|
Phase-locked Loop Range
The terms hold-in range, pull-in range (acquisition range), and lock-in range are widely used by engineers for the concepts of frequency deviation ranges within which phase-locked loop-based circuits can achieve lock under various additional conditions. History In the classic books on phase-locked loop A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is fixed relative to the phase of an input signal. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and ou ...s, published in 1966, such concepts as hold-in, pull-in, lock-in, and other frequency ranges for which PLL can achieve lock, were introduced. They are widely used nowadays (see, e.g. contemporary engineering literature and other publications). Usually in engineering literature only non-strict definitions are given for these concepts. Many years of using definitions based on the above concepts has led to the advice given in a handbook o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is fixed relative to the phase of an input signal. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same, thus a phase-locked loop can also track an input frequency. Furthermore, by incorporating a frequency divider, a PLL can generate a stable frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are used for clock synchronization, demodulation, frequency synthesis, clock multipliers, and signal recovery from a noisy communication channel. Since 1969, a single integrated circuit can provide a complete PLL building block, and nowadays have output frequencies from a fraction of a hertz up to many gigahertz. Thus, PLLs are widely employed in radio, telecommunications, computers (e.g. to distribute precisely timed clock signals in microprocessors), grid-tie inverters (electronic power converters used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floyd M
Floyd may refer to: As a name * Floyd (given name), a list of people and fictional characters * Floyd (surname), a list of people and fictional characters Places in the United States * Floyd, Arkansas, an unincorporated community * Floyd, Iowa, a city in Floyd County * Floyd, Ray County, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Floyd, Washington County, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Floyd, New Mexico, a village * Floyd, New York, a town * Floyd, Texas, an unincorporated community * Floyd, Virginia, a town in Floyd County * Floyd County (other) * Floyd River, Iowa, a tributary of the Missouri River * Floyd Township (other) * Camp Floyd / Stagecoach Inn State Park and Museum, a short-lived U.S. Army post near Fairfield, Utah * Floyd's Bluff, a hill near Sioux City, Iowa Storms * Hurricane Floyd, major hurricane of 1999 * Tropical Storm Floyd (other), for other storms named Floyd Sports * Floyd (horse), a National Hunt rac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyapunov Stability
Various types of stability may be discussed for the solutions of differential equations or difference equations describing dynamical systems. The most important type is that concerning the stability of solutions near to a point of equilibrium. This may be discussed by the theory of Aleksandr Lyapunov. In simple terms, if the solutions that start out near an equilibrium point x_e stay near x_e forever, then x_e is Lyapunov stable. More strongly, if x_e is Lyapunov stable and all solutions that start out near x_e converge to x_e, then x_e is said to be ''asymptotically stable'' (see asymptotic analysis). The notion of '' exponential stability'' guarantees a minimal rate of decay, i.e., an estimate of how quickly the solutions converge. The idea of Lyapunov stability can be extended to infinite-dimensional manifolds, where it is known as structural stability, which concerns the behavior of different but "nearby" solutions to differential equations. Input-to-state stability (ISS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidden Attractor
In the bifurcation theory, a bounded oscillation that is born without loss of stability of stationary set is called a hidden oscillation. In nonlinear control theory, the birth of a hidden oscillation in a time-invariant control system with bounded states means crossing a boundary, in the domain of the parameters, where local stability of the stationary states implies global stability (see, e.g. Kalman's conjecture). If a hidden oscillation (or a set of such hidden oscillations filling a compact subset of the phase space of the dynamical system) attracts all nearby oscillations, then it is called a hidden attractor. For a dynamical system with a unique equilibrium point that is globally attractive, the birth of a hidden attractor corresponds to a qualitative change in behaviour from monostability to bi-stability. In the general case, a dynamical system may turn out to be multistable and have coexisting local attractors in the phase space. While trivial attractors, i.e. stable equ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
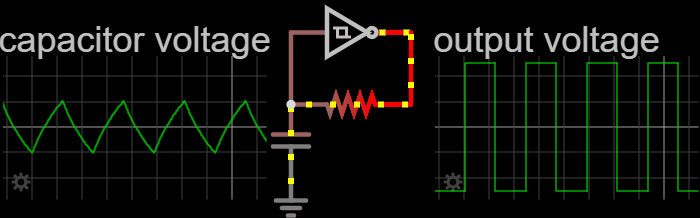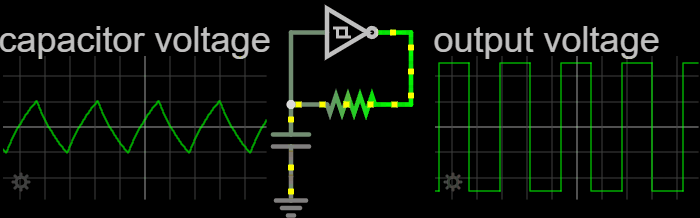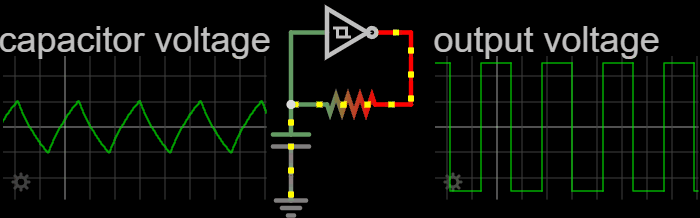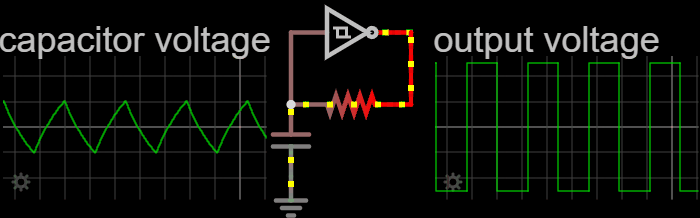
Electronic Oscillators
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating or alternating current (AC) signal, usually a sine wave, square wave or a triangle wave, powered by a direct current (DC) source. Oscillators are found in many electronic devices, such as radio receivers, television sets, radio and television broadcast transmitters, computers, computer peripherals, cellphones, radar, and many other devices. Oscillators are often characterized by the frequency of their output signal: *A low-frequency oscillator (LFO) is an oscillator that generates a frequency below approximately 20 Hz. This term is typically used in the field of audio synthesizers, to distinguish it from an audio frequency oscillator. *An audio oscillator produces frequencies in the audio range, 20 Hz to 20 kHz. *A radio frequency (RF) oscillator produces signals above the audio range, more generally in the range of 100 kHz to 100 GHz. There are two general typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Circuits
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not only transmits meaning but also creates it. Models of communication are simplified overviews of its main components and their interactions. Many models include the idea that a source uses a coding system to express information in the form of a message. The message is sent through a channel to a receiver who has to decode it to understand it. The main field of inquiry investigating communication is called communication studies. A common way to classify communication is by whether information is exchanged between humans, members of other species, or non-living entities such as computers. For human communication, a central contrast is between verbal and non-verbal communication. Verbal communication involves the exchange of messages in linguistic for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Design
''Electronic Design'' magazine, founded in 1952, is an electronics and electrical engineering trade magazine and website. History Hayden Publishing Company began publishing the bi-weekly magazine Electronic Design in December 1952, and was later published by InformaUSA, Inc. In 1986, Verenigde Nederlandse Uitgeverijen, purchased Hayden Publishing Inc. In June 1988, Verenigde Nederlandse Uitgeverijen, purchased ''Electronic Design'' from McGraw-Hill. In July 1989, Penton Media, purchased ''Electronic Design'', then in Hasbrouck, N.J., from Verenigde Nederlandse Uitgeverijen. In July 2007, Penton Media's OEM electronics publication, ''EE Product News'', merged with Penton Media's "Electronic Design" magazine. ''EE Product News'' was founded in 1941, as a monthly publication. In September 2016, Informa, purchased Penton Media, including ''Electronic Design''. In November 2019, Endeavor Business Media purchased ''Electronic Design'' from Informa. Content Section ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Electronics
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver; this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track objects like ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |