|
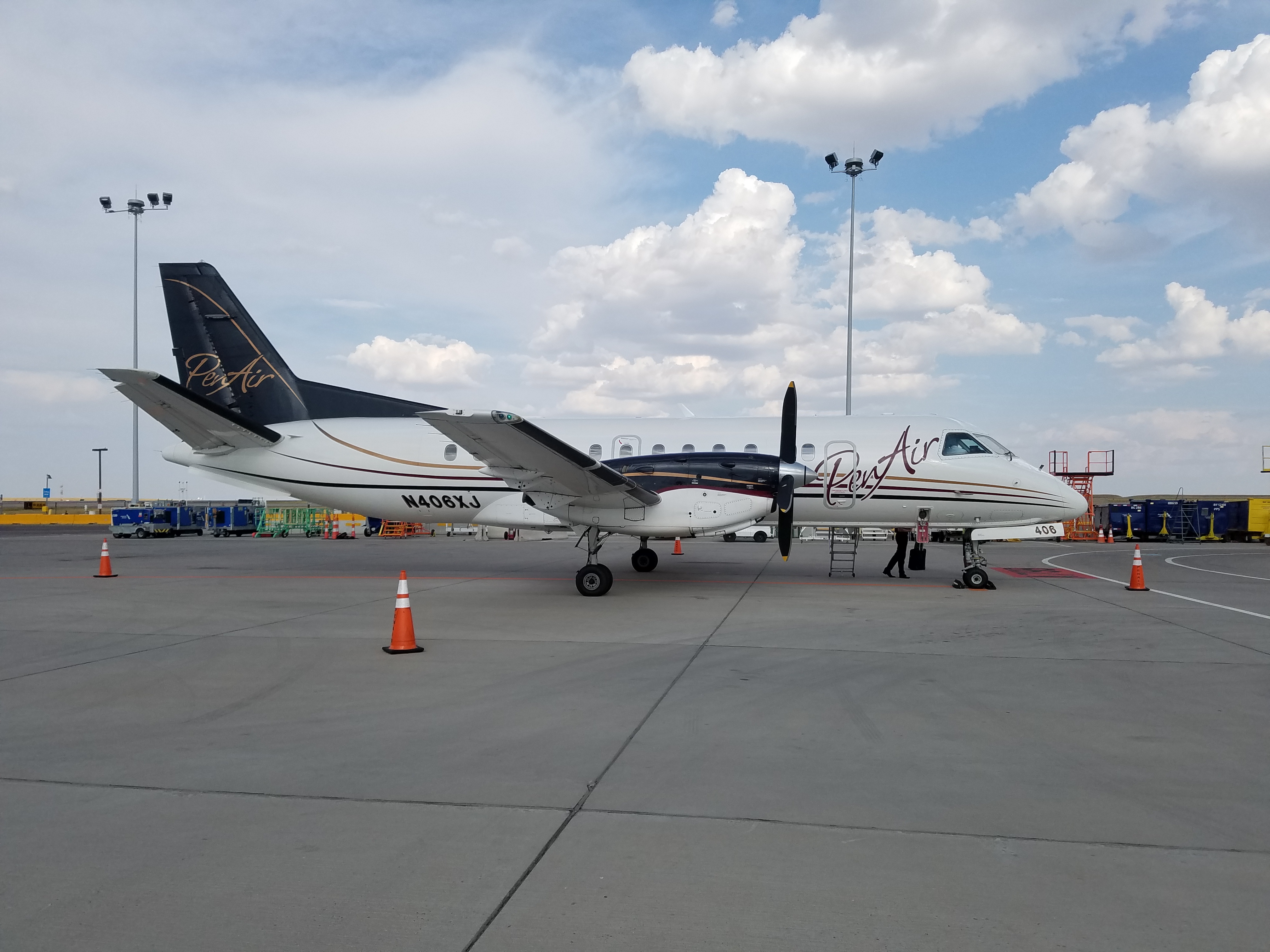
PenAir
Peninsula Airways, operated as PenAir, was a U.S.-based regional airline headquartered in Anchorage, Alaska. It was Alaska's second-largest commuter airline operating scheduled passenger service, as well as charter and medevac services throughout the state. Its main base was Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport. PenAir had a code sharing agreement in place with Alaska Airlines with its flights operated in the state of Alaska. History Peninsula Airways was founded by Orin Seybert in 1955. Seybert was 19 years old, living in Pilot Point, Alaska, and owned a 1946 two-seat Taylorcraft. In 1956, a four-seat Piper Tri-Pacer was added. On March 1, 1965, Peninsula Airways became incorporated and purchased the fixed base operation ( FBO) in King Salmon. In 1967, Peninsula Airways became a full-time subcontractor to Reeve Aleutian Airways, meeting Reeve's certificate obligations to Chignik, Perryville and Ivanoff Bay. In 1969, Peninsula Airways acquired all assets of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grumman Goose
The Grumman G-21 Goose is an amphibious flying boat designed by Grumman to serve as an eight-seat "commuter" aircraft for businessmen in the Long Island area. The Goose was Grumman's first monoplane to fly, its first twin-engined aircraft, and its first aircraft to enter commercial airline service. During World War II, the Goose became an effective transport for the US military (including the United States Coast Guard), as well as serving with many other air forces. During hostilities, the Goose took on an increasing number of combat and training roles. Design and development In 1936, a group of wealthy residents of Long Island, including E. Roland Harriman, approached Grumman and commissioned an aircraft that they could use to fly to New York City."Goose." ''Antilles Seaplanes history page''. Retrieved: August 30, 2008. In response, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchorage, Alaska
Anchorage, officially the Municipality of Anchorage, is the List of cities in Alaska, most populous city in the U.S. state of Alaska. With a population of 291,247 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it contains nearly 40 percent of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Matanuska-Susitna Borough, Alaska, Matanuska-Susitna Borough, had a population of 398,328 in 2020, accounting for more than half the state's population. At of land area, the city is the List of cities in the United States by area, fourth-largest by area in the U.S. Anchorage is in Southcentral Alaska, at the terminus of the Cook Inlet, on a peninsula formed by the Knik Arm to the north and the Turnagain Arm to the south. First settled as a tent city near the mouth of Ship Creek, Alaska, Ship Creek in 1915 when construction on the Alaska Railroad began, Anchorage was incorporated as a city in November 1920. In September 1975, the City of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
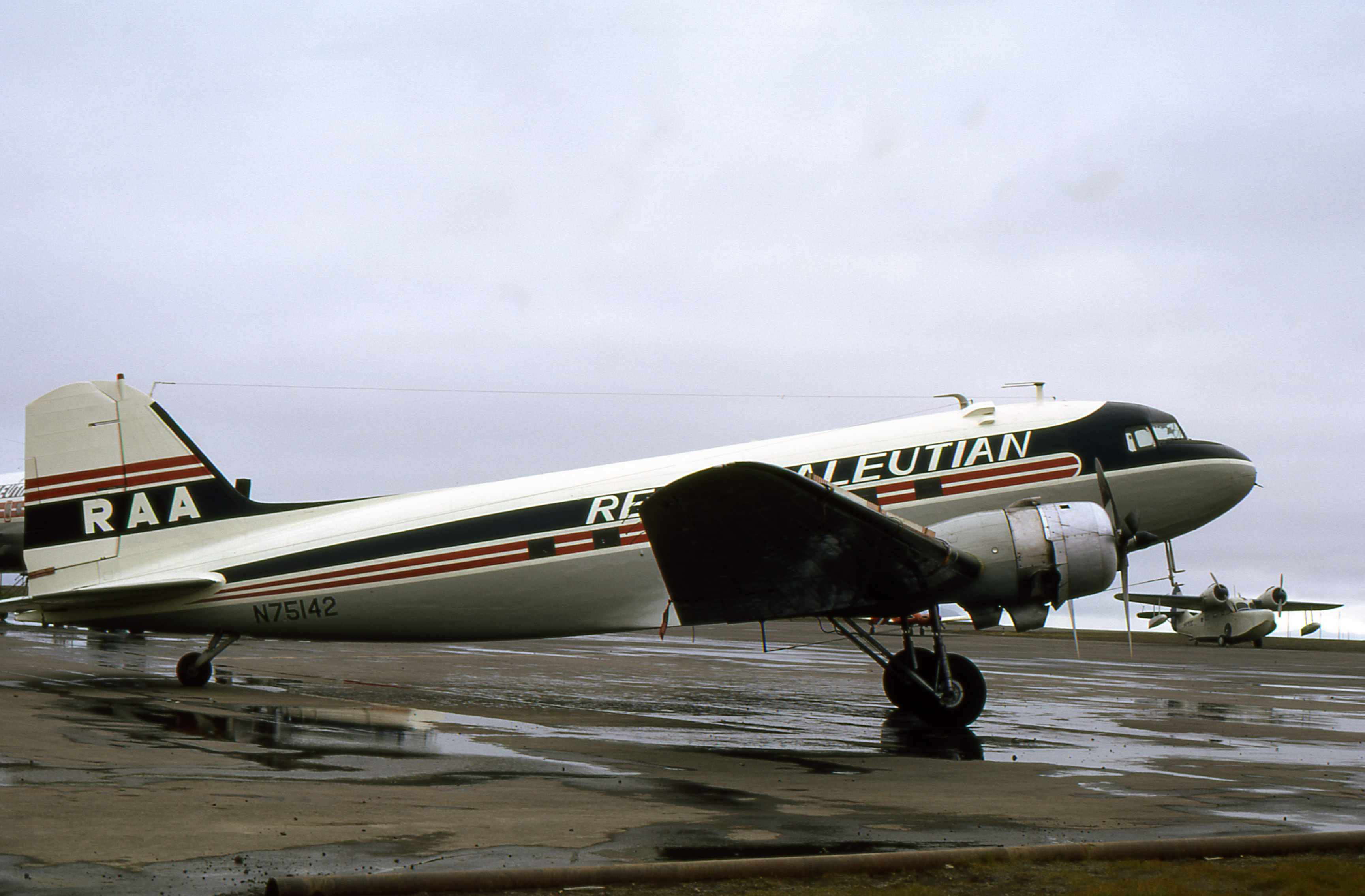
Reeve Aleutian Airways
Reeve Aleutian Airways was an airline headquartered in Anchorage, Alaska, Anchorage, Alaska, United States. It ceased operations on December 5, 2000. Reeve Aleutian was named, possibly as a pun on the word revolution, by combining founder Robert Campbell Reeve, Robert C. Reeve's surname and the Aleutian Islands, its primary destination. History Founding In February 1946, Robert Campbell Reeve, Bob Reeve received a call informing him that some ex-USAAF Douglas C-47 Skytrain, C-47s and Douglas DC-3s were for sale (the C-47 being the military version of the DC-3). Reeve bought his first DC-3 for $20,000 with $3,000 down and the balance payable over 3 years. The cost of conversion to civilian standard was quoted at $50,000, but Reeve did the work himself at a cost of $5,000. A strike by sailors on steamships operating between Seattle and Anchorage started on April 6, 1946. Reeve, along with Merritt Boyle and Bill Borland began flying between Seattle and Anchorage, with stops at Jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commuter Airline
A regional airline is a general classification of airline which typically operates scheduled passenger air service, using regional airliner, regional aircraft, between communities lacking sufficient demand or infrastructure to attract Mainline (air travel), mainline flights. In North America, most regional airlines are classified as "fee-for-departure" carriers, operating their revenue flights as Codeshare agreement, codeshare services contracted by one or more major airline partners. A number of regional airlines, particularly during the 1960s and 1970s, were classified as commuter airlines in the Official Airline Guide (OAG). History Background Decades before the advent of jet airliners and high-speed, long-range air service, commercial aviation was structured similarly to rail transport networks. In this era, technological limitations on air navigation and propeller-driven aircraft performance imposed strict constraints on the potential length of each flight; some rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the northernmost, westernmost, and easternmost (the Aleutian Islands cross the 180th meridian into the eastern hemisphere) state in the United States. It borders the Canadian territory of Yukon and the province of British Columbia to the east. It shares a western maritime border, in the Bering Strait, with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean lie to the north, and the Pacific Ocean lies to the south. Technically, it is a semi-exclave of the U.S., and is the largest exclave in the world. Alaska is the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the following three largest states of Texas, California, and Montana combined, and is the seventh-largest subnational division i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Bay, Alaska
Cold Bay (,; Sugpiaq: ''Pualu'') is a city in Aleutians East Borough, Alaska, United States. As of the 2010 census, the population was 108, but at the 2020 census this had reduced to 50. Cold Bay is one of the main commercial centers of the Alaska Peninsula, which extends west towards the Aleutian Islands, and is home to Cold Bay Airport. History There is evidence of prehistoric occupation by Aleuts and later Russian encampments. Cold Bay's significance to American history began with the Japanese invasion of the Aleutians in World War II. General Simon Bolivar Buckner, Jr. ordered the creation of Fort Randall, an airbase on the shores of Cold Bay, in 1942 as a part of a general expansion of American assets in the Aleutians. It (along with Otter Point) served as a base for the 11th Air Force to provide protection to the only deep water port in the Aleutians at the time, Dutch Harbor. This protection was necessary when during Yamamoto's Midway Campaign, a diversionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
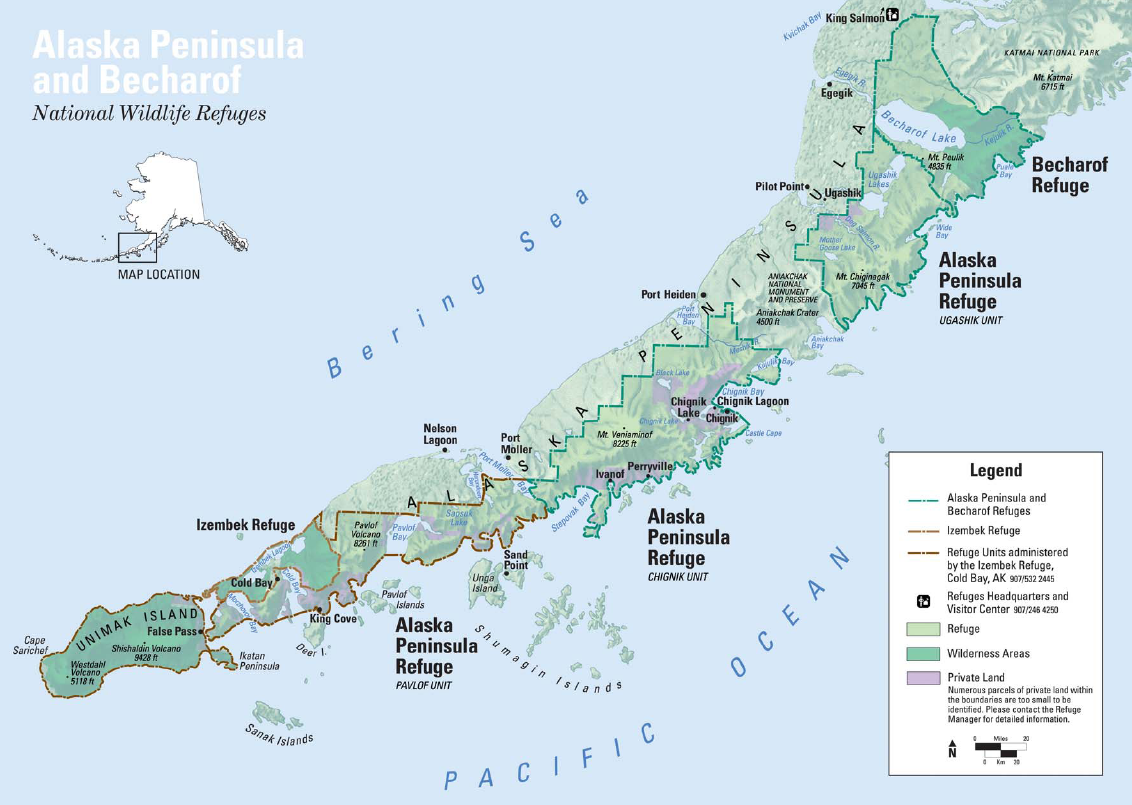
Alaskan Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The peninsula separates the Pacific Ocean from Bristol Bay, an arm of the Bering Sea. In literature (especially Russian), the term ''Alaska Peninsula'' was used to denote the entire northwestern protrusion of the North American continent, or all of what is now the state of Alaska, exclusive of its panhandle and islands. The Lake and Peninsula borough, the Alaskan equivalent of a county, is named after the peninsula. The Alaska/Aleutian Peninsula is also grouped into Southwest Alaska. The other largest peninsulas in Alaska include the Kenai Peninsula and Seward Peninsula. Geography The base of the Alaska Peninsula extends outward from the end of the Alaska Range. The Aleutian Range is a very active volcanic mountain range which runs along the entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naknek
Naknek () is a census-designated place located in and the borough seat of Bristol Bay Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2020 census, the population of the CDP was 470, down from 544 in 2010. Naknek is located on the north bank of the Naknek River, close to where the river runs into the Kvichak Bay arm of the northeastern end of Bristol Bay. South Naknek is on the other side of the river. Geography Naknek is located at (58.739857, -156.971704). According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of , of which, is land and is water. The total area is 0.85% water. History Captain Vasiliav of the Imperial Russian Navy (IRN) reported an Eskimo village here around 1821, naming it "Naugiek". Lieutenant Sarichev, also of the IRN, listed it as "Naugvik" in 1826, while Captain Tebenkov of the IRN spelled it "Naknek" in 1852. Fort Surarov or "Sowaroff" was built nearby, if not at this location. The Naknek post office was established in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibious Aircraft
An amphibious aircraft, or amphibian, is an aircraft that can Takeoff, take off and Landing, land on both solid ground and water. These aircraft are typically Fixed-wing aircraft, fixed-wing, though Amphibious helicopter, amphibious helicopters do exist as well. Fixed-wing amphibious aircraft are seaplanes (flying boats and floatplanes) which are equipped with Landing gear, retractable wheels, at the expense of extra weight and complexity, plus diminished range and fuel economy compared with planes designed specifically for land-only or water-only operation. Design Floatplanes often have floats that are interchangeable with wheeled landing gear (thereby producing a conventional land-based aircraft). However, in cases where this is not practical, amphibious floatplanes, such as the amphibious version of the de Havilland Canada DHC-3 Otter, DHC Otter, incorporate retractable wheels within their floats. Some amphibians are fitted with reinforced keels which act as skis, allowing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grumman G-44 Widgeon
The Grumman G-44 Widgeon is a five-person, twin-engined, amphibious aircraft. It was designated J4F by the United States Navy and Coast Guard and OA-14 by the United States Army Air Corps and United States Army Air Forces. Design and development The Widgeon was originally designed for the civil market. It is smaller, but otherwise similar to Grumman's earlier G-21 Goose, and was produced from 1941 to 1955. The aircraft was used during World War II as a small patrol and utility machine by the US Navy, US Coast Guard, and Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm. The first prototype flew in 1940, and the first production aircraft went to the US Navy as an antisubmarine aircraft. In total, 276 were built by Grumman, including 176 for the military. During World War II, they served with the US Navy, Coast Guard, Civil Air Patrol, and Army Air Force, as well as with the British Royal Navy, which gave it the service name Gosling. Operational history United States Coast Guard On August 1, 1942, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |