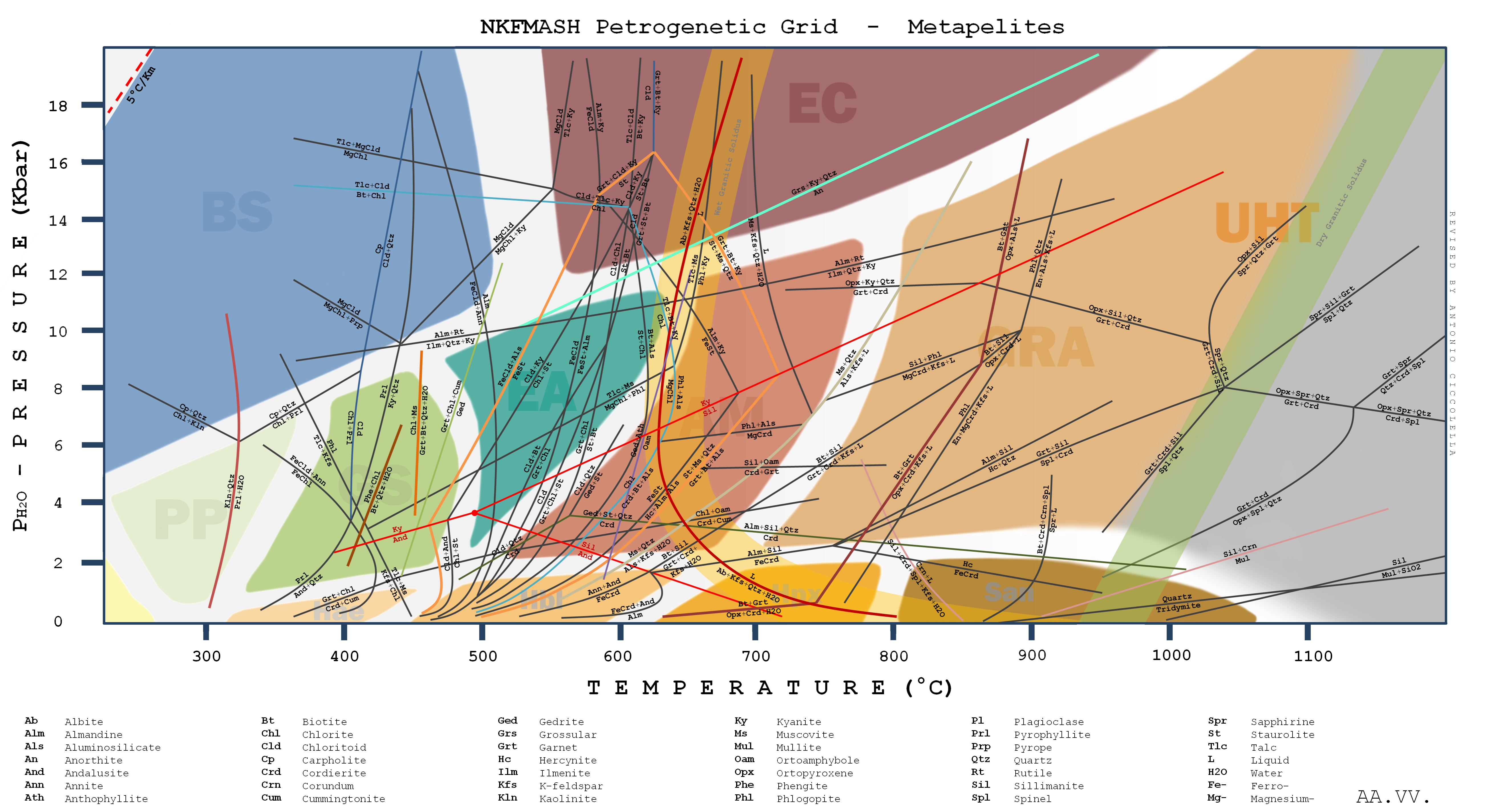
|
Pelitic
A pelite () or metapelite is a metamorphosed fine-grained sedimentary rock, i.e. mudstone or siltstone. The term was earlier used by geologists to describe a clay-rich, fine-grained clastic sediment or sedimentary rock, i.e. mud or a mudstone, the metamorphosed version of which would technically have been a ''metapelite''. It was equivalent to the now little-used Latin-derived term lutite.Potter, P.E., J.B. Maynard, and P.J. Depetris (2005) ''Muds and Mudstones.'' New York, New York, Springer. 279 pp. Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. A semipelite is defined in part as having similar chemical composition but being of a crystalloblastic nature. Pettijohn (1975) gives the following descriptive terms based on grain size, avoiding the use of terms such as clay or argillaceous which carry an implication of chemical composition. The Ancient Greek terms are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including Regional metamorphism, regional, Contact metamorphism, contact, Hydrothermal metamorphism, hydrothermal, Shock metamorphism, shock, and Dynamic metamorphism, dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argillite
Argillite () is a fine-grained sedimentary rock composed predominantly of Friability, indurated clay particles. Argillaceous rocks are basically lithified muds and Pelagic sediment, oozes. They contain variable amounts of silt-sized particles. The argillites grade into shale when the Fissility (geology), fissile layering typical of shale is developed. Another name for poorly lithified argillites is ''mudstone''. These rocks, although variable in composition, are typically high in aluminium and silica with variable alkali and alkaline earth cations. The term pelite, ''pelitic'' or ''pelite'' is often applied to these sediments and rocks. Metamorphism of argillites produces slate, phyllite, and pelitic schist. Belt Supergroup The Belt Supergroup, an assemblage of rocks of late Precambrian (Mesoproterozoic) age, includes thick sequences of argillite, as well as other metamorphosed or semi-metamorphosed mudstones.Schieber, J. 1990. Significance of styles of epicontinental shale sedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudite
Rudite is a general name used for a sedimentary rock composed of rounded or angular detrital grains, i.e. granules, pebbles, cobbles, and boulders, which are coarser than sand in size. Rudites include sedimentary rocks composed of both siliciclastic, i.e. conglomerate and breccia, and carbonate grains, i.e. calcirudite and rudstone. This term is equivalent to the Greek-derived term, psephite. Rudite was initially proposed by GrabauGrabau, A.W. (1904) ''On the classification of sedimentary rocks.'' American Geologist. vol. 33, pp. 228-247. as "rudyte". It is derived from the Latin word ''rudus'' for "crushed stone", "rubbish", "debris", and "rubble".U.S. Bureau of Mines Staff (1996) ''Dictionary of Mining, Mineral, & Related Terms.'' Report SP-96-1, U.S. Department of Interior, U.S. Bureau of Mines, Washington, D.C.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, J.A., eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyanite
Kyanite is a typically blue aluminosilicate mineral, found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and sedimentary rock. It is the high pressure Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of andalusite and sillimanite, and the presence of kyanite in metamorphic rocks generally indicates metamorphism deep in the Earth's crust. Kyanite is also known as disthene or cyanite. Kyanite is strongly anisotropy, anisotropic, in that its Mohs scale of mineral hardness, hardness varies depending on its crystallographic direction. In kyanite, this anisotropism can be considered an identifying characteristic, along with its characteristic blue color. Its name comes from the same origin as that of the color cyan, being derived from the Ancient Greek word κύανος. This is typically rendered into English as ''kyanos'' or ''kuanos'' and means "dark blue." Kyanite is used as a raw material in the manufacture of ceramics and abrasives, and it is an important index mineral used by geologists t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorite Group
The chlorites are the group of phyllosilicate minerals common in low-grade metamorphic rocks and in Mineral alteration, altered igneous rocks. Greenschist, formed by metamorphism of basalt or other low-silica volcanic rock, typically contains significant amounts of chlorite. Chlorite minerals show a wide variety of compositions, in which magnesium, iron, aluminium, and silicon substitute for each other in the crystal structure. A complete solid solution series exists between the two most common end members, magnesium-rich clinochlore and iron-rich chamosite. In addition, manganese, zinc, lithium, and calcium species are known. The great range in composition results in considerable variation in physical, optical, and X-ray diffraction, X-ray properties. Similarly, the range of chemical composition allows chlorite group minerals to exist over a wide range of temperature and pressure conditions. For this reason chlorite minerals are ubiquitous minerals within low and medium temperat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutite
Lutite is old terminology, which is not widely used, by Earth scientists in field descriptions for fine-grained, sedimentary rocks, which are composed of silt-size sediment, clay-size sediment, or a mixture of both. When mixed with water lutites often disintegrate into mud. Because this is a field term, there is a lack of any precise definition for it based upon specific grain-size characteristics. Lutites include a variety of fine-grained sedimentary rocks, including calcisiltite, calcilutite, claystone, mudstone, shale, and siltstone. It is equivalent to the term mudstone and the Greek-derived term pelite A pelite () or metapelite is a metamorphism, metamorphosed fine-grained sedimentary rock, i.e. mudstone or siltstone. The term was earlier used by geologists to describe a clay-rich, fine-grained clastic sediment or sedimentary rock, i.e. mud or ....Potter, P.E., J.B. Maynard, and P.J. Depetris (2005) Muds and Mudstones. New York, New York, Springer. 279 pp. Neuendorf, K.K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arenite
Arenite (from the Latin ''arena'', "sand") is a sedimentary clastic rock with sand grain size between 0.0625 mm (0.00245 in) and 2 mm (0.08 in) and containing less than 15% matrix. The related adjective is ''arenaceous''. The equivalent Greek-derived term is psammite, though this is more commonly used for metamorphosed sediments. Since it refers to grain size rather than chemical composition, the term is used for example in the classification of clastic carbonatic limestones, as the granulometrically equivalent term sandstone is not appropriate for limestone. Other arenites include sandstones, arkoses, greensands, and greywackes. Arenites mainly form by erosion of other rocks or turbiditic re-deposition of sands. Some arenites contain a varying amount of carbonatic components and thus belong to the rock-category of carbonatic sandstones or silicatic limestones. Arenites often appear as massive or bedded medium-grained rocks with a middling- to wide-space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psammite
Psammite (Greek: ''psammitēs'' "(made) from sand", from ''psammos'' "sand") is a general term for sandstone. It is equivalent to the Latin-derived term areniteU.S. Bureau of Mines Staff (1996) ''Dictionary of Mining, Mineral, & Related Terms.'' Report SP-96-1, U.S. Department of Interior, U.S. Bureau of Mines, Washington, D.C.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, J.A., eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute, Washington, DC 779 pp. and is commonly used in various publications to describe a metamorphosed sedimentary rock with a dominantly sandstone protolith A protolith () is the original, unmetamorphosed rock from which a given metamorphic rock is formed. For example, the protolith of a slate is a shale or mudstone. Metamorphic rocks can be derived from any other kind of non-metamorphic rock and ....Tyrell, G. W. (1921) ''Some points in petrographic nomenclature.'' Geological Magazine. v. 58, no. 11, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psephite
Psephite (Greek: ''psephos'', "pebble") is either a sediment or sedimentary rock composed of fragments that are coarser than sand and which are enclosed in a matrix that varies in kind and amount. It is equivalent to a rudite. Shingle, gravel, breccia, and especially conglomerate, would all be considered psephites. It is equivalent to the Latin-derived term rudite. Psephite is more commonly used for a metamorphosed Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ... rudite.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, J.A., eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. Pettijohn Pettijohn F. J. (1975), ''Sedimentary Rocks'', Harper & Row, gives the following descriptive terms based on grain size, avoiding the us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sillimanite
Sillimanite or fibrolite is an aluminosilicate mineral with the chemical formula Al2SiO5. Sillimanite is named after the American chemist Benjamin Silliman (1779–1864). It was first described in 1824 for an occurrence in Chester, Connecticut. Occurrence Sillimanite or fibrolite is one of three aluminosilicate polymorphs, the other two being andalusite and kyanite. A common variety of sillimanite is known as ''fibrolite'', so named because the mineral appears like a bunch of fibres twisted together when viewed in thin section or even by the naked eye. Both the fibrous and traditional forms of sillimanite are common in metamorphosed sedimentary rocks. It is an index mineral indicating high temperature but variable pressure. Example rocks include gneiss and granulite. It occurs with andalusite, kyanite, potassium feldspar, almandine, cordierite, biotite and quartz in schist, gneiss, hornfels and also rarely in pegmatites. Dumortierite and mullite are similar mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staurolite
Staurolite is a reddish brown to black, mostly opaque, nesosilicate mineral with a white streak. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, has a Mohs hardness of 7 to 7.5 and the chemical formula: Fe2+2Al9O6(SiO4)4(O,OH)2. Magnesium, zinc and manganese substitute in the iron site and trivalent iron can substitute for aluminium. Properties Staurolite often occurs twinned in a characteristic cross-shape, called cruciform penetration twinning. In handsamples, macroscopically visible staurolite crystals are of prismatic shape. The mineral often forms porphyroblasts. In thin sections staurolite is commonly twinned and shows lower first order birefringence similar to quartz, with the twinning displaying optical continuity. It can be identified in metamorphic rocks by its swiss cheese appearance (with poikilitic quartz) and often mantled porphyroblastic character. Name The name is derived from the Greek, ''stauros'' for cross and ''lithos'' for stone in reference to the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives. Garnet minerals, while sharing similar physical and crystallographic properties, exhibit a wide range of chemical compositions, defining distinct species. These species fall into two primary solid solution series: the pyralspite series (pyrope, almandine, spessartine), with the general formula [Mg,Fe,Mn]3Al2(SiO4)3; and the ugrandite series (uvarovite, grossular, andradite), with the general formula Ca3[Cr,Al,Fe]2(SiO4)3. Notable varieties of grossular include Grossular#Hessonite, hessonite and tsavorite. Etymology The word ''garnet'' comes from the 14th-century Middle English word ''gernet'', meaning 'dark red'. It is borrowed from Old French ''grenate'' from Latin language, Latin ''granatus,'' from ''granum'' ('grain, seed'). This is possibly a reference to ''mela granatum'' or even ''pomum granatum'' ('pomegranate', ''Punica granatum''), a plant whose fruits conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |