|
Penny Black (research Project)
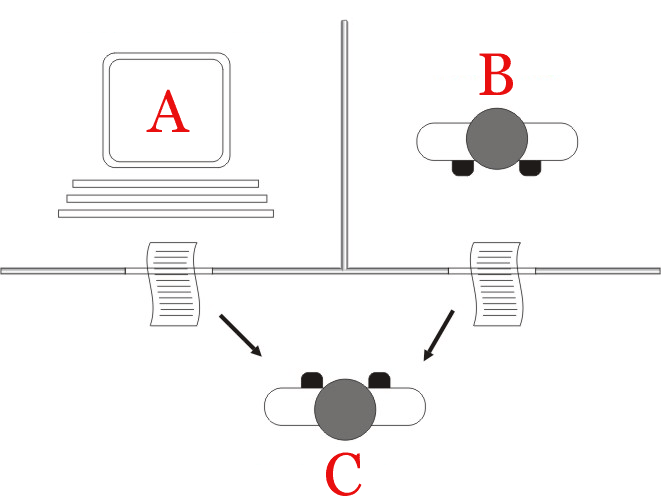
The Penny Black Project is a Microsoft Research project that tries to find effective and practical ways of fighting spam. Because identifying spams consumes a recipient's time, the idea is to make the sender of emails "pay" a certain amount for sending them. The currency or the mode of payment could be CPU cycles, Turing tests or memory cycles. Such a payment would limit spammers' ability to send out large quantities of emails quickly. The project's name is derived from the Penny Black, the world's first adhesive stamp used for prepaid postage. Objective The goal of the project is to move the e-mail costs from the receiver to the sender. The general idea is that if the sender must prove that they have expended a certain amount of effort specifically for the receiver and the message alone. The project aims to devise a method to do this without introducing additional challenge-response mechanisms and third parties, and without requiring extra maintenance and updates, while retaining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Research
Microsoft Research (MSR) is the research subsidiary of Microsoft. It was created in 1991 by Richard Rashid, Bill Gates and Nathan Myhrvold with the intent to advance state-of-the-art computing and solve difficult world problems through technological innovation in collaboration with academic, government, and industry researchers. The Microsoft Research team has more than 1,000 computer scientists, physicists, engineers, and mathematicians, including Turing Award winners, Fields Medal winners, MacArthur Fellows, and Dijkstra Prize winners. Between 2010 and 2018, 154,000 AI patents were filed worldwide, with Microsoft having by far the largest percentage of those patents, at 20%.Louis Columbus, January 6, 201Microsoft Leads The AI Patent Race Going Into 2019 ''Forbes'' According to estimates in trade publications, Microsoft spent about $6 billion annually in research initiatives from 2002 to 2010 and has spent from $10–14 billion annually since 2010. Microsoft Research has made si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spam (e-mail)
Email spam, also referred to as junk email, spam mail, or simply spam, refers to unsolicited messages sent in bulk via email. The term originates from a Monty Python sketch, where the name of a canned meat product, "Spam," is used repetitively, mirroring the intrusive nature of unwanted emails. Since the early 1990s, spam has grown significantly, with estimates suggesting that by 2014, it comprised around 90% of all global email traffic. Spam is primarily a financial burden for the recipient, who may be required to manage, filter, or delete these unwanted messages. Since the expense of spam is mostly borne by the recipient, it is effectively a form of "postage due" advertising, where the recipient bears the cost of unsolicited messages. This cost imposed on recipients, without compensation from the sender, makes spam an example of a "negative externality" (a side effect of an activity that affects others who are not involved in the decision). The legal definition and status of sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
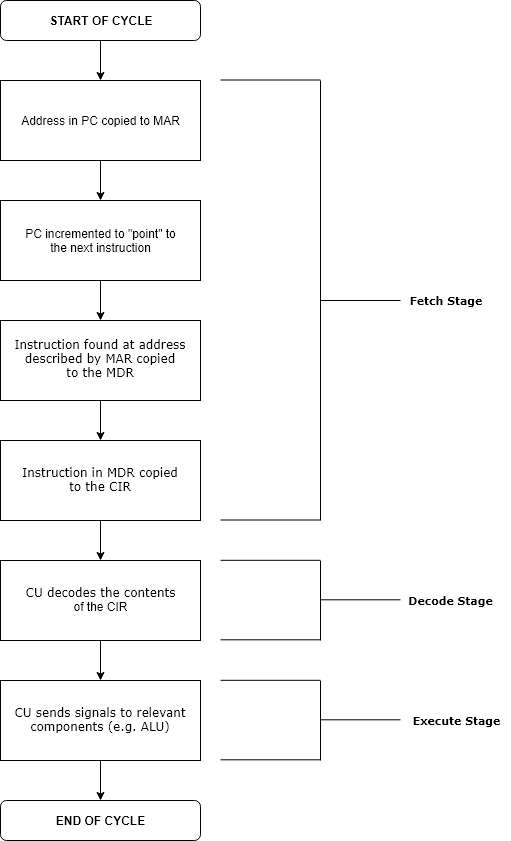
CPU Cycle
The instruction cycle (also known as the fetch–decode–execute cycle, or simply the fetch–execute cycle) is the cycle that the central processing unit (CPU) follows from boot-up until the computer has shut down in order to process instructions. It is composed of three main stages: the fetch stage, the decode stage, and the execute stage. In simpler CPUs, the instruction cycle is executed sequentially, each instruction being processed before the next one is started. In most modern CPUs, the instruction cycles are instead executed concurrently, and often in parallel, through an instruction pipeline: the next instruction starts being processed before the previous instruction has finished, which is possible because the cycle is broken up into separate steps. Role of components Program counter The program counter (PC) is a register that holds the memory address of the next instruction to be executed. After each instruction copy to the memory address register (MAR), the PC can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Test
The Turing test, originally called the imitation game by Alan Turing in 1949,. Turing wrote about the ‘imitation game’ centrally and extensively throughout his 1950 text, but apparently retired the term thereafter. He referred to ‘ istest’ four times—three times in pp. 446–447 and once on p. 454. He also referred to it as an ‘experiment’—once on p. 436, twice on p. 455, and twice again on p. 457—and used the term ‘viva voce’ (p. 446). See also #Versions, below. Turing gives a more precise version of the question later in the paper: " ese questions reequivalent to this, 'Let us fix our attention on one particular digital computer C. Is it true that by modifying this computer to have an adequate storage, suitably increasing its speed of action, and providing it with an appropriate programme, C can be made to play satisfactorily the part of A in the imitation game, the part of B being taken by a man? is a test of a machine's ability to exhibit intellige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Cycle
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory processor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penny Black
The Penny Black was the world's first adhesive postage stamp used in a public Mail, postal system. It was first issued in the United Kingdom on 1 May 1840 but was not valid for use until 6 May. The stamp features a profile of Queen Victoria. In 1837, British postal rates were high, complex and anomalous. To simplify matters, Sir Rowland Hill proposed an adhesive stamp to indicate pre-payment of postage. At the time it was normal for the recipient to pay postage on delivery, charged by the sheet and on distance travelled. By contrast, the Penny Black allowed letters of up to to be delivered at a flat rate of one penny, regardless of distance. Treasury competition On 13 February 1837, Sir Rowland Hill proposed to a government enquiry both the idea of a pre-paid Postage stamp, stamp and a pre-paid envelope, a separate sheet folded to form an enclosure for carrying letters. Hill was given a two-year contract to run the new system, and together with Henry Cole (inventor), Henr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proof Of Work
Proof of work (also written as proof-of-work, an abbreviated PoW) is a form of cryptographic proof in which one party (the ''prover'') proves to others (the ''verifiers'') that a certain amount of a specific computational effort has been expended. Verifiers can subsequently confirm this expenditure with minimal effort on their part. The concept was first implemented in Hashcash by Moni Naor and Cynthia Dwork in 1993 as a way to deter denial-of-service attacks and other service abuses such as spam on a network by requiring some work from a service requester, usually meaning processing time by a computer. The term "proof of work" was first coined and formalized in a 1999 paper by Markus Jakobsson and Ari Juels. The concept was adapted to digital tokens by Hal Finney in 2004 through the idea of "reusable proof of work" using the 160-bit secure hash algorithm 1 (SHA-1). Proof of work was later popularized by Bitcoin as a foundation for consensus in a permissionless decentralized n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proof-of-work System
Proof of work (also written as proof-of-work, an abbreviated PoW) is a form of Cryptography, cryptographic proof (truth), proof in which one party (the ''prover'') proves to others (the ''verifiers'') that a certain amount of a specific computational effort has been expended. Verifiers can subsequently confirm this expenditure with minimal effort on their part. The concept was first implemented in Hashcash by Moni Naor and Cynthia Dwork in 1993 as a way to deter denial-of-service attacks and other service abuses such as spam (electronic), spam on a network by requiring some work from a service requester, usually meaning processing time by a computer. The term "proof of work" was first coined and formalized in a 1999 paper by Markus Jakobsson and Ari Juels. The concept was adapted to digital tokens by Hal Finney (computer scientist), Hal Finney in 2004 through the idea of "reusable proof of work" using the 160-bit secure hash algorithm 1 (SHA-1). Proof of work was later popularized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hashcash
Hashcash is a proof-of-work system used to limit email spam and denial-of-service attacks. Hashcash was proposed in 1997 by Adam Back and described more formally in Back's 2002 paper "Hashcash – A Denial of Service Counter-Measure". In Hashcash the client has to concatenate a random number with a string several times and hash this new string. It then has to do so over and over until a hash beginning with a certain number of zeros is found. Background The idea "...to require a user to compute a moderately hard, but not intractable function..." was proposed by ynthia Dworkand oni Naorin their 1992 paper "Pricing via Processing or Combatting Junk Mail".{Cite book, last1=Dwork, first1=Cynthia, pages=139–147, last2=Naor, first2=Moni, title=Advances in Cryptology — CRYPTO' 92 , chapter=Pricing via Processing or Combatting Junk Mail , series=Lecture Notes in Computer Science, publisher=Springer, doi=10.1007/3-540-48071-4_10, date=2001-05-18, volume=740, isbn=978-3-540-57340-1, doi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Mail 2000
Internet Mail 2000 is an Internet mail architecture proposed by Daniel J. Bernstein (and in subsequent years separately proposed by several others), designed with the precept that the initial storage of mail messages be the responsibility of the sender, and not of the recipient as it is with the SMTP-based Internet mail architecture. Whereas the SMTP-based Internet mail architecture has a close analogue in the architecture of paper mail, this is not the case for ''Internet Mail 2000''. Its architecture depends on various things that are unique to the natures of the Internet and to electronic messages. One of its goals is to reduce spam. Implementations Over the years since Daniel J. Bernstein proposed it, several attempts have been made to design and to implement a real ''Internet Mail 2000'' system, with varying degrees of achievement. The closest thing to a concrete, open implementation of the system is Meng Weng Wong's StubMail, which was presented at Google in July 2006 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-spam Techniques
Various anti-spam techniques are used to prevent email spam (unsolicited bulk email). No technique is a complete solution to the spam problem, and each has trade-offs between incorrectly rejecting legitimate email (false positives) as opposed to not rejecting all spam email ( false negatives) – and the associated costs in time, effort, and cost of wrongfully obstructing good mail. Anti-spam techniques can be broken into four broad categories: those that require actions by individuals, those that can be automated by email administrators, those that can be automated by email senders and those employed by researchers and law enforcement officials. End-user techniques There are a number of techniques that individuals can use to restrict the availability of their email addresses, with the goal of reducing their chance of receiving spam. Discretion Sharing an email address only among a limited group of correspondents is one way to limit the chance that the address will be "harve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |