in an approximately 24-hour cycle. The SCN also interacts with many other regions of the brain. It contains several cell types, neurotransmitters and peptides, including vasopressin and vasoactive intestinal peptide. Disruptions or damage to the SCN has been associated with different mood disorders and sleep disorders, suggesting the significance of the SCN in regulating circadian timing. Neuroanatomy The SCN is situated in the anterior part of the hypothalamus immediately dorsal, or ''superior'' (hence supra) to the optic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoreceptor Cell
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential. There are currently three known types of photoreceptor cells in mammalian eyes: rod cell, rods, cone cell, cones, and intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells. The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods and cones, each contributing information used by the visual system to form an image of the environment, Visual perception, sight. Rods primarily mediate scotopic vision (dim conditions) whereas cones primarily mediate photopic vision (bright conditions), but the processes in each that supports phototransduction is similar. The intrinsically photosen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRY2
Cryptochromes (from the Greek κρυπτός χρώμα, "hidden colour") are a class of flavoproteins found in plants and animals that are sensitive to blue light. They are involved in the circadian rhythms and the sensing of magnetic fields in a number of species. The name ''cryptochrome'' was proposed as a ''portmanteau'' combining the '' chromatic'' nature of the photoreceptor, and the '' cryptogamic'' organisms on which many blue-light studies were carried out. The genes ''CRY1'' and ''CRY2'' encode the proteins CRY1 and CRY2, respectively. Cryptochromes are classified into plant Cry and animal Cry. Animal Cry can be further categorized into insect type (Type I) and mammal-like (Type II). CRY1 is a circadian photoreceptor whereas CRY2 is a clock repressor which represses Clock/Cycle (Bmal1) complex in insects and vertebrates. In plants, blue-light photoreception can be used to cue developmental signals. Besides chlorophylls, cryptochromes are the only proteins known t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |