|
Phonofilm
Phonofilm is an optical sound-on-film system developed by inventors Lee de Forest and Theodore Case in the early 1920s. In 1919 and 1920, de Forest, inventor of the audion tube, filed his first patents on a sound-on-film process, DeForest Phonofilm, which recorded sound directly onto film as parallel lines. These parallel lines photographically recorded electrical waveforms from a microphone, which were translated back into sound waves when the movie was projected. The Phonofilm system, which recorded synchronized sound directly onto film, was used to record vaudeville acts, musical numbers, political speeches, and opera singers. The quality of Phonofilm was poor at first and while it improved somewhat in later years, it was never able to match the fidelity of sound-on-disc systems such as Vitaphone, or later sound-on-film systems such as RCA Photophone or Fox Movietone. The films of de Forest were short films made primarily as demonstrations to try to interest major studios i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Sound
Optical sound is a means of storing sound recordings on transparent film. Originally developed for military purposes, the technology first saw widespread use in the 1920s as a sound-on-film format for motion pictures. Optical sound eventually superseded all other sound film technologies until the advent of digital sound became the standard in cinema projection booths. Optical sound has also been used for multitrack recording and for creating effects in some musical synthesizers. 1914-1921: Naval and military use Building on the principle first demonstrated by the Photophone of Alexander Graham Bell in 1880, optical sound was developed by several inventors with an interest in wireless communication through transmission of light, primarily for nautical, ship-to-ship use. The idea was that sound pulses could be converted into light pulses, beamed out from one ship and picked up by another, where the light pulses would then be reconverted into sound. A pioneer in this technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movietone Sound System
The Movietone sound system is an optical sound, optical sound-on-film method of recording sound for motion pictures, ensuring synchronization between sound and picture. It achieves this by recording the sound as a variable-density optical track on the same strip of film that records the pictures. The initial version of this system was capable of reproducing sounds up to 8500 Hz. Although modern sound films use variable-area tracks instead, modern motion picture theaters (excluding those that have transitioned to digital cinema) can play a Movietone film without modification to the projector (though if the projector's sound unit has been fitted with red LED or laser light sources, the reproduction quality from a variable density track will be significantly impaired). Movietone was one of four motion picture sound systems under development in the U.S. during the 1920s. The others were DeForest's Phonofilm, Warner Brothers' Vitaphone, and RCA Photophone. However, Phonofilm was p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Case
Theodore Willard Case (December 12, 1888 – May 13, 1944) was an American chemist who invented the Movietone sound system, Movietone sound-on-film, sound-on-sound film, film system. Early life and education Case was born on December 12, 1888 in Auburn, New York, to Willard Erastus Case (1857–1918) and Eva Fidelia Caldwell Case (1857–1952). He attended a few boarding schools as a youth including The Manlius School near Syracuse, New York and Cloyne House School in Newport, Rhode Island, He also attended the St. Paul School in Concord, New Hampshire, to finish his secondary education. Following his high school graduation he attended Yale University from 1908 to 1912, where he earned his Bachelor of Arts, BA in chemistry. He then attended Harvard University where he studied law. He did not find this as fulfilling as pursuing science so he left after about a year. During the years prior to opening the Case Research Lab he worked with his father in laboratories set u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
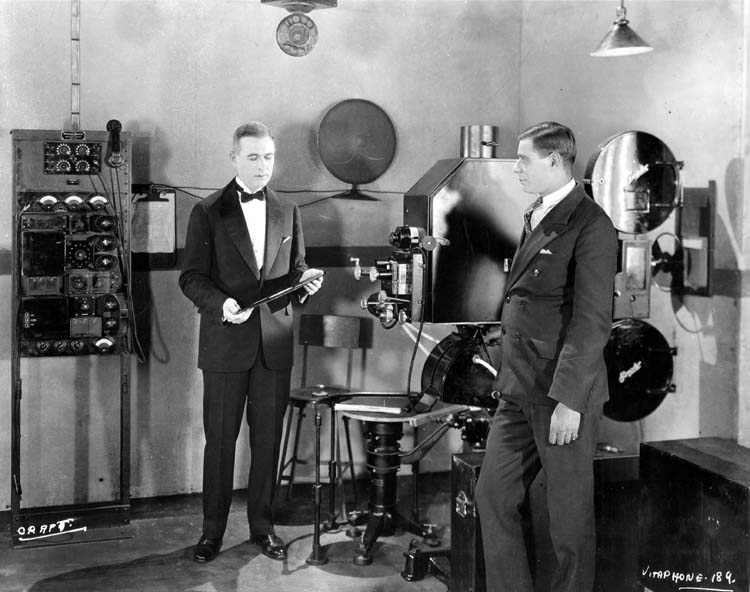
Vitaphone
Vitaphone was a sound film system used for feature films and nearly 1,000 short subjects made by Warner Bros. and its sister studio First National Pictures, First National from 1926 to 1931. Vitaphone is the last major analog sound-on-disc system and the only one that was widely used and commercially successful. The soundtrack is not printed on the film, but issued separately on Gramophone record, phonograph records. The discs, recorded at Revolutions per minute, rpm (a speed first used for this system) and typically in diameter, are played on a turntable physically coupled to the projector motor while the film is projected. Its frequency response is 4300 Hz. Many early sound film, talkies, such as ''The Jazz Singer'' (1927), used the Vitaphone system. The name "Vitaphone" derived from the Latin and Greek words, respectively, for "living" and "sound". The "Vitaphone" trademark was later associated with cartoons and other short subjects that had sound-on-film, optica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Riesenfeld
Hugo Riesenfeld (January 26, 1879 – September 10, 1939) was an Austrian-American composer. As a film director, he began to write his own orchestral compositions for silent films in 1917, and co-created modern production techniques where film scoring serves an integral part of the action. Riesenfeld composed about 100 film scores in his career. His most successful compositions were for Cecil B. DeMille's ''Joan the Woman'' (1917), ''The Ten Commandments (1923 film), The Ten Commandments'' (1923) and ''The King of Kings (1927 film), The King of Kings'' (1927); D. W. Griffith's ''Abraham Lincoln (1930 film), Abraham Lincoln'' (1930); and the original scores to F. W. Murnau's ''Sunrise: A Song of Two Humans'' (1927) and ''Tabu: A Story of the South Seas, Tabu'' (1931). Life and work Born in Vienna, Riesenfeld's musical career began at the age of seven with a violin study at the Conservatory of the Gesellschaft der Musikfreunde in his city of birth, where he graduated at the ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound-on-film
Sound-on-film is a class of sound film processes where the sound accompanying a picture is recorded on photographic film, usually, but not always, the same strip of film carrying the picture. Sound-on-film processes can either record an Analog signal, analog sound track or Digital data, digital sound track, and may record the signal either optical sound, optically or magnetism, magnetically. Earlier technologies were sound-on-disc, meaning the film's soundtrack would be on a separate phonograph record. History Sound on film can be dated back to the early 1880s, when Charles E. Fritts filed a patent claiming the idea. In 1923 a patent was filed by E. E. Ries, for a variable density soundtrack recording, which was submitted to the SMPE (now Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers, SMPTE), which used the mercury vapor lamp as a modulating device to create a variable-density soundtrack. Later, Theodore Case, Case Laboratories and Lee De Forest#Phonofilm sound-on-film pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RCA Photophone
RCA Photophone was the trade name given to one of four major competing technologies that emerged in the American film industry in the late 1920s for synchronizing electrically recorded audio to a motion picture image. RCA Photophone was an optical sound, "variable-area" film exposure system, in which the modulated area (width) corresponded to the waveform of the audio signal. The four other major technologies were the Warner Bros. Vitaphone sound-on-disc system, as well as three "variable-density" sound-on-film systems, Lee De Forest's Phonofilm, and Fox- Case's Movietone, and the German system Tri-Ergon. When Joseph P. Kennedy and other investors merged Film Booking Offices of America (FBO) with the Keith-Albee-Orpheum theater chain and Radio Corporation of America; the resulting movie studio RKO Radio Pictures used RCA Photophone as its primary sound system. In March 1929, RKO released ''Syncopation'', the first live-recorded film made with RCA Photophone. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Ross Taggart
Charles Ross Taggart (19 March 1871, Washington, D.C. – 4 July 1953, Kents Hill, Maine) was an American comedy, comedian and folklore, folklorist who appeared all over North America as "The Man From Vermont" and "The Old Country Fiddler" from 1895 to 1938. Career On the Chautauqua circuit, Taggart would perform folk music on his violin, sing, play the piano, do ventriloquism, and tell outlandish stories that supposedly took place in rural New England. Taggart retired from performing less than a year after suffering a stroke in 1937. Taggart grew up in Topsham, Vermont, later living in Newbury for many years, in a house he called "Elmbank," which overlooked the railroad depot. He would make over 40 recordings of his "Old Country Fiddler" and "Pineville Folks" monologues with various labels, starting in the 1910s, including Edison, Victor, Columbia, and Brunswick. Lee DeForest filmed Taggart for a short film "The Old Country Fiddler at the Singing School" made in the DeForest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phil Baker (comedian)
Phil Baker (August 26, 1896 – November 30, 1963) was an American comedian and emcee on radio. Baker was also a vaudeville actor, composer, songwriter, accordionist and author. Biography He was born on August 26, 1896, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Baker went to school in Boston, and his first stage appearance was in a Boston amateur show. Baker began in vaudeville playing the piano for violinist Ed Janis, and he was 19 when he teamed with Ben Bernie for the vaudeville act "Bernie and Baker." This originally was a serious musical act with Baker on accordion and Bernie on violin but eventually ended up with comic elements. After breaking with Bernie shortly after World War I, Baker partnered with Sid Silvers up until 1928. Baker went on to pursue a successful solo career. His solo act included him singing, playing the accordion, telling jokes and being heckled by a planted audience member called Jojo. With this act, Baker played the Palace Theatre (New York City), Palace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Few Moments With Eddie Cantor
''A Few Moments with Eddie Cantor'' also known as ''A Few Moments with Eddie Cantor, Star of "Kid Boots"'' is an early sound film made in Lee De Forest's sound-on-film Phonofilm process in late 1923 or early 1924 starring Eddie Cantor in an excerpt from the Broadway show ''Kid Boots''. Some sources say the film premiered along with other De Forest phonofilms at the Rivoli Theater in New York City on April 15, 1923. However, ''Kid Boots'' opened on Broadway somewhat later, on December 31, 1923. It contains two songs: "The Dumber They Are, the Better I Like 'Em," and "Oh, Gee, Georgie." The rest of the recorded material would be considered standup comedy Stand-up comedy is a performance directed to a live audience, where the performer stands on a stage (theatre), stage and delivers humour, humorous and satire, satirical monologues sometimes incorporating physical comedy, physical acts. These .... In all, the recording is nearly seven minutes long. The music was orchestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Chauve Souris
''La Chauve-Souris'' (French: ''The Bat'') was the name of a touring revue during the early 1900s. Originating in Moscow and then Paris, and directed by Nikita Balieff, the revue toured the United States, Europe, and South Africa. The show consisted of songs, dances, and sketches, most of which had been originally performed in Russia. The revue was enormously successful in the U.S., and one of its legacies is the popularization of the jaunty tune '' The Parade of the Wooden Soldiers'' by Leon Jessel. Early production history in Moscow, Paris, and London In 1906, Russian-Armenian actor Nikita Balieff moved to Moscow, and took a job at the Moscow Art Theatre under Constantin Stanislavski. After years of only non-speaking roles, and with a desire to perform comedy rather than drama, Balieff, along with theatre devotee Nikolai Tarasov, co-created his own theatre group in a basement near the Moscow Art Theatre. He named the cabaret and troupe ''The Bat'', after a well-known cabaret in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roy Smeck
Leroy George Alfred "Roy" Smeck (6 February 1900 – 5 April 1994) was an American musician. His skill on the banjo, guitar, and ukulele earned him the nickname "The Wizard of the Strings". Background Smeck was born in Reading, Pennsylvania. He started on the vaudeville circuit. His style was influenced by Eddie Lang, Ikey Robinson, banjoist Harry Reser, Johnny Marvin and steel guitarist Sol Hoʻopiʻi. Smeck could not sing well, so he developed novelty dances and trick playing to supplement his act. Vaudeville Smeck was one of only two vaudeville artists to play the octachord, an 8-string lap steel guitar. He was introduced to the instrument by Sam Moore when he played on the bill with Moore and Davis in 1923. Like so many of the performers during the era, he was a big fan of the instruments created by the C.F. Martin & Company and used a variety of their instruments. Smeck was unsuccessful in obtaining an endorsement deal with Martin, who limited their support to a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |