|
Perdiccas II
Perdiccas II () was the king of Macedonia from 454 BC until his death in 413 BC. During the Peloponnesian War, he frequently switched sides between Sparta and Athens. Biography Family Perdiccas II was the oldest son of Alexander I. He had four brothers: Alcetas, Amyntas, Menelaus, and Philip. Menelaus was the father of the future king Amyntas II while Amyntas' grandson would be king Amyntas III. Around 429/428 BC, Perdiccas successfully negotiated an end to a Thracian invasion of Macedonia by arranging for his sister Stratonice to marry Seuthes, nephew of the Thracian king Sitalces. During his reign, Perdiccas married at least two women: Simache and Cleopatra. The former, mother of Archelaus and Aeropus II, is accused by Plato, through his interlocutors in Gorgias, of having been a slave of Alcetas. It is doubtful, however, that Archelaus would have been treated as legitimate if his mother had been a slave and therefore Simache was most likely a member of the Macedoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Macedonia
Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia, also called Macedon, was ruled continuously by kings from its inception around the middle of the seventh century BC until its conquest by the Roman Republic in 168 BC. Government of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Kingship in Macedonia, its earliest attested political institution, was hereditary, exclusively male, and characterized by dynastic politics. Information regarding the origins of the Argead dynasty, Argeads, Macedonia's founding dynasty, is very scarce and often contradictory. The Argeads themselves claimed descent from the royal house of Argos, Peloponnese, Argos, the Temenus, Temenids, but this story is viewed with skepticism by some scholars as a fifth century BC fiction invented by the Argead court "to 'prove' Greek lineage". It is more likely that the Argeads first surfaced either as part of a tribe living near Vermio Mountains, Mount Bermion who, possibly under the authority of Perdiccas I of Macedon, Perdiccas, subjugated neigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynkestis
Lynkestis, Lyncestis, Lyngistis, Lynkos or Lyncus ( or Λύγκος or ''Lyncus'') was a region and principality traditionally located in Upper Macedonia. It was the northernmost mountainous region of Upper Macedonia, located east of the Prespa Lakes. In its earlier history, Lynkestis was an independent polity ruled by a local dynasty which claimed descent from the Bacchiadae, a Greek aristocratic family from ancient Corinth.: "The kings of Lyncestae, however, were Greek-speaking, and claimed descent from the Bacchiadae, an important aristocratic Corinthian family." They were ruled by a basileus, as did the rest of the tribes in Lower and Upper Macedonia. The few existing primary sources show that before the rise of Macedon it maintained connections with the Illyrians and was frequently in hostilities with the Argeads. The inhabitants of Lynkestis were known as Lyncestae or Lynkestai (. Hecataeus (6th century BC) included them among the Molossians, while Thucydides (5th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ograzhden (mountain)
Ograzhden (, pronounced in Bulgarian and in Macedonian) is a mountain range shared by southwestern Bulgaria and southeastern North Macedonia. The highest peak of the mountain is located in North Macedonia, Ograzhdenets () at 1,744 m, while the highest in Bulgaria is Bilska Chuka () at 1,644 m. Geography Ograzhden is part of the Belasitsa- Osogovo mountain group. To the north the valley of the river Lebnitsa (right tributary of the Struma) separates it from the Maleshevo Mountain; and to the southwest, south and southeast its slopes descend steeply to the Strumitsa and Sandanski–Petrich Valleys, north of the Belasitsa mountain range. To the west the valley of the river Turia (left tributary of Strumeshnitsa) separates it from Dragolevska Mountain. East of the Struma river lies the Pirin mountain range. The main ridge of Ograzhden stretches from west to east for about 50 km, and its width reaches 17 km. The main mountain ridge is wide and flat with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Macedonia
Lower Macedonia (, ''Kato Makedonia'') or Macedonia proper or Emathia is a geographical term used in Antiquity referring to the coastal plain watered by the rivers Haliacmon, Axius on the west and bounded by Strymon on the east. Its districts were: Pieria, Bottiaea, Emathia, Crestonia, Mygdonia and Bisaltia. There were also included the subregions Anthemous and Crousis in it which were originally part of Chalcidice but were annexed earlier. The region corresponds roughly to the modern Greek region of Central Macedonia, except for the Chalcidice peninsula. The center and two capitals ( Aigai and Pella) of the ancient Macedonian Kingdom lay in Emathia and Bottiaea respectively, from where the Macedonians conquered gradually the Thracian-inhabited areas east of the Axius in the 5th and 4th centuries BC. For this reason the regions of Edonis, Sintice, Odomantis and Pieris, conquered by Philip II, were termed in Latin ''Macedonia Adjecta'' (Επίκτητος Μακεδ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thucydides
Thucydides ( ; ; BC) was an Classical Athens, Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts Peloponnesian War, the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of "scientific history" by those who accept his claims to have applied strict standards of impartiality and evidence-gathering and analysis of cause and effect, without reference to intervention by the Ancient Greek religion, gods, as outlined in his introduction to his work. Thucydides has been called the father of the school of political realism, which views the political behavior of individuals and the subsequent outcomes of relations between states as ultimately mediated by, and constructed upon, fear and self-interest. His text is still studied at universities and military colleges worldwide. The Melian dialogue is regarded as a seminal text of international relations theory, while his version of Pericles's Funeral O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
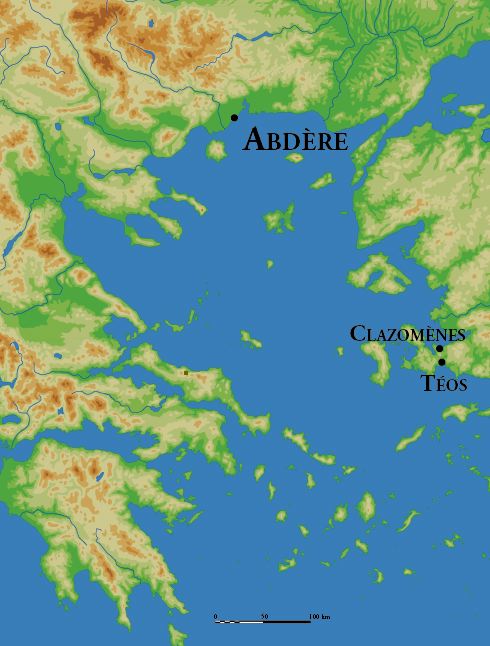
Abdera, Thrace
Abdera () is a municipality in the Xanthi regional unit of Thrace, Greece. In classical antiquity, it was a major Greek ''polis'' on the Thracian coast. The ancient polis is to be distinguished from the municipality, which was named in its honor. The polis lay 17 km east-northeast of the mouth of the Nestos River, almost directly opposite the island of Thasos. It was a colony placed in previously unsettled Thracian territory, not then a part of Hellas, during the age of Greek colonization. The city that developed from it became of major importance in ancient Greece. After the 4th centuryAD it declined, contracted to its acropolis, and was abandoned, never to be reoccupied except by archaeologists. During the Early Middle Ages, a new settlement emerged near the ancient city. It was called Polystylon (), and later considered as the New Abdera (). In 2011 the modern municipality of Abdera was synoecized from three previous municipalities comprising a number of modern settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sybota
The Battle of Sybota () took place in 433 BC between Corcyra (modern Corfu) and Corinth. It was one of the immediate catalysts for the Peloponnesian War. History Corinth had been in dispute with Corcyra, an old Corinthian colony which no longer wanted to remain under Corinthian influence (see Affair of Epidamnus for background). Corcyra, which had the third largest navy in Greece at the time, allied itself with Athens, an enemy of Corinth (as Corinth was allied with Sparta). Athens sent ten ships to Corcyra to reinforce the Corcyraean fleet, with instructions not to fight the Corinthian fleet unless they attempted to land on the island. Corinth, meanwhile, assembled a fleet of ships under the command of Xenoclides and prepared to sail to Corcyra. Corcyra gathered a fleet under Miciades, Aisimides and Eurybatus, who made the Sybota islands their base of operations. The Athenian commanders, Lacedaimonius (the son of Cimon), Diotimus, and Proteas, sailed with them. Corcyra had 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of the Corinth (municipality), municipality of Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. It is the capital of Corinthia. It was founded as Nea Korinthos (), or New Corinth, in 1858 after an earthquake destroyed the existing settlement of Corinth, which had developed in and around the site of the ancient city. History Corinth derives its name from Ancient Corinth, a city-state of antiquity. The site was occupied from before 3000 BC. Ancient Greece Historical references begin with the early 8th century BC, when ancient Corinth began to develop as a commercial center. Between the 8th and 7th centuries, the Bacchiad family ruled Corinth. Cypselus overthrew the Bacchiad f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pydna
Pydna (; Greek: Πύδνα, ''Pýdna'') is a small town and a former municipality in the northeastern part of Pieria regional unit, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Pydna-Kolindros, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 105.059 km2, the community 41.334 km2. Pydna is situated in fertile land close to the Thermaic Gulf coast. The main village of the former municipality is Kitros. It lies 6 km north of Korinos, 8 km south of Methoni and 13 km northeast of Katerini. The A1 motorway and the Piraeus–Platy railway (nearest station at Korinos) pass east of the village. Population See also * List of settlements in the Pieria regional unit This is a list of settlements in the Pieria (regional unit), Pieria regional unit, Greece. * Agiannis, Pieria, Agiannis * Agia Varvara, Pieria, Agia Varvara * Agios Dimitrios, Pieria, Agios Dimitrios, Katerini * Agios Dimitrios, Dio-Olympos * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therma
Therma or Thermē (, ) is the unknown city incorporated into the new city of Thessaloniki by the Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonians on its synoecism and foundation. Little is known of literary Therma, including its exact location. Thessaloniki is the second-largest city in Greece. It surrounds the entire north of the Thermaic Gulf, named after its predecessor. Exactly where Therma was remains a mystery. There is not much room for archaeological excavation between all the modern skyscrapers, and the parklands are valued as such. However, two large habitation mounds remain available and have been extensively excavated. No literary or inscriptional fragment ties them to Therma. The pottery is Greek, but such is the case for any settlement of the times around the Aegean, regardless of known language or ethnic connections. Nearly all of Lower Macedonia was Macedonianized in classical times by the aggressive Argead dynasty, in which the original Thessalonike of Macedon, Thessalon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoplites
Hoplites ( ) ( ) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The formation discouraged the soldiers from acting alone, for this would compromise the formation and minimize its strengths. The hoplites were primarily represented by free citizens – propertied farmers and artisans – who were able to afford a linen or bronze armour suit and weapons (estimated at a third to a half of its able-bodied adult male population). Some states maintained a small elite professional unit, known as the '' epilektoi'' or logades ('the chosen') because they were picked from the regular citizen infantry. These existed at times in Athens, Sparta, Argos, Thebes, and Syracuse, among other places. Hoplite soldiers made up the bulk of ancient Greek armies. In the 8th or 7th century BC, Greek armies adopted the phalanx formation. The formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |