|
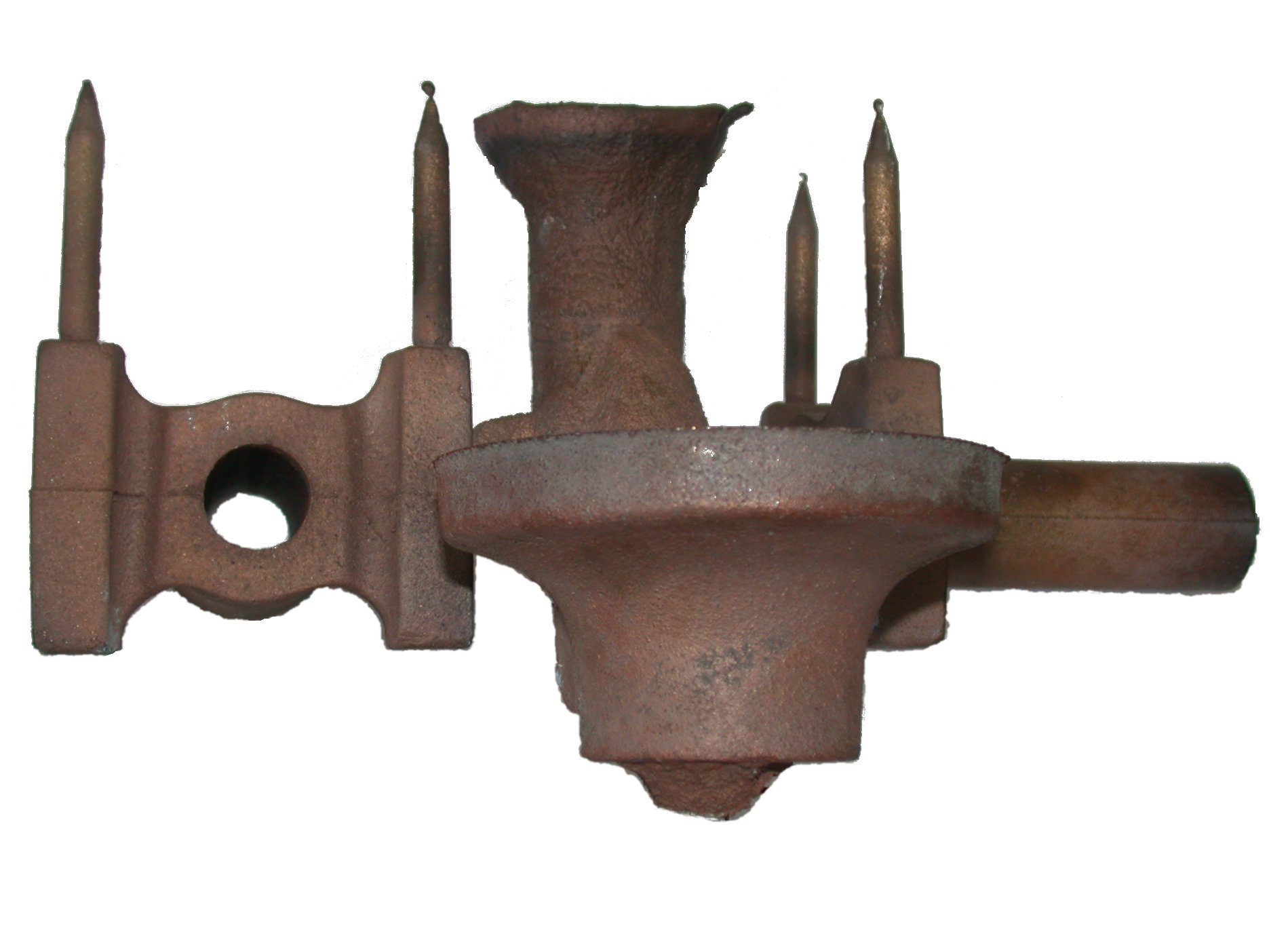
Pattern (casting)
In casting, a pattern is a replica of the object to be cast, used to form the sand mould cavity into which molten metal is poured during the casting process. Once the pattern has been used to form the sand mould cavity, the pattern is then removed, molten metal is then poured into the sand mould cavity to produce the casting. The pattern is non consumable and can be reused to produce further sand moulds almost indefinitely. Due to the fact that almost all metals contract or shrink as their temperature falls, casting patterns must be made larger in size than the actual casting they will produce. Aluminium casting contraction is ~1.3% for example, so patternwork for a cast aluminium part would be made 1.3% bigger than the cast part itself. Patterns used in sand casting may be made of wood, metal, plastics or other materials. Patterns are made to exacting standards of construction, so that they can last for a reasonable length of time, according to the quality grade of the pattern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roue En Bois
Roue is a synonym for rake (character). Roue or La Roue may also refer to: *''La Roue'', a 1923 film by Abel Gance *La Roue (Brussels), a district **La Roue/Het Rad metro station, in Brussels *Rõue, a village in Estonia *William James Roué (1879–1970), a naval architect famous for his design of the ''Bluenose'' fishing schooner {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sprue (molding)
A sprue is a large diameter vertical channel through which liquid material is introduced into a mold. It connects the pouring basin to the runner. In many cases it controls the flow of material into the mold. During casting or molding, the material in the sprue will solidify and need to be removed from the finished part. It is usually tapered downwards to minimize turbulence and formation of air bubbles. Casting In casting, a sprue is the passage through which a molten material is introduced into a mold, and the term also refers to the excess material which solidifies in the sprue passage. Function Sprues can serve as filters, as heat sinks, and as feeders. Bronze Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ..., in particular, has a high shrinkage rate as it is cooling. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
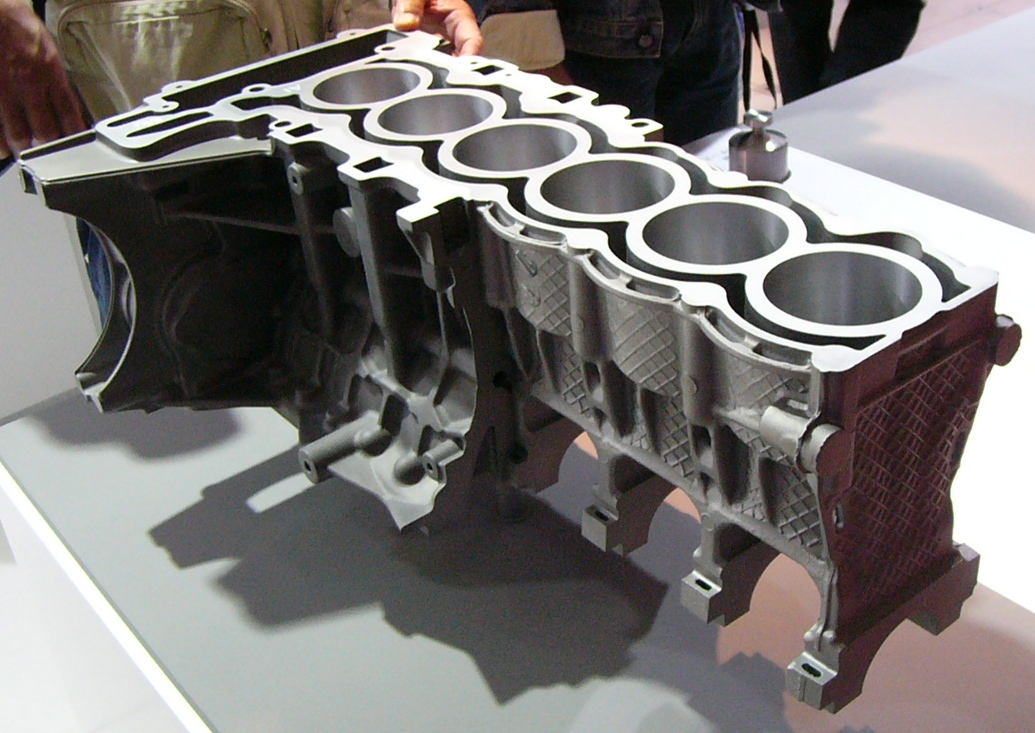
Selective Laser Melting
Selective laser melting (SLM) is one of many proprietary names for a metal Additive Manufacturing, additive manufacturing (AM) technology that uses a bed of powder with a source of heat to create metal parts. Also known as direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), the ASTM standard term is powder bed fusion (PBF). PBF is a rapid prototyping, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing technique designed to use a high power-density laser to melt and fuse metallic powders together. History Selective laser melting is one of many proprietary powder bed fusion technologies, started in 1995 at the Fraunhofer Institute ILT in Aachen, Germany. A research project run by Wilhelm Meiners, Konrad Wissenbach, and Andres Gasser resulted in the so-called basic ILT SLM patent. The ASTM International F42 standards committee has grouped selective laser melting into the category of "laser sintering", although this is an acknowledged misnomer because the process fully melts the metal into a solid homogeneou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selective Laser Sintering
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing (AM) technique that uses a laser as the power and heat source to sinter powdered material (typically nylon or polyamide), aiming the laser automatically at points in space defined by a 3D model, binding the material together to create a solid structure. It is similar to selective laser melting; the two are instantiations of the same concept but differ in technical details. SLS (as well as the other mentioned AM techniques) is a relatively new technology that so far has mainly been used for rapid prototyping and for low-volume production of component parts. Production roles are expanding as the commercialization of AM technology improves. History Selective laser sintering (SLS) was developed and patented by Dr. Carl Deckard and academic adviser, Dr. Joe Beaman at the University of Texas at Austin in the mid-1980s, under sponsorship of DARPA. Deckard and Beaman were involved in the resulting start up company Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
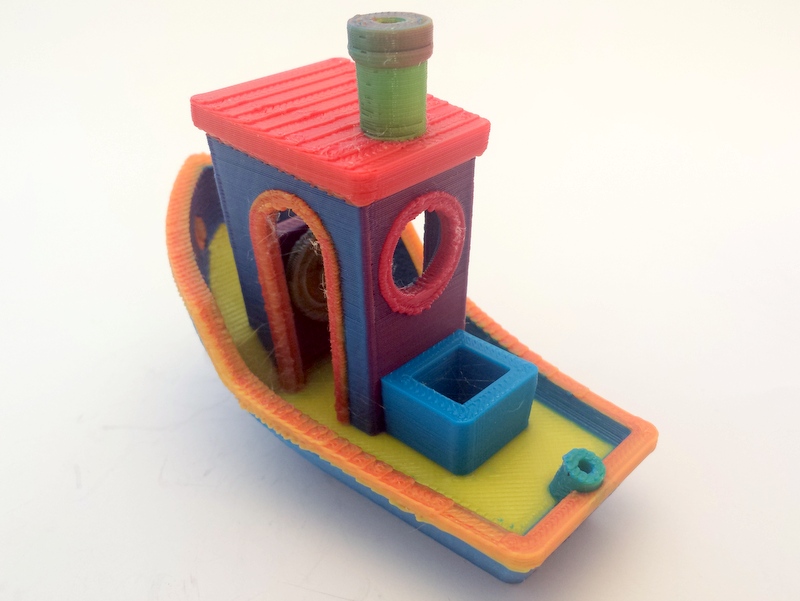
3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with the material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology; in this context, the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very complex shapes or geometries that would be otherwise infeasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Casting
Die casting is a casting (metalworking), metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel die (manufacturing), dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection molding, injection mold during the process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used. The casting equipment and the metal dies represent large capital costs and this tends to limit the process to high-volume production. Manufacture of parts using die casting is relatively simple, involving only four main steps, which keeps the incremental cost per item low. It is especially suited for a large quantity of small- to medium-sized castings, which is why die casting produces more castings than any other casting proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grinding (abrasive Cutting)
Grinding is a type of abrasive machining process which uses a grinding wheel as cutting tool. A wide variety of machines are used for grinding, best classified as portable or stationary: * Portable power tools such as angle grinders, die grinders and cut-off saws * Stationary power tools such as bench grinders and cut-off saws * Stationary hydro- or hand-powered sharpening stones Milling practice is a large and diverse area of manufacturing and toolmaking. It can produce very fine finishes and very accurate dimensions; yet in mass production contexts, it can also rough out large volumes of metal quite rapidly. It is usually better suited to the machining of very hard materials than is "regular" machining (that is, cutting larger chips with cutting tools such as tool bits or milling cutters), and until recent decades it was the only practical way to machine such materials as hardened steels. Compared to "regular" machining, it is usually better suited to taking very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machining
Machining is a manufacturing process where a desired shape or part is created using the controlled removal of material, most often metal, from a larger piece of raw material by cutting. Machining is a form of subtractive manufacturing, which utilizes machine tools, in contrast to ''additive manufacturing'' (e.g. 3D printing processes, 3D printing), which uses controlled addition of material. Machining is a major process of the manufacture of many metal products, but it can also be used on other materials such as wood, plastic, ceramic, and composite material, composites. A person who specializes in machining is called a machinist. As a commercial venture, machining is generally performed in a machine shop, which consists of one or more workrooms containing primary machine tools. Although a machine shop can be a standalone operation, many businesses maintain internal machine shops or tool rooms that support their specialized needs. Much modern-day machining uses Numerical control, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruler
A ruler, sometimes called a rule, scale, line gauge, or metre/meter stick, is an instrument used to make length measurements, whereby a length is read from a series of markings called "rules" along an edge of the device. Usually, the instrument is rigid and the edge itself is a straightedge ("ruled straightedge"), which additionally allows one to draw straighter lines. Rulers are an important tool in geometry, geography and mathematics. They have been used since at least 2650 BC. Variants Rulers have long been made from different materials and in multiple sizes. Historically, they were mainly wood but plastics have also been used. They can be created with length markings instead of being wikt:scribe, scribed. Metal is also used for more durable rulers for use in the workshop; sometimes a metal edge is embedded into a wooden desk ruler to preserve the edge when used for straight-line cutting. Typically in length, though some can go up to 100 cm, it is useful for a ruler to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraction Rule
In metalworking and jewelry making, casting is a process in which a liquid metal is delivered into a mold (usually by a crucible) that contains a negative impression (i.e., a three-dimensional negative image) of the intended shape. The metal is poured into the mold through a hollow channel called a sprue. The metal and mold are then cooled, and the metal part (the ''casting'') is extracted. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Casting processes have been known for thousands of years, and have been widely used for sculpture (especially in bronze), jewelry in precious metals, and weapons and tools. Highly engineered castings are found in 90 percent of durable goods, including cars, trucks, aerospace, trains, mining and construction equipment, oil wells, appliances, pipes, hydrants, wind turbines, nuclear plants, medical devices, defense products, toys, and more. Traditional techniques include l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Metal
In printing, type metal refers to the metal alloys used in traditional Movable type, typefounding and hot metal typesetting. Historically, type metal was an alloy of lead, tin and antimony in different proportions depending on the application, be it individual character mechanical casting for hand setting, mechanical line casting or individual character mechanical typesetting and stereo plate casting. The proportions used are in the range: lead 50‒86%, antimony 11‒30% and tin 3‒20%. Antimony and tin are added to lead for durability while reducing the difference between the coefficients of expansion of the matrix and the alloy. Apart from durability, the general requirements for type-metal are that it should produce a true and sharp cast, and retain correct dimensions and form after cooling down. It should also be easy to cast, at reasonable low Melting point, melting temperature, iron should not dissolve in the molten metal, and mould and nozzles should stay clean and easy t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AutoCAST
AutoCAST is a software program for casting methods design, simulation and optimization developed by Indian Institute of Technology Bombay. Software AutoCAST uses geometric reasoning for automating the design of casting methods elements – cores, mold cavity layout, feeders, feed aids and gating channels. Fast and intelligent simulation technology is employed to visualize mold filling and casting solidification in near-real time. Foundry A foundry is a factory that produces metal castings. Metals are cast into shapes by melting them into a liquid, pouring the metal into a mold, and removing the mold material after the metal has solidified as it cools. The most common metals pr ... engineers can quickly import a 3D model of cast part, create methods elements, simulate the casting, predict internal defects (like shrinkage porosity and sand inclusion), and modify the methods design to improve quality and yield. Product designers can improve the casting design for manufactur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |